18-1 Enolates (PPT)
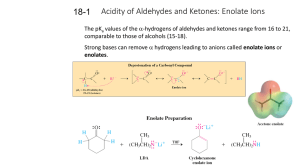
... However, for acetaldehyde, the enol form is about 100-times more stable than that of acetone because the less substituted aldehyde carbonyl is more stable than the more substituted ketone carbonyl. ...
... However, for acetaldehyde, the enol form is about 100-times more stable than that of acetone because the less substituted aldehyde carbonyl is more stable than the more substituted ketone carbonyl. ...
Chapter One
... ©1998 Dr. Norberto Cysne Coimbra M.Sc., Ph.D., Laboratory of Neuroanatomy and Neuropsychobiology, Faculty of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto of the University of são Paulo; Neuroscience Art Galleries Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... ©1998 Dr. Norberto Cysne Coimbra M.Sc., Ph.D., Laboratory of Neuroanatomy and Neuropsychobiology, Faculty of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto of the University of são Paulo; Neuroscience Art Galleries Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Eat Right To Play Right
... Carbohydrates are very important and come in two different types: A. Complex =spaghetti, potatoes, lasagna, unsweetened cereal, rice, baked beans, peas, lentils, sweet corn and other grain products B. Simple = fruits, milk, honey and sugar Complex “carbs” should be given priority because they provid ...
... Carbohydrates are very important and come in two different types: A. Complex =spaghetti, potatoes, lasagna, unsweetened cereal, rice, baked beans, peas, lentils, sweet corn and other grain products B. Simple = fruits, milk, honey and sugar Complex “carbs” should be given priority because they provid ...
Human Body Systems Final Assessment
... Mechanical digestion-physically breaking down food, for example, teeth cutting, tearing and grinding, the tongue pushing food around, action of muscles in stomach Chemical digestion-chemicals, such as enzymes, that break down various nutrients Enzymes are molecules (proteins) that are capable of spe ...
... Mechanical digestion-physically breaking down food, for example, teeth cutting, tearing and grinding, the tongue pushing food around, action of muscles in stomach Chemical digestion-chemicals, such as enzymes, that break down various nutrients Enzymes are molecules (proteins) that are capable of spe ...
Respiration - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... Respiration which uses oxygen is called aerobic respiration. During aerobic respiration reactions take place which use glucose and oxygen to release energy. These reactions are summarised by the equation: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy ...
... Respiration which uses oxygen is called aerobic respiration. During aerobic respiration reactions take place which use glucose and oxygen to release energy. These reactions are summarised by the equation: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy ...
sample pages from Biology - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... Respiration which uses oxygen is called aerobic respiration. During aerobic respiration reactions take place which use glucose and oxygen to release energy. These reactions are summarised by the equation: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy ...
... Respiration which uses oxygen is called aerobic respiration. During aerobic respiration reactions take place which use glucose and oxygen to release energy. These reactions are summarised by the equation: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy ...
final review blue packet 2015
... Diameter of high-power field of view = Magnification of scanning-power objective X Diameter of low-power FOV Magnification of high-power objective For example, a microscope has a scanning-power objective with a magnification of 4X and a high-power objective with a magnification of 40X. If the low-po ...
... Diameter of high-power field of view = Magnification of scanning-power objective X Diameter of low-power FOV Magnification of high-power objective For example, a microscope has a scanning-power objective with a magnification of 4X and a high-power objective with a magnification of 40X. If the low-po ...
File
... – Non-vital – we notice no side effects when it is removed – Thought to house important bacteria needed for balance in body – Could possibly play a role in immunity – In evolutionary past – scientists believe that there were 180 vestigial structures – today there are virtually none!!! ...
... – Non-vital – we notice no side effects when it is removed – Thought to house important bacteria needed for balance in body – Could possibly play a role in immunity – In evolutionary past – scientists believe that there were 180 vestigial structures – today there are virtually none!!! ...
Lab 8 - FIU Faculty Websites
... Glucose catabolism begins with glycolysis in the cytoplasm (Fig. 3). Glycolysis includes a series of reactions where each entering glucose molecule (6 carbons) is split into 2 molecules of pyruvate (3 carbons). In total, glycolysis yields 4 ATP molecules, however, 2 ATPs are used for the priming rea ...
