The Magellan 20 Telescope Science Goals
... performance over ~1.6’ fields with high Strehl ratios. This mode may be best exploited with deployable IFUs or deployable high-resolution imaging modules. The details of the implementation of the MCAO system are currently being modeled. Much will be learned from MCAO systems that are currently under ...
... performance over ~1.6’ fields with high Strehl ratios. This mode may be best exploited with deployable IFUs or deployable high-resolution imaging modules. The details of the implementation of the MCAO system are currently being modeled. Much will be learned from MCAO systems that are currently under ...
Lecture 2 ppt - Physics 1025 Introductory Astronomy
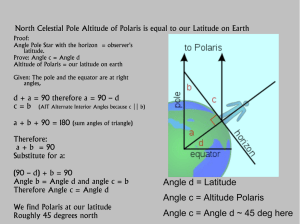
... – Analogous to latitude, but on the celestial sphere; it is the angular north-south distance between the celestial equator and a location on the celestial sphere. – Measured in degrees: » 0 ° to 90 ° – north from celestial equator » 0 ° to -90 ° – south from celestial equator ...
... – Analogous to latitude, but on the celestial sphere; it is the angular north-south distance between the celestial equator and a location on the celestial sphere. – Measured in degrees: » 0 ° to 90 ° – north from celestial equator » 0 ° to -90 ° – south from celestial equator ...
Galaxy Spiral Arms
... It was later determined that the Sun has a mass which is 330,000 times greater than the Earth, which makes these two equations virtually identical. However, the first is approximate and the second is far more precise. Newton also used the Calculus (Fluxions) which he invented, to discover another im ...
... It was later determined that the Sun has a mass which is 330,000 times greater than the Earth, which makes these two equations virtually identical. However, the first is approximate and the second is far more precise. Newton also used the Calculus (Fluxions) which he invented, to discover another im ...
THE INNER CORE OF A NEUTRON STAR Part 1
... star composition makes it so heavy that its density is at least twice the mass of Earth’s Sun. Current thinking subscribes to the possibility that a neutron star is primarily made up of almost entirely sub-atomic particles without net electrical charge. Neutron stars are very hot and are supported a ...
... star composition makes it so heavy that its density is at least twice the mass of Earth’s Sun. Current thinking subscribes to the possibility that a neutron star is primarily made up of almost entirely sub-atomic particles without net electrical charge. Neutron stars are very hot and are supported a ...
Homework
... away from our galaxy, and the more distant galaxies are moving away faster. That means that all of the galaxies in the universe (or at least the materials from which they were formed) were all together around 14 billions years ago and they have been moving apart ever since. That is a scientific fact ...
... away from our galaxy, and the more distant galaxies are moving away faster. That means that all of the galaxies in the universe (or at least the materials from which they were formed) were all together around 14 billions years ago and they have been moving apart ever since. That is a scientific fact ...
THE EARTH AND THE UNIVERSE
... We will now try to see if the length of days and nights are the same everywhere on the planet. Click on the night control and observe the north pole. Is it on the dark or the light side or the planet? (Remember: you can use the vertical rot. control to get a better view). Now use the equator an ...
... We will now try to see if the length of days and nights are the same everywhere on the planet. Click on the night control and observe the north pole. Is it on the dark or the light side or the planet? (Remember: you can use the vertical rot. control to get a better view). Now use the equator an ...
Mar 2016 - Bays Mountain Park
... like. I think we would all like to be out under the stars a little more ...
... like. I think we would all like to be out under the stars a little more ...
Lecture 2: A Modern View of the Universe
... Astronomical Union Definition • A celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces, so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. ...
... Astronomical Union Definition • A celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces, so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. ...
Magnitude. . . ?
... is Sterngröße, in Czech hvězdná velikost. Or is it a disadvantage? Faintness rises, when the star gets fainter, and everybody would expect it to do so. It is far from being the case for Sterngröße. I insist that magnitude should never be used as a name of the quantity. Using it as a synonym for a br ...
... is Sterngröße, in Czech hvězdná velikost. Or is it a disadvantage? Faintness rises, when the star gets fainter, and everybody would expect it to do so. It is far from being the case for Sterngröße. I insist that magnitude should never be used as a name of the quantity. Using it as a synonym for a br ...
DoAr21_AAS2005 - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... Weak-lined T Tauri Star (WTTS), having shown H-alpha in emission in the 1950s but without H-alpha emission reported subsequently and without a strong IR excess. It is only about 1 Myr old (left) and has already been identified, via lowresolution x-ray spectroscopy, to have strong, hard, and variable ...
... Weak-lined T Tauri Star (WTTS), having shown H-alpha in emission in the 1950s but without H-alpha emission reported subsequently and without a strong IR excess. It is only about 1 Myr old (left) and has already been identified, via lowresolution x-ray spectroscopy, to have strong, hard, and variable ...
Neutron Stars
... neutron star that is part of a binary system will accrete material from the companion. Once enough material is accumulated o nthe surface of the neutron star, hydrogen fusion will occur. ...
... neutron star that is part of a binary system will accrete material from the companion. Once enough material is accumulated o nthe surface of the neutron star, hydrogen fusion will occur. ...
File
... Consider a relatively nearby, single star, that is, a star that is not a member of a binary system and has no known orbiting planets. Listed below are a few properties of this star. Classify each property as either something that we can observe or measure directly (with the aid of a telescope and in ...
... Consider a relatively nearby, single star, that is, a star that is not a member of a binary system and has no known orbiting planets. Listed below are a few properties of this star. Classify each property as either something that we can observe or measure directly (with the aid of a telescope and in ...
Here
... The Sun and the Stars • The Sun is the nearest example of a star. • Basic questions to ask: – What do stars look like on their surfaces? Look at the Sun since it is so close. – How do stars work on their insides? Look at both the Sun and the stars to get many ...
... The Sun and the Stars • The Sun is the nearest example of a star. • Basic questions to ask: – What do stars look like on their surfaces? Look at the Sun since it is so close. – How do stars work on their insides? Look at both the Sun and the stars to get many ...
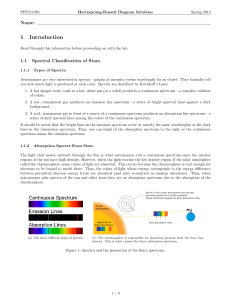
1 Introduction - High Point University
... right on an axis. The Luminosity scale on the left axis is dimmest on the bottom and gets brighter towards the top. This places the cooler, dimmer stars towards the lower right and the hotter, more luminous stars at the upper left. Our own star, the Sun, is nearly in the middle of both the temperatu ...
... right on an axis. The Luminosity scale on the left axis is dimmest on the bottom and gets brighter towards the top. This places the cooler, dimmer stars towards the lower right and the hotter, more luminous stars at the upper left. Our own star, the Sun, is nearly in the middle of both the temperatu ...
Preface 1 PDF
... perturbations to the frequencies of these oscillations the rotation of the deep interior can be inferred. Thanks to helioseismology, we know that the Sun rotates as a solid body in the radiative interior and that the convective envelope rotates differentially, with a shear layer in between. Such a s ...
... perturbations to the frequencies of these oscillations the rotation of the deep interior can be inferred. Thanks to helioseismology, we know that the Sun rotates as a solid body in the radiative interior and that the convective envelope rotates differentially, with a shear layer in between. Such a s ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.