Concept Map Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Graphic
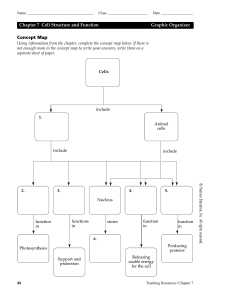
... Using information from the chapter, complete the concept map below. If there is not enough room in the concept map to write your answers, write them on a separate sheet of paper. ...
... Using information from the chapter, complete the concept map below. If there is not enough room in the concept map to write your answers, write them on a separate sheet of paper. ...
Parts of a Cell
... Breakdown sugar and make ATP (adenosine triphosphate). • Large amounts of energy are released during breakdown of sugars. • Mitochondria gathers this energy and stores it. 5. More active the cell-more mitochondria. ...
... Breakdown sugar and make ATP (adenosine triphosphate). • Large amounts of energy are released during breakdown of sugars. • Mitochondria gathers this energy and stores it. 5. More active the cell-more mitochondria. ...
Photo Album
... – double membranes = 2 membranes – semi-autonomous organelles • move, change shape, divide ...
... – double membranes = 2 membranes – semi-autonomous organelles • move, change shape, divide ...
Unit 4 Cell Transport Notes Packet - Dallastown Area School District
... Unit 4 = Cell Transport Honors Biology ...
... Unit 4 = Cell Transport Honors Biology ...
Fluid Mosaic Model - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... Hypertonic—an area of high solute concentration Hypotonic—an area of low solute concentration Isotonic—two areas of the same solute concentration ...
... Hypertonic—an area of high solute concentration Hypotonic—an area of low solute concentration Isotonic—two areas of the same solute concentration ...
Pre – AP Biology
... – This acts as a control center for all activities performed by the cell. (Like the principal’s office for a school.) – It is the source of genetic information (DNA). It “acts as the vault for the million dollar blueprint of a cell”. ...
... – This acts as a control center for all activities performed by the cell. (Like the principal’s office for a school.) – It is the source of genetic information (DNA). It “acts as the vault for the million dollar blueprint of a cell”. ...
Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport
... substances into and out of the cell. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable, allowing only certain substances to pass through. Proteins embedded within the plasma membrane help to move hydrophilic, polar molecules into the cell. The cytoplasm is the internal medium for cell transport. Vesicle ...
... substances into and out of the cell. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable, allowing only certain substances to pass through. Proteins embedded within the plasma membrane help to move hydrophilic, polar molecules into the cell. The cytoplasm is the internal medium for cell transport. Vesicle ...
Cell Organelle Reading
... the nucleus of the cell stand out. It also makes individual cells stand out by staining the cell membrane. The cell membrane is a thin layer that separates the inside of the cell from its outside environment. The Cell Membrane regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. It keeps the ...
... the nucleus of the cell stand out. It also makes individual cells stand out by staining the cell membrane. The cell membrane is a thin layer that separates the inside of the cell from its outside environment. The Cell Membrane regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. It keeps the ...
File
... 6. Which two elements are found in all organic molecules? Use the very back of the textbook if necessary. 7. Label the following as either organic (O) or inorganic (I). a. Carbon dioxide (CO2) ______ b. Oxygen (O2) _____ ...
... 6. Which two elements are found in all organic molecules? Use the very back of the textbook if necessary. 7. Label the following as either organic (O) or inorganic (I). a. Carbon dioxide (CO2) ______ b. Oxygen (O2) _____ ...
Intervention Cells and Reproduction Pack
... 14. The function of the _____________ is to digest (break down) food. 15. The function of the _____________ is to pump blood around the body. 16. Chloroplasts contain _____________ that absorbs sunlight and uses it in photosynthesis. 17. The _____________ gives support and is found in plant cells bu ...
... 14. The function of the _____________ is to digest (break down) food. 15. The function of the _____________ is to pump blood around the body. 16. Chloroplasts contain _____________ that absorbs sunlight and uses it in photosynthesis. 17. The _____________ gives support and is found in plant cells bu ...
document
... • Wall of each centriole is made of 9 triplets of tubes arranged at an angle Function • During cell division they migrate to opposite poles to produce the spindle – which helps to move the chromosomes during cell division ...
