Reminder Cell Composition Early Cell Discoveries Cell Theory
... evolved from ancient bacteria that were engulfed, not digested. 4. Mitochondrial DNA is only inherited from the mother and can be used to trace maternal lineages. Useful in forensics. ...
... evolved from ancient bacteria that were engulfed, not digested. 4. Mitochondrial DNA is only inherited from the mother and can be used to trace maternal lineages. Useful in forensics. ...
Life is Cellular
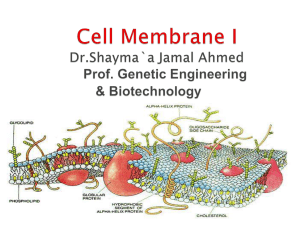
... III. Cell Membrane A. Thin layer of lipids and proteins that separate cell contents B. Selectively Permeable ...
... III. Cell Membrane A. Thin layer of lipids and proteins that separate cell contents B. Selectively Permeable ...
PGS: 124 – 138
... b. It flows from High Ψ to Low Ψ. (It can be affected by the pressure of a plant cell wall.) c. Pushing is positive pressure being exerted on the cell. (+ΨP) d. Pulling away from is negative pressure (-ΨP) being exerted on a cell. (Important when you consider a plant is having water pulled out of it ...
... b. It flows from High Ψ to Low Ψ. (It can be affected by the pressure of a plant cell wall.) c. Pushing is positive pressure being exerted on the cell. (+ΨP) d. Pulling away from is negative pressure (-ΨP) being exerted on a cell. (Important when you consider a plant is having water pulled out of it ...
Cell Functions
... Function: Support structure of cell and transport materials/organelles throughout the cell. The highway of the cell. Made of Microtubules (thin hollow cylinders) and Microfilaments (thin solid ...
... Function: Support structure of cell and transport materials/organelles throughout the cell. The highway of the cell. Made of Microtubules (thin hollow cylinders) and Microfilaments (thin solid ...
Plant/Animal Cell Info
... In eukaryotic cells, including the cells of your body, ATP is produced within special membrane-bound organelles called mitochondria. During this process, electrons are shuttled through an iron-containing cytochrome enzyme system along membranes of the cristae which result in the phosphorylation of A ...
... In eukaryotic cells, including the cells of your body, ATP is produced within special membrane-bound organelles called mitochondria. During this process, electrons are shuttled through an iron-containing cytochrome enzyme system along membranes of the cristae which result in the phosphorylation of A ...
Science 8 Questions 1. What does Organelle mean? 2. What is
... 19. What is the job of cilia and flagella? 20. What is the difference between cilia and flagella? 21. What cells have a cell wall? 22. What is the job of the cell wall? 23. What is the job of chloroplast? 24. What is the job of the vacuole? 25. How do plant and animal cells differ in regards to vacu ...
... 19. What is the job of cilia and flagella? 20. What is the difference between cilia and flagella? 21. What cells have a cell wall? 22. What is the job of the cell wall? 23. What is the job of chloroplast? 24. What is the job of the vacuole? 25. How do plant and animal cells differ in regards to vacu ...
Notes - Cell Processes
... • The movement of water into or out of the cell from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration - Osmosis. – Perhaps the most important substance that passes through the cell membrane is WATER. – Cells can’t function properly without adequate amount of water. ...
... • The movement of water into or out of the cell from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration - Osmosis. – Perhaps the most important substance that passes through the cell membrane is WATER. – Cells can’t function properly without adequate amount of water. ...
Science Menu: Cells
... create a model of the cell you chose. It must be 3-dimensional. This means it needs to have a front, back, and sides. It cannot be a piece of paper with things glued on it. Make sure to include all the main structures of the cell and the function of each. You will need to use materials you have at h ...
... create a model of the cell you chose. It must be 3-dimensional. This means it needs to have a front, back, and sides. It cannot be a piece of paper with things glued on it. Make sure to include all the main structures of the cell and the function of each. You will need to use materials you have at h ...
Cell Membranes - Lovejoy High School
... Diffusion Diffusion - the process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration, to areas of low concentration. Passive Transport-requires no energy ...
... Diffusion Diffusion - the process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration, to areas of low concentration. Passive Transport-requires no energy ...
cell-a-brate life
... composed of cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of all life as we know it. Thanks to the invention of the microscope, Robert Hooke in the late 1600's was the first to named the tiny compartments of cork tree, cells. Just like we have organs that perform certain tasks, cells have tiny organs c ...
