CELL ORGANELLES – VOCABULARY REFERENCE SHEET
... Chains of amino acids that make up and carry out all processes in a cell and living organisms. They may be enzymes, build the structure of a cell or cell part, or send signals to repair the cell or fight off intruding organisms. ...
... Chains of amino acids that make up and carry out all processes in a cell and living organisms. They may be enzymes, build the structure of a cell or cell part, or send signals to repair the cell or fight off intruding organisms. ...
Course outline - E-Learning/An
... Text Book: Becker’s World of the Cell 8th edition (2012). Hardin, Bertoni and Kliensmith. Course description: This course is concerned primarily with eukaryotic cells. Lectures are devoted to structural details and the molecular functions of the different parts of the cell. Lectures will introduce t ...
... Text Book: Becker’s World of the Cell 8th edition (2012). Hardin, Bertoni and Kliensmith. Course description: This course is concerned primarily with eukaryotic cells. Lectures are devoted to structural details and the molecular functions of the different parts of the cell. Lectures will introduce t ...
Parts of the Cell
... Which statement about the cell membrane is not true? A – it helps give the cell its shape B – it is found only in animal cells C – it provides some protection for the cell D – it helps maintain homeostasis ...
... Which statement about the cell membrane is not true? A – it helps give the cell its shape B – it is found only in animal cells C – it provides some protection for the cell D – it helps maintain homeostasis ...
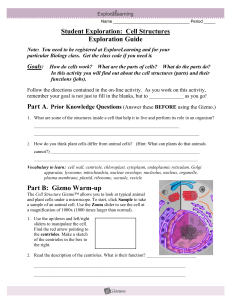
HW Cell Structures Gizmo Gizmo Cell Structures final
... 1. Use the up/down and left/right sliders to manipulate the cell. Find the red arrow pointing to the centrioles. Make a sketch of the centrioles in the box to the right. 2. Read the description of the centrioles. What is their function? ________________________ ______________________________________ ...
... 1. Use the up/down and left/right sliders to manipulate the cell. Find the red arrow pointing to the centrioles. Make a sketch of the centrioles in the box to the right. 2. Read the description of the centrioles. What is their function? ________________________ ______________________________________ ...
Everything you wanted to know about organelles
... Everything you wanted to know about organelles Membrane bound structures with particular functions in a eukaryotic cell ...
... Everything you wanted to know about organelles Membrane bound structures with particular functions in a eukaryotic cell ...
HERE - Gallopade International
... digest the cell’s “food” and turn it into power for the cell. I am the chief conductor of cellular respiration. You can find me and my many brothers and sisters in the cytoplasm.” 2) “I work hard to build material for the cell. My job is to connect amino acids together to make long chains of protei ...
... digest the cell’s “food” and turn it into power for the cell. I am the chief conductor of cellular respiration. You can find me and my many brothers and sisters in the cytoplasm.” 2) “I work hard to build material for the cell. My job is to connect amino acids together to make long chains of protei ...
Cell Membrane Notes - Ms. Stevens` Class
... Carbs are found on the surface of every eukaryotic cell & allow for cell recognition (like an ID tag) Cell Recognition: Ability of a cell to distinguish one cell from another Important For: • Cell signaling • Immune System – how our WBCs recognize foreign pathogens • Organ & Tissue growth & developm ...
... Carbs are found on the surface of every eukaryotic cell & allow for cell recognition (like an ID tag) Cell Recognition: Ability of a cell to distinguish one cell from another Important For: • Cell signaling • Immune System – how our WBCs recognize foreign pathogens • Organ & Tissue growth & developm ...
BIOLOGY BINGO BOARD
... proteins, they make the “finishing touches” and then package the products to be sent out around the cell Tissue – a group of cells all working together to do the same job, EX: many muscle cells work together as the muscle tissue to contract and move your arm Cilia – small hair-like extensions of the ...
... proteins, they make the “finishing touches” and then package the products to be sent out around the cell Tissue – a group of cells all working together to do the same job, EX: many muscle cells work together as the muscle tissue to contract and move your arm Cilia – small hair-like extensions of the ...
Microbes Viruses Bacteria Fungi
... caused by them. 1. Viruses cannot reproduce outside of a living cell. Should they be classed as living organisms? Explain your answer. 2. Bacteria belong to the Prokaryotic Kingdom. Prokaryotic means ‘before nucleus’. Look at the diagram of a bacterium. Why is it classed as a prokaryote and not as a ...
... caused by them. 1. Viruses cannot reproduce outside of a living cell. Should they be classed as living organisms? Explain your answer. 2. Bacteria belong to the Prokaryotic Kingdom. Prokaryotic means ‘before nucleus’. Look at the diagram of a bacterium. Why is it classed as a prokaryote and not as a ...
cell analogies collage
... ____ endoplasmic reticulum ____ large central water vacuole ____ nuclear envelope ...
... ____ endoplasmic reticulum ____ large central water vacuole ____ nuclear envelope ...
Unit 1 Lesson 3 - Epiphany Catholic School
... • Use a ruler and a pencil to mark strips on a piece of paper that are 8 inches long and 1 inch wide • Use scissors to cut out each strip • Use a pen or pencil to write the entire ...
... • Use a ruler and a pencil to mark strips on a piece of paper that are 8 inches long and 1 inch wide • Use scissors to cut out each strip • Use a pen or pencil to write the entire ...