... • Wall of each centriole is made of 9 triplets of tubes arranged at an angle Function • During cell division they migrate to opposite poles to produce the spindle – which helps to move the chromosomes during cell division ...
Basic Cell Structure
... have a nucleus • May be single celled – Kingdom Protista • May have billions of cells like plant and animal kingdoms ...
... have a nucleus • May be single celled – Kingdom Protista • May have billions of cells like plant and animal kingdoms ...
Cell organelles and functions
... membrane encloses nucleoplasm and nucleolus. Nuclear membrane is double layered and porous in nature. This allows the nucleoplasm to communicate (exchange of material) with the cytoplasm. Nucleoplasm is a gel like substance that contains large quantities of DNA, which forms the gene. One or mo ...
... membrane encloses nucleoplasm and nucleolus. Nuclear membrane is double layered and porous in nature. This allows the nucleoplasm to communicate (exchange of material) with the cytoplasm. Nucleoplasm is a gel like substance that contains large quantities of DNA, which forms the gene. One or mo ...
GCMS lesson plan September 5
... brings the stories they developed to life. Today is the final day for the students to draw and color their cell city. The student’s projects will be submitted Wednesday. Teacher Input: TTW monitor the students as they develop their projects using PowerPoint. TTW assist the students as needed. Closur ...
... brings the stories they developed to life. Today is the final day for the students to draw and color their cell city. The student’s projects will be submitted Wednesday. Teacher Input: TTW monitor the students as they develop their projects using PowerPoint. TTW assist the students as needed. Closur ...
Cells
... Dictyosomes Flat stacks of organelles throughout the cell Collecting, packaging and delivering centers Post Offices ...
... Dictyosomes Flat stacks of organelles throughout the cell Collecting, packaging and delivering centers Post Offices ...
Unit 2 Review Answer Key
... 11. A bacterial cell fits into what cell category? prokaryote 12. What organelle digests worn out cells? lysosome 13. Name the organelles found in a plant cell that are not found in an animal cell. cell wall, central vacuole, chloroplast 14. Where is the cytoplasm in the cell? all around—it’s the su ...
... 11. A bacterial cell fits into what cell category? prokaryote 12. What organelle digests worn out cells? lysosome 13. Name the organelles found in a plant cell that are not found in an animal cell. cell wall, central vacuole, chloroplast 14. Where is the cytoplasm in the cell? all around—it’s the su ...
Cell Processes Notes
... example, when an organism needs more energy, the mitochondria will speed up their activity. An organisms feedback system signals an increase or decrease in cell activity to permit homeostasis. CELL TRANSPORT PROCESSES Living cells need many kinds of substances to remain alive, such as water, sugar f ...
... example, when an organism needs more energy, the mitochondria will speed up their activity. An organisms feedback system signals an increase or decrease in cell activity to permit homeostasis. CELL TRANSPORT PROCESSES Living cells need many kinds of substances to remain alive, such as water, sugar f ...
Cells Notes
... B. No organelles C. Large and complex T/F Eukaryotes have no nucleus Which of the following is not part of the cell theory A. Basic unit of life B. Come from pre-existing cells C. Are non living ...
... B. No organelles C. Large and complex T/F Eukaryotes have no nucleus Which of the following is not part of the cell theory A. Basic unit of life B. Come from pre-existing cells C. Are non living ...
Y7 Cells - Marshfields School
... 14. The function of the _____________ is to digest (break down) food. 15. The function of the _____________ is to pump blood around the body. 16. Chloroplasts contain _____________ that absorbs sunlight and uses it in photosynthesis. 17. The _____________ gives support and is found in plant cells bu ...
... 14. The function of the _____________ is to digest (break down) food. 15. The function of the _____________ is to pump blood around the body. 16. Chloroplasts contain _____________ that absorbs sunlight and uses it in photosynthesis. 17. The _____________ gives support and is found in plant cells bu ...
Transport PRactice - Mayfield City Schools
... 10. Label: endocytosis and exocytosis in the diagram below. Explain what is happening in both sides of this diagram. Please use scientific words when possible. ...
... 10. Label: endocytosis and exocytosis in the diagram below. Explain what is happening in both sides of this diagram. Please use scientific words when possible. ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑























