Student_Work_files/how cells keep us alive[1]
... smallest part of any living thing. There are many parts of a cell. Each part of a cell completes a ...
... smallest part of any living thing. There are many parts of a cell. Each part of a cell completes a ...
Biology Cell unit
... Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke: saw a honeycomb structure when examining cork under the microscope Named these structures cells, meaning “storage rooms” ...
... Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke: saw a honeycomb structure when examining cork under the microscope Named these structures cells, meaning “storage rooms” ...
HW 9/26 Eukaryotic Cells
... 17. This genetic material containing organelle is inside the nucleus and is responsibl e for growth and reproduction is called the ________________________. 18. These two organelles work together to package protein and produce protein and are called ____________________ and ________________________. ...
... 17. This genetic material containing organelle is inside the nucleus and is responsibl e for growth and reproduction is called the ________________________. 18. These two organelles work together to package protein and produce protein and are called ____________________ and ________________________. ...
Plasma Membrane (cell membrane)
... 2. Aerobic respiration converts oxygen and nutrients into ATP 3. ATP is the chemical energy that powers the activities of the cell 4. Has its own DNA only passed on from the mother 5. Reproduces independently of the cell 6. Double membrane system, inner membrane is known as the folded Cristae Lysoso ...
... 2. Aerobic respiration converts oxygen and nutrients into ATP 3. ATP is the chemical energy that powers the activities of the cell 4. Has its own DNA only passed on from the mother 5. Reproduces independently of the cell 6. Double membrane system, inner membrane is known as the folded Cristae Lysoso ...
Transport Unit Study Guide
... membrane and which kind need to use a transport protein Be able to explain the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis and give examples Be able to predict the effect of a hypotonic, isotonic or hypertonic solution on a cell Be able to di ...
... membrane and which kind need to use a transport protein Be able to explain the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis and give examples Be able to predict the effect of a hypotonic, isotonic or hypertonic solution on a cell Be able to di ...
answer_key_review_classification_protists_prokaryotes__fungi
... Scientific names are created so that the entire scientific community, no matter the culture and language, can understand what organism is being discussed 2. How do domains and kingdoms differ? There are only 3 domains (Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya), and there are 6 kingdoms (Eubacteria, Archaeabac ...
... Scientific names are created so that the entire scientific community, no matter the culture and language, can understand what organism is being discussed 2. How do domains and kingdoms differ? There are only 3 domains (Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya), and there are 6 kingdoms (Eubacteria, Archaeabac ...
Lectures 1-10 (word)
... To appreciate diversity at the broadest level, we need some understanding of structure, which requires learning some morphology and terminology. That too is what this course is about. ...
... To appreciate diversity at the broadest level, we need some understanding of structure, which requires learning some morphology and terminology. That too is what this course is about. ...
Chapter 4 Summary 2401
... I. Microfilaments - smallest component; thin, flexible. example actin. II. Intermediate filaments - larger, more rigid filaments; ex. keratin. III. Microtubules - largest component, form the backbone of the cytoskeleton with the other 2 filaments running between them like latticework. H. Centrosome ...
... I. Microfilaments - smallest component; thin, flexible. example actin. II. Intermediate filaments - larger, more rigid filaments; ex. keratin. III. Microtubules - largest component, form the backbone of the cytoskeleton with the other 2 filaments running between them like latticework. H. Centrosome ...
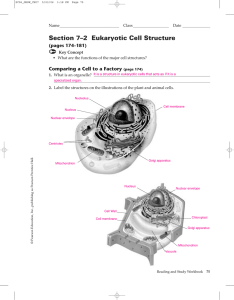
Section 7–2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... 22. What are mitochondria? Mitochondria are organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. ...
... 22. What are mitochondria? Mitochondria are organelles that convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use. ...
4 Prokaryote Cells
... membrane semipermiablity, which allows it to take in certain substances and keep out other substances. ...
... membrane semipermiablity, which allows it to take in certain substances and keep out other substances. ...
Station 1 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... Some organisms of this cell type produce endospores during extreme conditions. Reproduce only asexually, usually by fission or budding. Exist only as a single-celled organism, some move around using flagellum. ...
