AQA B2 ESQ - Mitosis and Meiosis 1
... What happens to the genetic material before the cell divides? ...
... What happens to the genetic material before the cell divides? ...
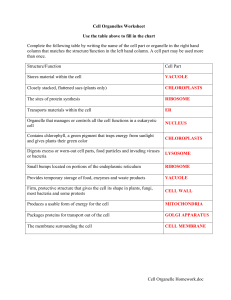
Cell Organelle Worksheet
... microtubules that function in cell division in animal cells. They anchor the spindle fibers during cell division and allow chromosomes to be moved to the opposite ends of the cell. ...
... microtubules that function in cell division in animal cells. They anchor the spindle fibers during cell division and allow chromosomes to be moved to the opposite ends of the cell. ...
Lab Retreat 2011
... In theory, the rate of irreversible deformation (or “growth”) depends on the mechanical stress in the cell wall, and therefore on the turgor pressure. See Gaurav’s and Jen’s talks. ...
... In theory, the rate of irreversible deformation (or “growth”) depends on the mechanical stress in the cell wall, and therefore on the turgor pressure. See Gaurav’s and Jen’s talks. ...
Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... Sporulation: Endospore formation Germination: Return to vegetative state ...
... Sporulation: Endospore formation Germination: Return to vegetative state ...
Cell Boundaries - Deans Community High School
... Active Transport is the movement of molecules and ions across the plasma membrane from a Low Concentration to a High Concentration. i.e. Against a Concentration Gradient. Active transport requires Energy as it is working in the opposite direction to the passive process of diffusion. ...
... Active Transport is the movement of molecules and ions across the plasma membrane from a Low Concentration to a High Concentration. i.e. Against a Concentration Gradient. Active transport requires Energy as it is working in the opposite direction to the passive process of diffusion. ...
Bacteria Bacterial Structure Bacteria differ from eukaryotes in 7 ways
... a. Purple non-sulfur (use organic compounds as source for photosynthesis) b. Green sulfur (use sulfur compounds as source for photosynthesis) i. Live in anaerobic (Oxygen-free) environment c. Purple sulfur (use sulfur compounds as source for photosynthesis) i. Live in anaerobic (Oxygen-free) environ ...
... a. Purple non-sulfur (use organic compounds as source for photosynthesis) b. Green sulfur (use sulfur compounds as source for photosynthesis) i. Live in anaerobic (Oxygen-free) environment c. Purple sulfur (use sulfur compounds as source for photosynthesis) i. Live in anaerobic (Oxygen-free) environ ...
Ch3 Cell City Analogy Web Quest Worksheet
... better understand how cells work and the specific functions of each cell structure or organelle. Then think of any other type of analogy you can make to help you better understand the cell structure and function? Explain. ...
... better understand how cells work and the specific functions of each cell structure or organelle. Then think of any other type of analogy you can make to help you better understand the cell structure and function? Explain. ...
Organelles for support and locomotion
... The cytoskeleton Forms a framework for the cell It can be dismantled in one place and reassembled somewhere else changing the cell’s shape Microtubules – thin, hollow cylinders made of protein Microfillaments – smaller, solid protein fibers ...
... The cytoskeleton Forms a framework for the cell It can be dismantled in one place and reassembled somewhere else changing the cell’s shape Microtubules – thin, hollow cylinders made of protein Microfillaments – smaller, solid protein fibers ...
Cell Project
... and takes the players water when a time out is called and when the game is being played. ...
... and takes the players water when a time out is called and when the game is being played. ...
Cell Wall • Like animal cells, plant cells contain a cell membrane
... Since plants are immobile, they must have these huge reservoirs to stock up on water/nutrients when they are available o They must stay nourished in the event of a shortage In the event of a drought, the cell will utilize its water reserves o As this occurs, the turgor pressure in the cell wall decr ...
... Since plants are immobile, they must have these huge reservoirs to stock up on water/nutrients when they are available o They must stay nourished in the event of a shortage In the event of a drought, the cell will utilize its water reserves o As this occurs, the turgor pressure in the cell wall decr ...
