Bioenergetics and Metabolism
... it replaces the 2 ATP that were used in stage 1 to prime the glycolytic pathway. Remember, this occurs twice for every glucose that entered glycolysis. This is an example of a substrate level [ADP] phosphorylation reaction, i.e., ATP synthesis that is not the result of aerobic respiration or photoph ...
... it replaces the 2 ATP that were used in stage 1 to prime the glycolytic pathway. Remember, this occurs twice for every glucose that entered glycolysis. This is an example of a substrate level [ADP] phosphorylation reaction, i.e., ATP synthesis that is not the result of aerobic respiration or photoph ...
1 Metabolism Metabolic pathways
... Can be run backward, called gluconeogenesis, using different enzymes for irreversible steps. – Direction is regulated by phosphofructokinase versus fructose1,6-bisphosphatase (which reverses it). Don't want both, since that would produce energy consuming futile cycles! ...
... Can be run backward, called gluconeogenesis, using different enzymes for irreversible steps. – Direction is regulated by phosphofructokinase versus fructose1,6-bisphosphatase (which reverses it). Don't want both, since that would produce energy consuming futile cycles! ...
PS 3 Answers
... An irregularly shaped "shaft" linked to the Fo proton pore rotates relative to the F1 proteins, which are arranged in a ring, when H+ ions flow through Fo. The conformation of each b subunit changes sequentially, as it interacts with the rotating shaft. Each of the 3 b subunits is in a different sta ...
... An irregularly shaped "shaft" linked to the Fo proton pore rotates relative to the F1 proteins, which are arranged in a ring, when H+ ions flow through Fo. The conformation of each b subunit changes sequentially, as it interacts with the rotating shaft. Each of the 3 b subunits is in a different sta ...
Zhan-3-Enzyme
... are competitive (which increases the apparent Km) and noncompetitive (which decreases the Vmax). In contrast, the multi-subunit allosteric enzymes frequently show a sigmoidal curve similar in shape to the oxygen dissociation curve of hemoglobin. They are frequently found catalyzing the committed (ra ...
... are competitive (which increases the apparent Km) and noncompetitive (which decreases the Vmax). In contrast, the multi-subunit allosteric enzymes frequently show a sigmoidal curve similar in shape to the oxygen dissociation curve of hemoglobin. They are frequently found catalyzing the committed (ra ...
Tricarboxylic acid cycle
... 1. Citrate synthase: inhibited by ATP, NADH, acyl CoA and succinyl CoA 2. Isocitrate dehydrogenase: Inhibited by ATP and NADH and activated by ADP 3. -KG dehydrogenase inhibited by NADH & succinyl CoA The availability of ADP: Important for proceeding the TCA cycle if not oxidation of NADH and FADH2 ...
... 1. Citrate synthase: inhibited by ATP, NADH, acyl CoA and succinyl CoA 2. Isocitrate dehydrogenase: Inhibited by ATP and NADH and activated by ADP 3. -KG dehydrogenase inhibited by NADH & succinyl CoA The availability of ADP: Important for proceeding the TCA cycle if not oxidation of NADH and FADH2 ...
BCH 201 – GENERAL BIOCHEMISTRY 1 – (3 UNITS) DR
... Enzymes have enormous catalytic power i.e they can accelerate reaction rate by at least a million Enzymes are highly specific i.e highly specific both in the choice of substrate and in reaction catalysed Activities of some enzymes are regulated i.e different kind of regulatory mechanisms affect enzy ...
... Enzymes have enormous catalytic power i.e they can accelerate reaction rate by at least a million Enzymes are highly specific i.e highly specific both in the choice of substrate and in reaction catalysed Activities of some enzymes are regulated i.e different kind of regulatory mechanisms affect enzy ...
Here is a practice Test
... 24. The chemical reaction that involves pyruvate and lactate may require either oxidation or reduction of a coenzyme, and the direction depends on the relative concentrations of the reactants. a. true b. false 25. In order to be oxidized for the eventual formation of ATP, amino acids must first be b ...
... 24. The chemical reaction that involves pyruvate and lactate may require either oxidation or reduction of a coenzyme, and the direction depends on the relative concentrations of the reactants. a. true b. false 25. In order to be oxidized for the eventual formation of ATP, amino acids must first be b ...
Student Questions and Answers October 15, 2002
... Q 13. How can the enzyme lower the activation energy of a reaction (to reach the transition state) when, in fact, as you mentioned, the substrate turns into the transition state by itself? Does the enzyme catch the substrate a little bit earlier? Is the transition state with an enzyme at a lower ene ...
... Q 13. How can the enzyme lower the activation energy of a reaction (to reach the transition state) when, in fact, as you mentioned, the substrate turns into the transition state by itself? Does the enzyme catch the substrate a little bit earlier? Is the transition state with an enzyme at a lower ene ...