... Glucose catabolism begins with glycolysis in the cytoplasm (Fig. 3). Glycolysis includes a series of reactions where each entering glucose molecule (6 carbons) is split into 2 molecules of pyruvate (3 carbons). In total, glycolysis yields 4 ATP molecules, however, 2 ATPs are used for the priming rea ...
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
... • How do the boiling points compare to alcohols? – Why? ...
... • How do the boiling points compare to alcohols? – Why? ...
Chapter Summary for Nutrition: Concepts and
... extend endurance. After strenuous training, eating foods with a high glycemic index may help restore glycogen most rapidly. Highly trained muscles use less glucose and more fat than do untrained muscles to perform the same work, so their glycogen lasts longer. Athletes who eat high-fat diets may bur ...
... extend endurance. After strenuous training, eating foods with a high glycemic index may help restore glycogen most rapidly. Highly trained muscles use less glucose and more fat than do untrained muscles to perform the same work, so their glycogen lasts longer. Athletes who eat high-fat diets may bur ...
Chapter_Sixteen_lecture
... Be able to specify where aldehydes and ketones are found & list their major applications Be able to describe and predict the products of the oxidation and reduction of aldehydes and ketones. Be able to recognize hemiacetals and acetals, describe the conditions under which they are formed, and predic ...
... Be able to specify where aldehydes and ketones are found & list their major applications Be able to describe and predict the products of the oxidation and reduction of aldehydes and ketones. Be able to recognize hemiacetals and acetals, describe the conditions under which they are formed, and predic ...
Carbohydrates, Lectures 16-17 Quadrant - vtu-nptel
... 3. Cellulose, a b(1->4)-linked glucose polysaccharide 4. The glycosidic bond joins glucose and fructose to form sucrose 5. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins all contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and proteins also contains nitrogen 6. Cereals are a good sources of carbohydrate are 7. A kilocalor ...
... 3. Cellulose, a b(1->4)-linked glucose polysaccharide 4. The glycosidic bond joins glucose and fructose to form sucrose 5. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins all contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and proteins also contains nitrogen 6. Cereals are a good sources of carbohydrate are 7. A kilocalor ...
Chapter 2
... Carbon: unique element for basic building block of molecules of life • Carbon has 4 valence electrons: Can form four covalent bonds – Can form single , double, triple bonds. – Can form large, complex, branching molecules and rings. – Carbon atoms easily bond to C, N, O, H, P, S. • Huge variety of m ...
... Carbon: unique element for basic building block of molecules of life • Carbon has 4 valence electrons: Can form four covalent bonds – Can form single , double, triple bonds. – Can form large, complex, branching molecules and rings. – Carbon atoms easily bond to C, N, O, H, P, S. • Huge variety of m ...
StudyGuideMolecularBiologywithblanksred
... Molecular Biology Study Guide Name ______________________________________ Period __ 8. L.5.1 1. Food provides molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms. a.Plants use the energy in light to make sugars out of carbon dioxide and water. This food can be used for fuel or mater ...
... Molecular Biology Study Guide Name ______________________________________ Period __ 8. L.5.1 1. Food provides molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms. a.Plants use the energy in light to make sugars out of carbon dioxide and water. This food can be used for fuel or mater ...
Full Unit Summary Booklet
... A fuel is a chemical which burns to give out energy. When a fuel burns the chemical reaction is known as combustion. When combustion takes place the fuel is reacting with oxygen from the air and energy is given out. This means that combustion is an example of an exothermic reaction. Coal, oil and na ...
... A fuel is a chemical which burns to give out energy. When a fuel burns the chemical reaction is known as combustion. When combustion takes place the fuel is reacting with oxygen from the air and energy is given out. This means that combustion is an example of an exothermic reaction. Coal, oil and na ...
aldehydes and ketones
... • Using the root alkane name, drop the –e ending and change to –one. • Number the longest carbon chain so the C=O group has the lowest number. • Name and number other substituents as before. • Examples: ...