Document
... •A membrane-bound, fluidfilled sac that occupies much of the volume of a plant cell. •The pressure of the central vacuole makes it possible for plants to support heavy structures like leaves and stems •Also functions as a place to store water, since plants can’t move to get water like animals can. ...
... •A membrane-bound, fluidfilled sac that occupies much of the volume of a plant cell. •The pressure of the central vacuole makes it possible for plants to support heavy structures like leaves and stems •Also functions as a place to store water, since plants can’t move to get water like animals can. ...
Archaebacteria_and_Eubacteria_Notes
... o Archaebacteria are found in anaerobic and extreme conditions (high [salt], high temperature, and low pH), similar to what are believed to be the conditions on the early Earth. Earth’s early atmosphere did not contain oxygen, therefore the earliest organisms were anaerobic. o Eubacteria includes ...
... o Archaebacteria are found in anaerobic and extreme conditions (high [salt], high temperature, and low pH), similar to what are believed to be the conditions on the early Earth. Earth’s early atmosphere did not contain oxygen, therefore the earliest organisms were anaerobic. o Eubacteria includes ...
CLIL IS… - Share Dschola
... changes into liquid as rain, hail and snow. When rain water falls back to the Earth a part soaks into the ground; then through the roots it passes to plants and then flows to the oceans crossing to the rivers and ground water level. ...
... changes into liquid as rain, hail and snow. When rain water falls back to the Earth a part soaks into the ground; then through the roots it passes to plants and then flows to the oceans crossing to the rivers and ground water level. ...
Eukaryotic Cells: The Inside Story
... Contains the nucleolus which stores the materials that will be used to make ribosomes Largest and most visible organelle ...
... Contains the nucleolus which stores the materials that will be used to make ribosomes Largest and most visible organelle ...
FIRST HOUR EXAM REGISTRATION NO.: ……… March 25, 2014
... ………………..6. the most common types of Gram positive cell walls is an S-layer composed of glycoprotein or protein F, archeae …………………7. Dry heat sterilization is generally faster than moist heat sterilization F, slower …………………8. A sterile object is completely free of viable MO T ...
... ………………..6. the most common types of Gram positive cell walls is an S-layer composed of glycoprotein or protein F, archeae …………………7. Dry heat sterilization is generally faster than moist heat sterilization F, slower …………………8. A sterile object is completely free of viable MO T ...
Cell Organelle Homework.doc Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria ...
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria ...
Rotavirus
... – Lipoteichoic acid links to plasma membrane – Wall teichoic acid links to peptidoglycan May regulate movement of cations (+ charge) ...
... – Lipoteichoic acid links to plasma membrane – Wall teichoic acid links to peptidoglycan May regulate movement of cations (+ charge) ...
Gram Staining and Cell Wall Structure
... having. Bacterial cell walls do NOT contain cellulose like plant cell walls do. Bacterial cell walls are made mostly of a chemical called peptidogly (made of polypeptides bonded to modified sugars), but the amount and location of the peptidoglycan are different in the two possible types of cell wall ...
... having. Bacterial cell walls do NOT contain cellulose like plant cell walls do. Bacterial cell walls are made mostly of a chemical called peptidogly (made of polypeptides bonded to modified sugars), but the amount and location of the peptidoglycan are different in the two possible types of cell wall ...
A1979HZ27200001
... Tumor Institute in Houston in an attempt to demonstrate just where the tissues of inbred maize and their heterotic hybrids showed differences in the nature or number of ...
... Tumor Institute in Houston in an attempt to demonstrate just where the tissues of inbred maize and their heterotic hybrids showed differences in the nature or number of ...
organelles - La Paz Wiki
... break down molecules into smaller ones that can be used. • If a lysosome breaks open inside the cell, it dissolves the cell itself! ...
... break down molecules into smaller ones that can be used. • If a lysosome breaks open inside the cell, it dissolves the cell itself! ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.