Lecture 17 Glycolysis (continued) Recap Phases: priming: glucose
... ΔGo’ =+6.3 kJ/mol ΔG’ = -1.29 kJ/mol Near equilibrium: not regulated Note that the acid C is oxidized (from aldehyde to acid) Reaction 7 ΔGo’ =-18.9 kJ/mol ΔG’ = +0.1 kJ/mol Near equilibrium: not regulated Note “substrate level phosphorylation” of ADP Reaction 8 ΔGo’ =+4.4 kJ/mol ΔG’ = +0.83 kJ/mol ...
... ΔGo’ =+6.3 kJ/mol ΔG’ = -1.29 kJ/mol Near equilibrium: not regulated Note that the acid C is oxidized (from aldehyde to acid) Reaction 7 ΔGo’ =-18.9 kJ/mol ΔG’ = +0.1 kJ/mol Near equilibrium: not regulated Note “substrate level phosphorylation” of ADP Reaction 8 ΔGo’ =+4.4 kJ/mol ΔG’ = +0.83 kJ/mol ...
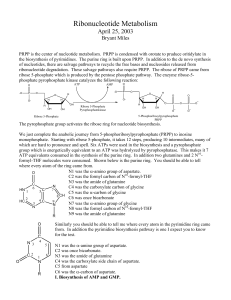
Ribonucleotide Metabolism
... hydroxyl group to form Xanthosine monophosphate. GMP synthetase (another glutamine amido transferase enzyme) transfers the amide nitrogen of glutamine to an activated C2 carbon to produce GMP. This reaction requires ATP to activate the C2 carbon for nucleophilic attack by the ammonia. The mechanisms ...
... hydroxyl group to form Xanthosine monophosphate. GMP synthetase (another glutamine amido transferase enzyme) transfers the amide nitrogen of glutamine to an activated C2 carbon to produce GMP. This reaction requires ATP to activate the C2 carbon for nucleophilic attack by the ammonia. The mechanisms ...
Protein structure is conceptually divided into four levels of organization
... within the funnel formed by the C-termini of the strands and the loops connecting them to the subsequent helices. (b) A view from the top of the barrel of the active site of the enzyme RuBisCo (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase), which is involved in CO2 fixation in plants. A substrate analog (red) ...
... within the funnel formed by the C-termini of the strands and the loops connecting them to the subsequent helices. (b) A view from the top of the barrel of the active site of the enzyme RuBisCo (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase), which is involved in CO2 fixation in plants. A substrate analog (red) ...
Electron Transport Chain, Oxidative phosphorylation and Pentose
... (rotation of the shaft) –to-- chemical energy (ATP) 2. How many Co-enzyme Q10 molecules will be needed to oxidize one molecule of NADH, or one molecule of FADH2. One molecule of CoQ10 3. Fe++/Fe+++ plays major role in the transfer electron s from one molecule to other during mitochondrial ETC and ma ...
... (rotation of the shaft) –to-- chemical energy (ATP) 2. How many Co-enzyme Q10 molecules will be needed to oxidize one molecule of NADH, or one molecule of FADH2. One molecule of CoQ10 3. Fe++/Fe+++ plays major role in the transfer electron s from one molecule to other during mitochondrial ETC and ma ...
Enzymes Activation and Deactivation
... Cyanide does not compete for the active sites of the enzyme because it has no similarity to the substrate cytochrome Cyanide attaches to another site on the enzyme and disrupts the enzyme's shape. This brings the electron transport chain to a halt No energy can be derived out of respiration Hydrogen ...
... Cyanide does not compete for the active sites of the enzyme because it has no similarity to the substrate cytochrome Cyanide attaches to another site on the enzyme and disrupts the enzyme's shape. This brings the electron transport chain to a halt No energy can be derived out of respiration Hydrogen ...
Glycolysis 2
... ATP binds with equal affinity to the catalytic site regardless of the T or R state conformation of PFK-1 ATP binding to the allosteric effector site is highest when the protein is in the T state which functions to decrease fructose-6-P binding to the catalytic site AMP binding to the allosteric eff ...
... ATP binds with equal affinity to the catalytic site regardless of the T or R state conformation of PFK-1 ATP binding to the allosteric effector site is highest when the protein is in the T state which functions to decrease fructose-6-P binding to the catalytic site AMP binding to the allosteric eff ...
BCHM 463 Supplemental Problems for Friday, April 2, 2004 1. Write
... 2. During glycolysis, how many ADP molecules are converted to ATP. Explain this answer with regard to your answer to #1. 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolicall ...
... 2. During glycolysis, how many ADP molecules are converted to ATP. Explain this answer with regard to your answer to #1. 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolicall ...
Answer Key for the Supplemental Problem Set #1
... 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolically irreversible steps of glycolysis? What general type of reaction is catalyzed by these enzymes? Why are these reactions ...
... 4 ADP molecules are converted into ATP. There is a net gain of only 2 ATP molecules because 2 are consumed during the first stage of glycolysis. 3. What are the three metabolically irreversible steps of glycolysis? What general type of reaction is catalyzed by these enzymes? Why are these reactions ...