Unit 3: Cell and Cell Transport (Chapter 7) 7.1 Cell Theory • are the
... – All existing cells are produced by ________________________. – The cell is ________________________. ...
... – All existing cells are produced by ________________________. – The cell is ________________________. ...
3-2 organelle
... –helps position and transport organelles –provides strength –assists in cell division –aids in cell movement –Refer to page 73 in your text book ...
... –helps position and transport organelles –provides strength –assists in cell division –aids in cell movement –Refer to page 73 in your text book ...
Mitosis Vocabulary Review
... _____ 5. The first three phases of the life cycle of a cell are called a. anaphase. c. the first gap phase. b. interphase. d. the synthesis phase. _____ 6. What is the process during which the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei? a. the cell cycle c. mitosis b. nucleosome d. cytokinesis ___ ...
... _____ 5. The first three phases of the life cycle of a cell are called a. anaphase. c. the first gap phase. b. interphase. d. the synthesis phase. _____ 6. What is the process during which the nucleus of a cell is divided into two nuclei? a. the cell cycle c. mitosis b. nucleosome d. cytokinesis ___ ...
Cell Transport
... Until “dynamic equilibrium” is reached. What is dynamic? Dynamic refers to constant movement – once equal, molecules constantly move in/out at same rate Ex) Air freshener Diagram on the board ...
... Until “dynamic equilibrium” is reached. What is dynamic? Dynamic refers to constant movement – once equal, molecules constantly move in/out at same rate Ex) Air freshener Diagram on the board ...
JOB DESCRIPTION Role: 2 Positions Assay Scientist/ Senior Assay
... Experience of isolating, working with and maintaining primary cell lines in culture Being able to carry out mammalian transfections with plasmid DNA and maintain transient or stable mammalian cell lines Previous experience of molecular biology or small scale protein expression and purification would ...
... Experience of isolating, working with and maintaining primary cell lines in culture Being able to carry out mammalian transfections with plasmid DNA and maintain transient or stable mammalian cell lines Previous experience of molecular biology or small scale protein expression and purification would ...
Archaea
... Prokaryo7c ancestor: ANAEROBIC 1.Lost the cell wall / phagocytosis of prokaryotes for nutrients 2.Formed symbio7c rela7onship with an engulfed aerobic bacteria 3.Photosynthe7c cyanobacteria promoted an oxic environment 4.Selected the above cell type 5.The endosymbio7c aerobic bacterium developed in ...
... Prokaryo7c ancestor: ANAEROBIC 1.Lost the cell wall / phagocytosis of prokaryotes for nutrients 2.Formed symbio7c rela7onship with an engulfed aerobic bacteria 3.Photosynthe7c cyanobacteria promoted an oxic environment 4.Selected the above cell type 5.The endosymbio7c aerobic bacterium developed in ...
Name: Date: Hour : _____ Cells and Their Organelles The cell is the
... transports materials through the cell and produces proteins in sacks called cistern which are sent to the Golgi body, or inserted into the cell membrane. The Golgi apparatus or Golgi complex is a flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes. The Golgi body modifies and ...
... transports materials through the cell and produces proteins in sacks called cistern which are sent to the Golgi body, or inserted into the cell membrane. The Golgi apparatus or Golgi complex is a flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes. The Golgi body modifies and ...
Biology Chapter 4: Cells and Their Environment Section 1 Notes
... 7. The movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration caused by the random motion of particles of the substance is called diffusion. ...
... 7. The movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration caused by the random motion of particles of the substance is called diffusion. ...
eprint_1_17645_235
... The bacteria are surrounding by rigid cell wall. The principle structural component of cell wall is peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan (PG) is complex of polysaccharide and polypeptide. Most bacteria are classified according to reaction of Gram stain with components of cell wall into major groups; Gram po ...
... The bacteria are surrounding by rigid cell wall. The principle structural component of cell wall is peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan (PG) is complex of polysaccharide and polypeptide. Most bacteria are classified according to reaction of Gram stain with components of cell wall into major groups; Gram po ...
Membrane Transport - Liberty Union High School District
... Membrane Transport • There are many molecules on (peripheral), within (trans), and inside (intracellular) the cell membranes. These all aid in getting necessary molecules into and out of the cell. They also play a role in cell to cell communication. • Most are proteins with or without carbohydrates ...
... Membrane Transport • There are many molecules on (peripheral), within (trans), and inside (intracellular) the cell membranes. These all aid in getting necessary molecules into and out of the cell. They also play a role in cell to cell communication. • Most are proteins with or without carbohydrates ...
Chapter 9: movement of material in and out of cell
... Movement of material in and out of cell: The basics & Passive Transport: *How does stuff move in and out of an animal cell? Cell membrane -Selectively permeable - things can go in and out of cell dependent on pore size. - this is done to maintain homeostasis or equilibrium. ...
... Movement of material in and out of cell: The basics & Passive Transport: *How does stuff move in and out of an animal cell? Cell membrane -Selectively permeable - things can go in and out of cell dependent on pore size. - this is done to maintain homeostasis or equilibrium. ...
Chapter 3
... • Reasons for Gram-positive bacteria to give gram-negative response – Cells are dead – When bacteria culture is older than 24 hours • Bacillus, Clostridium, and Mycobacterium becomes gram variable ...
... • Reasons for Gram-positive bacteria to give gram-negative response – Cells are dead – When bacteria culture is older than 24 hours • Bacillus, Clostridium, and Mycobacterium becomes gram variable ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.