Plant Cells
... Some metabolic steps of cellular respiration are catalyzed in the mitochondrial matrix Cristae present a large surface area for enzymes that synthesize ATP Intermembrane space ...
... Some metabolic steps of cellular respiration are catalyzed in the mitochondrial matrix Cristae present a large surface area for enzymes that synthesize ATP Intermembrane space ...
The Cell In Its Environment Slide Show Notes
... • Cells have structures that protect their contents from the world outside. • All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that separates the cell from the outside environment. • The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which lets some things enter and leave the cell. • Name 3 substances that ente ...
... • Cells have structures that protect their contents from the world outside. • All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that separates the cell from the outside environment. • The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which lets some things enter and leave the cell. • Name 3 substances that ente ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... What is the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesis? What organelle is considered a “factory”, because it takes in raw materials and converts them to cell products that can be used by the cell? ...
... What is the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesis? What organelle is considered a “factory”, because it takes in raw materials and converts them to cell products that can be used by the cell? ...
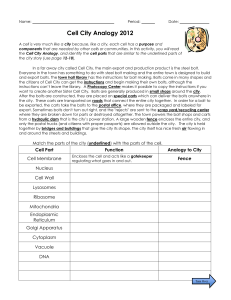
Cell City Analogy - Rochester Community Schools
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
Chapter 7
... • Found in the plasma membrane of animal cells • This protein pump is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of an energy-storing molecule • The pump uses the energy in order to transport sodium ions out of the cell while moving 2 potassium ions into the cell ...
... • Found in the plasma membrane of animal cells • This protein pump is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of an energy-storing molecule • The pump uses the energy in order to transport sodium ions out of the cell while moving 2 potassium ions into the cell ...
Unit 3: Cell and Cell Transport (Chapter 7) 7.1 Cell Theory • are the
... All cells share certain characteristics: – All cells have: A _____________________ (plasma membrane) that is ____________________. ________________ = jellylike material in cell Ribosomes = __________________ _______________ = protein filaments that provide ______________, ____________ and he ...
... All cells share certain characteristics: – All cells have: A _____________________ (plasma membrane) that is ____________________. ________________ = jellylike material in cell Ribosomes = __________________ _______________ = protein filaments that provide ______________, ____________ and he ...
Photo Album
... Figure 2.7 Examples of myosin motor proteins found in mammalian brain. Myosin heavy chains contain the motor domain, whereas light chains (small dumbbell-shaped structures) regulate motor function. Myosin II was the first molecular motor characterized biochemically from skeletal muscle and brain. G ...
... Figure 2.7 Examples of myosin motor proteins found in mammalian brain. Myosin heavy chains contain the motor domain, whereas light chains (small dumbbell-shaped structures) regulate motor function. Myosin II was the first molecular motor characterized biochemically from skeletal muscle and brain. G ...
Tour Of The Cell
... • Electron microscope - resolving power is greater since wavelengths of electrons is smaller than those of light. – SEM - 3D image – TEM - flat image • electron microscopes cannot use live specimens ...
... • Electron microscope - resolving power is greater since wavelengths of electrons is smaller than those of light. – SEM - 3D image – TEM - flat image • electron microscopes cannot use live specimens ...
Journey Through a Cell Rubric
... necessary for cells to function. Each type of organelle has an individual job that it is responsible for. In this assignment, you will take a “journey through a cell” and explain (IN YOUR OWN WORDS!!) the role of each of the organelles. Some organelles are only found in plant cells and some are only ...
... necessary for cells to function. Each type of organelle has an individual job that it is responsible for. In this assignment, you will take a “journey through a cell” and explain (IN YOUR OWN WORDS!!) the role of each of the organelles. Some organelles are only found in plant cells and some are only ...
Subject: Biology
... Surrounds the vacuole and regulates entry/exit of substances into/out of the vacuole Regulates entry and exit of substances into and out of the cell It is here that proteins manufactured in the cell are modified. Its surface is covered with ribosomes. Here, newly manufactured proteins pass along the ...
... Surrounds the vacuole and regulates entry/exit of substances into/out of the vacuole Regulates entry and exit of substances into and out of the cell It is here that proteins manufactured in the cell are modified. Its surface is covered with ribosomes. Here, newly manufactured proteins pass along the ...
Cytoplasm
... network of protein rods thru cytosol supports cell structure allows cell movement Types: 1. Microfilaments 2. Intermediate Filaments 3. Microtubules ...
... network of protein rods thru cytosol supports cell structure allows cell movement Types: 1. Microfilaments 2. Intermediate Filaments 3. Microtubules ...