Ch18.doc
... 2. Note that the question says “excess of pure lactate dehydrogenase and NADH”. This is important because alanine-transaminase will produce pyruvate which as soon as it is produced will be reduced to lactic acid using NADH. NADH has a strong absorbance at 340 nm, so the rate of decrease in 340 nm ab ...
... 2. Note that the question says “excess of pure lactate dehydrogenase and NADH”. This is important because alanine-transaminase will produce pyruvate which as soon as it is produced will be reduced to lactic acid using NADH. NADH has a strong absorbance at 340 nm, so the rate of decrease in 340 nm ab ...
ENZYMES: CLASSIFICATION, STRUCTURE
... • PLP is derived from Vit B6 family of vitamins PLP is a coenzyme for enzymes catalyzing reactions involving amino acid metabolism (isomerizations, decarboxylations, transamination) ...
... • PLP is derived from Vit B6 family of vitamins PLP is a coenzyme for enzymes catalyzing reactions involving amino acid metabolism (isomerizations, decarboxylations, transamination) ...
Detection of the reaction intermediates catalyzed by a copper amine
... position. We concluded that the product Schiff-base (TPQpsb) was formed as a result of fitting models for TPQssb and TPQpsb to the electron density map. This result almost corresponded to the ratio of the time change of the amount of TPQpsb in the crystal to that in solution from previous work by us ...
... position. We concluded that the product Schiff-base (TPQpsb) was formed as a result of fitting models for TPQssb and TPQpsb to the electron density map. This result almost corresponded to the ratio of the time change of the amount of TPQpsb in the crystal to that in solution from previous work by us ...
Topics To Know For Chapter 6
... 3. Know that photosynthesis involves redox reactions. 4. Know that photosynthesis is divided in two parts. Where in the chloroplast do they take place? - light dependent reactions - chemiosmosis - light independent reactions - phosphorylation - Calvin cycle - oxygen - NADP & NADPH - carbon fixation ...
... 3. Know that photosynthesis involves redox reactions. 4. Know that photosynthesis is divided in two parts. Where in the chloroplast do they take place? - light dependent reactions - chemiosmosis - light independent reactions - phosphorylation - Calvin cycle - oxygen - NADP & NADPH - carbon fixation ...
Stability, catalytic versatility and evolution of the
... helix α2 with strand β3 were shortened by deleting two residues at their tips. The reciprocal hydrophobic interactions were further weakened by replacing Phe55, which is located close to the twofold symmetry axis of the dimer, with either glutamine or glutamate. The Phe55Glu variant is purely monome ...
... helix α2 with strand β3 were shortened by deleting two residues at their tips. The reciprocal hydrophobic interactions were further weakened by replacing Phe55, which is located close to the twofold symmetry axis of the dimer, with either glutamine or glutamate. The Phe55Glu variant is purely monome ...
View Full PDF - Biochemical Society Transactions
... slopes of the primary double-reciprocal plots (of reaction rate against ATP concentration) as a function of inhibitor concentration were linear. When pyruvate was the variable substrate, however, non-linear-slope replots were obtained. Non-linear-slope effects normally reflect multiple combination o ...
... slopes of the primary double-reciprocal plots (of reaction rate against ATP concentration) as a function of inhibitor concentration were linear. When pyruvate was the variable substrate, however, non-linear-slope replots were obtained. Non-linear-slope effects normally reflect multiple combination o ...
Crystal Structure of the Carboxyltransferase Domain of Acetyl
... superfamily. The active site is at the interface of a dimer. Mutagenesis and kinetic studies reveal the functional roles of conserved residues here. The herbicides target the active site of CT, providing a lead for inhibitor development against human ACCs. Acetyl–coenzyme A carboxylases (ACCs) catal ...
... superfamily. The active site is at the interface of a dimer. Mutagenesis and kinetic studies reveal the functional roles of conserved residues here. The herbicides target the active site of CT, providing a lead for inhibitor development against human ACCs. Acetyl–coenzyme A carboxylases (ACCs) catal ...
Minimal domain of bacterial phytochrome required for chromophore binding and fluorescence
... encoded NIR probes used in studing metabolic processes noninvasively and deep tissue1. NIR light has advantages in penetrating mammalian tissues much deeper than visible light and resulting in less light scattering. Bacterial phytochrome photoreceptors (BphPs) are the most suitable templates for eng ...
... encoded NIR probes used in studing metabolic processes noninvasively and deep tissue1. NIR light has advantages in penetrating mammalian tissues much deeper than visible light and resulting in less light scattering. Bacterial phytochrome photoreceptors (BphPs) are the most suitable templates for eng ...
Luciferase

Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes used in bioluminescence and is distinct from a photoprotein. The name is derived from Lucifer, the root of which means 'light-bearer' (lucem ferre). One example is the firefly luciferase (EC 1.13.12.7) from the firefly Photinus pyralis. ""Firefly luciferase"" as a laboratory reagent often refers to P. pyralis luciferase although recombinant luciferases from several other species of fireflies are also commercially available.