... Some organisms of this cell type produce endospores during extreme conditions. Reproduce only asexually, usually by fission or budding. Exist only as a single-celled organism, some move around using flagellum. ...
Combining Forms Used as Prefixes
... around starch up against primitive enzyme gold arising from self small staff, rod life down pigment killing together cell reducing sulfur compounds two, double across, completely blood within intestine upon on red well, good outside origin sweet, sugar salt, saltwater blood liver different, other co ...
... around starch up against primitive enzyme gold arising from self small staff, rod life down pigment killing together cell reducing sulfur compounds two, double across, completely blood within intestine upon on red well, good outside origin sweet, sugar salt, saltwater blood liver different, other co ...
Ch 4 Modern Bio Cell Biology Student copy The History of Cell
... xii. Cytoskeleton 1. What is cytoskeleton in general 2. Discuss microtubules 3. Discuss microfilaments 4. Compare intermediate filaments to the previous to types ...
... xii. Cytoskeleton 1. What is cytoskeleton in general 2. Discuss microtubules 3. Discuss microfilaments 4. Compare intermediate filaments to the previous to types ...
Chapter 6
... Double membrane with inner one folded to increase the surface area (ISA) Cristae – inner folded membrane, contains enzymes for respiration Contains some DNA ...
... Double membrane with inner one folded to increase the surface area (ISA) Cristae – inner folded membrane, contains enzymes for respiration Contains some DNA ...
Name - SimplyBio
... 21.Some materials can move across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient by active transport 22.The levels of organization in a multicellular organism listed from simplest to most complicated are cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. ...
... 21.Some materials can move across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient by active transport 22.The levels of organization in a multicellular organism listed from simplest to most complicated are cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Found in plants, bacteria, and fungi • Protective outer covering that helps give plants their structure • Made of cellulose ...
... • Found in plants, bacteria, and fungi • Protective outer covering that helps give plants their structure • Made of cellulose ...
Document
... - contain the green pigment chlorophyll & enzymes that function in photosynthesis - found in leaves & other green organs of plants & algae * Belong to a group of plant organelles called plastids ...
... - contain the green pigment chlorophyll & enzymes that function in photosynthesis - found in leaves & other green organs of plants & algae * Belong to a group of plant organelles called plastids ...
Matching:
... Ability of bacteria to multiply within a host. Archaea that can live in the presence of high salt concentration. Asexual reproduction in bacteria. Bacteria living in the absence of oxygen. Bacteria that have a thick, outer peptidoglycan layer. Bacterial structures that functions in adhesion. Branche ...
... Ability of bacteria to multiply within a host. Archaea that can live in the presence of high salt concentration. Asexual reproduction in bacteria. Bacteria living in the absence of oxygen. Bacteria that have a thick, outer peptidoglycan layer. Bacterial structures that functions in adhesion. Branche ...
File
... (proteins, fats, polysaccharides, etc…). If a lot of lysosomes burst (“suicide sac”), the cell dies. Ex: Tadpole tails, and tissues between fingers of human embryos ...
... (proteins, fats, polysaccharides, etc…). If a lot of lysosomes burst (“suicide sac”), the cell dies. Ex: Tadpole tails, and tissues between fingers of human embryos ...
CHAPTER 4: Cell Structure and Function Review Crossword
... =_N_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 3. Sac of digestive enzymes involved in apoptosis = _L_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 4. _R_ __ __ __ __ ER is covered by ribosomes and transports proteins to the Golgi apparatus. 5. The _C_ _ __ __ _W_ __ __ __ is found outside the cell membrane in plants and bacteria and provid ...
... =_N_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 3. Sac of digestive enzymes involved in apoptosis = _L_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ 4. _R_ __ __ __ __ ER is covered by ribosomes and transports proteins to the Golgi apparatus. 5. The _C_ _ __ __ _W_ __ __ __ is found outside the cell membrane in plants and bacteria and provid ...
The Cell
... Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. ...
... Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.
![Student_Work_files/how cells keep us alive[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008096061_1-3bccda7a250f4b6d053f03d6cd844694-300x300.png)