Journey Through a Cell Rubric
... necessary for cells to function. Each type of organelle has an individual job that it is responsible for. In this assignment, you will take a “journey through a cell” and explain (IN YOUR OWN WORDS!!) the role of each of the organelles. Some organelles are only found in plant cells and some are only ...
... necessary for cells to function. Each type of organelle has an individual job that it is responsible for. In this assignment, you will take a “journey through a cell” and explain (IN YOUR OWN WORDS!!) the role of each of the organelles. Some organelles are only found in plant cells and some are only ...
CHAPTER 7
... Osmotic pressure inside cell decreases- plant wilts = flaccid HYPOTONIC- Solute concentration outside cell is less than inside Water will enter cellAnimal- cell will swell & burst = cytolysis Freshwater critters have contractile vacuoles to collect and remove excess water Plant – cell wall keeps cel ...
... Osmotic pressure inside cell decreases- plant wilts = flaccid HYPOTONIC- Solute concentration outside cell is less than inside Water will enter cellAnimal- cell will swell & burst = cytolysis Freshwater critters have contractile vacuoles to collect and remove excess water Plant – cell wall keeps cel ...
6 Tour of the Cell II
... • Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis, the conversion of light energy to chemical food energy – They are food production factories and are found only in plants and some protists (algae & seaweed) ...
... • Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis, the conversion of light energy to chemical food energy – They are food production factories and are found only in plants and some protists (algae & seaweed) ...
Cell Membrane - Dickinson ISD
... Concentration – the mass of solute in a given volume of solution. The cytoplasm of a cell is at a certain concentration. The fluid surrounding the cell is at another concentration. Diffusion – movement of particles from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration. When ...
... Concentration – the mass of solute in a given volume of solution. The cytoplasm of a cell is at a certain concentration. The fluid surrounding the cell is at another concentration. Diffusion – movement of particles from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration. When ...
THE CELL THEORY 1. All living things are composed of cells and
... ♦ Found at sites of highest metabolism (e.g. muscle cells) to produce energy-rich molecules of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) ♦ Mitochondria have a double membrane – the outer membrane around the entire mitochondrion, and the inner membrane folded back and forth for large surface area for chemical re ...
... ♦ Found at sites of highest metabolism (e.g. muscle cells) to produce energy-rich molecules of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) ♦ Mitochondria have a double membrane – the outer membrane around the entire mitochondrion, and the inner membrane folded back and forth for large surface area for chemical re ...
Chapter 31: Page 378
... This outer protection is similar to how a cell wall protects the inside of a plant cell. Every orange has a stem on its top. This is where the nutrients from an orange tree can be sent into the orange itself! A cell wall has many similar openings, allowing materials into and out of, the cell! Indepe ...
... This outer protection is similar to how a cell wall protects the inside of a plant cell. Every orange has a stem on its top. This is where the nutrients from an orange tree can be sent into the orange itself! A cell wall has many similar openings, allowing materials into and out of, the cell! Indepe ...
Ch 7.3 Cell Parts and Functions
... capturing energy from sunlight and converting it into useable energy • Thylakoid compartments containing chlorophyll ...
... capturing energy from sunlight and converting it into useable energy • Thylakoid compartments containing chlorophyll ...
Review Chapter 5
... Explain the types of passive transport. Diffusion: movement of molecules from an area of higher conc. to an area of lower concentration Example: Food coloring added to water (S.A) Osmosis: movement of water from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration (S.A) Facilitated Diff ...
... Explain the types of passive transport. Diffusion: movement of molecules from an area of higher conc. to an area of lower concentration Example: Food coloring added to water (S.A) Osmosis: movement of water from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration (S.A) Facilitated Diff ...
Cell membrane ppt notes File
... b. Hydrophobic tails (nonpolar) made out of fatty acids (Lipid) ...
... b. Hydrophobic tails (nonpolar) made out of fatty acids (Lipid) ...
lecture6(Eukaryote)
... peroxisomes usually self-‐replicate by enlarging and then dividing, although there is some indica1on that new ones may be formed directly. • Found in both plant and animal cells. ...
... peroxisomes usually self-‐replicate by enlarging and then dividing, although there is some indica1on that new ones may be formed directly. • Found in both plant and animal cells. ...
organelle function ws. - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... 2. uses energy from food to make high-energy compounds 3. provides support and protection for the cell ...
... 2. uses energy from food to make high-energy compounds 3. provides support and protection for the cell ...
Cells and Organelles
... – Creates ATP, an energy containing molecule that acts as a “battery” to power other cell reactions – ATP is the “energy currency” of the cell ...
... – Creates ATP, an energy containing molecule that acts as a “battery” to power other cell reactions – ATP is the “energy currency” of the cell ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