... • Using the root alkane name, drop the –e ending and change to –one. • Number the longest carbon chain so the C=O group has the lowest number. • Name and number other substituents as before. • Examples: ...
EXERCISE: The Effect On The Body
... The Heart • When exercising the main change that will occur with the heart is an increased cardiac output. This occurs for 2 main reasons. • 1- The amount of oxygen needed by working muscles increases • 2- The amount of waste products (CO2 and Lactic Acid) from the muscles increases ...
... The Heart • When exercising the main change that will occur with the heart is an increased cardiac output. This occurs for 2 main reasons. • 1- The amount of oxygen needed by working muscles increases • 2- The amount of waste products (CO2 and Lactic Acid) from the muscles increases ...
CHAPTER 6 -LIFE PROCESSES KEY CONCEPTS & GIST OF THE LESSON
... (i) Oxygenated blood & Deoxygenated blood are completely separate for efficient Oxygen supply. (ii) This is to fulfil higher energy needs and to maintain body temperature (warm blooded animals). Amphibians & reptilesThey have 3 chambered heat where little mixing of Oxygenated blood & Deoxygenated bl ...
... (i) Oxygenated blood & Deoxygenated blood are completely separate for efficient Oxygen supply. (ii) This is to fulfil higher energy needs and to maintain body temperature (warm blooded animals). Amphibians & reptilesThey have 3 chambered heat where little mixing of Oxygenated blood & Deoxygenated bl ...
Part I - Nutrition. I. How to obtain food: This is descriptive
... buffer (neutralizes acid). hydrolytic enzymes (e.g. trypsin; these break up proteins further) ...
... buffer (neutralizes acid). hydrolytic enzymes (e.g. trypsin; these break up proteins further) ...
Chapter 23 Respiratory System Functions: Provides for gas
... 2. External (pulmonary) respiration Exchange of gases between alveoli and blood 3. Internal (tissue) respiration Exchange of gases between systemic capillaries and tissue cells Supplies cellular respiration (makes ATP) ...
... 2. External (pulmonary) respiration Exchange of gases between alveoli and blood 3. Internal (tissue) respiration Exchange of gases between systemic capillaries and tissue cells Supplies cellular respiration (makes ATP) ...
Hole Chapter 2 - Chemical Basis of Life
... Structure of Matter Matter – anything that takes up space and has mass; composed of elements. Look around you. Everything you can see and touch is composed of matter! ...
... Structure of Matter Matter – anything that takes up space and has mass; composed of elements. Look around you. Everything you can see and touch is composed of matter! ...
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water); in other words, with the empirical formula Cm(H2O)n (where m could be different from n). Some exceptions exist; for example, deoxyribose, a sugar component of DNA, has the empirical formula C5H10O4. Carbohydrates are technically hydrates of carbon; structurally it is more accurate to view them as polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones.The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide, a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. In general, the monosaccharides and disaccharides, which are smaller (lower molecular weight) carbohydrates, are commonly referred to as sugars. The word saccharide comes from the Greek word σάκχαρον (sákkharon), meaning ""sugar."" While the scientific nomenclature of carbohydrates is complex, the names of the monosaccharides and disaccharides very often end in the suffix -ose. For example, grape sugar is the monosaccharide glucose, cane sugar is the disaccharide sucrose and milk sugar is the disaccharide lactose (see illustration).Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. Polysaccharides serve for the storage of energy (e.g., starch and glycogen) and as structural components (e.g., cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). The 5-carbon monosaccharide ribose is an important component of coenzymes (e.g., ATP, FAD and NAD) and the backbone of the genetic molecule known as RNA. The related deoxyribose is a component of DNA. Saccharides and their derivatives include many other important biomolecules that play key roles in the immune system, fertilization, preventing pathogenesis, blood clotting, and development.In food science and in many informal contexts, the term carbohydrate often means any food that is particularly rich in the complex carbohydrate starch (such as cereals, bread and pasta) or simple carbohydrates, such as sugar (found in candy, jams, and desserts).