... composed of cells. Cells are the basic building blocks of all life as we know it. Thanks to the invention of the microscope, Robert Hooke in the late 1600's was the first to named the tiny compartments of cork tree, cells. Just like we have organs that perform certain tasks, cells have tiny organs c ...
Slide 1 - Lewiston School District
... B) Rigid but varying from cell to cell C) Fluid but unorganized D) Very active E) Rigid and organized ...
... B) Rigid but varying from cell to cell C) Fluid but unorganized D) Very active E) Rigid and organized ...
Introduction to Cell Theory
... written on separate paper), describeing how the organelles in a cell work together to make and use proteins. Include at least 5 different organelles in your essay. ...
... written on separate paper), describeing how the organelles in a cell work together to make and use proteins. Include at least 5 different organelles in your essay. ...
Chapter Review - Paul J. Goodenough
... Then answer the questions below. Plants and animals are typically multicellular organisms. For a long time, scientists tried to classify any unicellular organism that had a nucleus as either a single-celled plant or a single-celled animal. One group of unicellular organisms, Euglenas, was particular ...
... Then answer the questions below. Plants and animals are typically multicellular organisms. For a long time, scientists tried to classify any unicellular organism that had a nucleus as either a single-celled plant or a single-celled animal. One group of unicellular organisms, Euglenas, was particular ...
Homeostasis, Osmosis, Transport Unit 6 – Chapter 5
... Osmosis is the name for an important type of diffusion. It is the diffusion of water across the cell membrane. _____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________. Too much water in or out of the cell can become a problem. Osmosis ...
... Osmosis is the name for an important type of diffusion. It is the diffusion of water across the cell membrane. _____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________. Too much water in or out of the cell can become a problem. Osmosis ...
CELLS- STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... ACTIVE MECHANISMS 3) Active Transport -Carriers move molecules from low to high concentration -~40% of energy used by our cells is used to operate these “pumps” ...
... ACTIVE MECHANISMS 3) Active Transport -Carriers move molecules from low to high concentration -~40% of energy used by our cells is used to operate these “pumps” ...
KEY | Cell Review Worksheet | Chapter 3
... 10. Which part of a phospholipid is polar? The head is polar ...
... 10. Which part of a phospholipid is polar? The head is polar ...
Multiple Choice
... Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Many marine organisms have body surfaces that are permeable to water but not to salt. Osmosis can change the pressure of their body fluids. Fortunately, the ocean is very stable in its salt content. Wh ...
... Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Many marine organisms have body surfaces that are permeable to water but not to salt. Osmosis can change the pressure of their body fluids. Fortunately, the ocean is very stable in its salt content. Wh ...
02.3 Eukaryotes
... that a plant has which an animal cell doesn’t is vacuoles, the vacuoles in a plant cell store food, water and waste products as well as other materials and nutrients as well as keeping the plant cell strong to keep the adult plant upright. There is one organelle that an animal cell has that a plant ...
... that a plant has which an animal cell doesn’t is vacuoles, the vacuoles in a plant cell store food, water and waste products as well as other materials and nutrients as well as keeping the plant cell strong to keep the adult plant upright. There is one organelle that an animal cell has that a plant ...
CELLS- STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... ACTIVE MECHANISMS 4) Pinocytosis (cell drinking) - This is one type of “endocytosis” - Cell membrane surrounds fluid - The sac pinches off and brings liquid inside ...
... ACTIVE MECHANISMS 4) Pinocytosis (cell drinking) - This is one type of “endocytosis” - Cell membrane surrounds fluid - The sac pinches off and brings liquid inside ...
The Cell (including cell division)
... just before nuclear division, chromatin condenses into chromatids (so they won’t break apart during division) and are held together by centromeres. ...
... just before nuclear division, chromatin condenses into chromatids (so they won’t break apart during division) and are held together by centromeres. ...
Cell Organelles
... Gel-like fluid that fills the cell Surrounded by cell membrane Constantly moving around the cell Contains all of the cell’s organelles ...
... Gel-like fluid that fills the cell Surrounded by cell membrane Constantly moving around the cell Contains all of the cell’s organelles ...
ch_03 - HCC Learning Web
... osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane in response to differing concentrations of solutes. Concentrations of solutes can be compared as follows: hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration of solutes than hypotonic solutions. For example, seawater is hyperto ...
... osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane in response to differing concentrations of solutes. Concentrations of solutes can be compared as follows: hypertonic solutions have a higher concentration of solutes than hypotonic solutions. For example, seawater is hyperto ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