Chromospherically young, kinematically old stars
... The chromospheric activity of a late-type star is frequently interpreted as a sign of its youth. Young dwarfs show high rotation rates, and the interaction between rotation and outer envelope convection is expected to drive the chromospheric activity. Nevertheless, not only young single stars presen ...
... The chromospheric activity of a late-type star is frequently interpreted as a sign of its youth. Young dwarfs show high rotation rates, and the interaction between rotation and outer envelope convection is expected to drive the chromospheric activity. Nevertheless, not only young single stars presen ...
A Question of Planets - Vanderbilt University
... A Question of Planets day, he cycled across the hilly country sides of Greece and Israel, made a number of new friends and had an extremely good time before giving the bike away and heading home. When he returned, Weintraub landed a job teaching astronomy at Santa Monica Community College and disco ...
... A Question of Planets day, he cycled across the hilly country sides of Greece and Israel, made a number of new friends and had an extremely good time before giving the bike away and heading home. When he returned, Weintraub landed a job teaching astronomy at Santa Monica Community College and disco ...
Chapter 18 - Origin and Evolution of Stars Chapter Preview
... Consider the evolution of a star’s in a cluster as a race, from the initial stage of pre-stellar cloud collapse through main sequence hydrogen fusion to stellar death (Figure 16). In today’s race we have three contestants. In the pole position is the odds on favorite a 10 solar mass star, nicknamed ...
... Consider the evolution of a star’s in a cluster as a race, from the initial stage of pre-stellar cloud collapse through main sequence hydrogen fusion to stellar death (Figure 16). In today’s race we have three contestants. In the pole position is the odds on favorite a 10 solar mass star, nicknamed ...
Stellar Masses
... stably. Objects with masses slightly below this limit are called brown dwarfs, and are ‘star like’ in the sense that nuclear burning of deuterium occurs in their core. Below a mass of 0.015M⊙ (roughly 16 times the mass of Jupiter) not even deuterium burning can occur, and these objects are perhaps b ...
... stably. Objects with masses slightly below this limit are called brown dwarfs, and are ‘star like’ in the sense that nuclear burning of deuterium occurs in their core. Below a mass of 0.015M⊙ (roughly 16 times the mass of Jupiter) not even deuterium burning can occur, and these objects are perhaps b ...
Calculate the Mass of the Milky Way Galaxy
... length of light waves in distant galaxies and discovering that the waves were longer and redder (redshift). He then calculated the distance to the galaxy and its redshift and found that there was a proportional relationship between the two. This relationship was that the more distant a galaxy, the g ...
... length of light waves in distant galaxies and discovering that the waves were longer and redder (redshift). He then calculated the distance to the galaxy and its redshift and found that there was a proportional relationship between the two. This relationship was that the more distant a galaxy, the g ...
PPT
... What have we learned? • How do we measure the distances to galaxies? – The distance-measurement chain begins with parallax measurements that build on radar ranging in our solar system – Using parallax and the relationship between luminosity, distance, and brightness, we can calibrate a series of st ...
... What have we learned? • How do we measure the distances to galaxies? – The distance-measurement chain begins with parallax measurements that build on radar ranging in our solar system – Using parallax and the relationship between luminosity, distance, and brightness, we can calibrate a series of st ...
What makes stars tick?
... almost everything about the object, from the core temperature, to how long the star lives, to how it dies. While the Sun and a star 10 times its mass may have similarities during the “adult” stages of their lives, they couldn’t be more different as they reach the later stages. Why do some end their ...
... almost everything about the object, from the core temperature, to how long the star lives, to how it dies. While the Sun and a star 10 times its mass may have similarities during the “adult” stages of their lives, they couldn’t be more different as they reach the later stages. Why do some end their ...
The Next Great Exoplanet Hunt Please share
... probability for transits is equal to the stellar diameter divided by the orbital diameter, which is only 0.1% for an Earth-like orbit around a Sun-like star. For this reason, a meaningful transit survey must include tens of thousands of stars, or more. Because faint stars far outnumber bright ones i ...
... probability for transits is equal to the stellar diameter divided by the orbital diameter, which is only 0.1% for an Earth-like orbit around a Sun-like star. For this reason, a meaningful transit survey must include tens of thousands of stars, or more. Because faint stars far outnumber bright ones i ...
Observational properties of stars
... spectrum, “B” corresponds to blue light, “V” is green, “R” is red and “I” is infrared. There are actually hundreds of different types of filters, some are telescope specific, or are used only by particular observatories. However, the filters given here are the most commonly used in stellar astronomy ...
... spectrum, “B” corresponds to blue light, “V” is green, “R” is red and “I” is infrared. There are actually hundreds of different types of filters, some are telescope specific, or are used only by particular observatories. However, the filters given here are the most commonly used in stellar astronomy ...
main sequence stars of a open cluster
... (1) Select one star in N1912Bs.fits, and write below coordinates and count value. Similarly, write below them for N1912Vs.fits. The values are shown in the upper left when you put the pointer on the star image. Image x coordinate y coordinate Count value N1912Bs.fits N1912Vs.fits (2) In which of B o ...
... (1) Select one star in N1912Bs.fits, and write below coordinates and count value. Similarly, write below them for N1912Vs.fits. The values are shown in the upper left when you put the pointer on the star image. Image x coordinate y coordinate Count value N1912Bs.fits N1912Vs.fits (2) In which of B o ...
Recipe for a Star
... draws these elements toward the core of the star. Lighter elements move outward to form a layer. The heaviest elements in the core then undergo more nuclear fusion, making heavier and heavier elements. Heavier elements displace lighter elements, forcing them outward from the core. The star has a lay ...
... draws these elements toward the core of the star. Lighter elements move outward to form a layer. The heaviest elements in the core then undergo more nuclear fusion, making heavier and heavier elements. Heavier elements displace lighter elements, forcing them outward from the core. The star has a lay ...
Atoms and Stars IST 3360 and IST 1990
... • Calculations were laying the foundation for calculus (invented by Newton later) – theory of area of irregular shapes • Clued in by numerical relationship which seemed at first like a coincidence • K: “The roads that lead man to knowledge are a wondrous as that knowledge itself.” ...
... • Calculations were laying the foundation for calculus (invented by Newton later) – theory of area of irregular shapes • Clued in by numerical relationship which seemed at first like a coincidence • K: “The roads that lead man to knowledge are a wondrous as that knowledge itself.” ...
Is the central binary system of the planetary nebula Henize 2
... line belonging to the primary star, and a narrow emission line coming from the compact dense nebula reported by Rodríguez et al. (2001), or which originates even much closer to the star from the wind itself. In this alternative explanation both emission and absorption lines change with orbital phase ...
... line belonging to the primary star, and a narrow emission line coming from the compact dense nebula reported by Rodríguez et al. (2001), or which originates even much closer to the star from the wind itself. In this alternative explanation both emission and absorption lines change with orbital phase ...
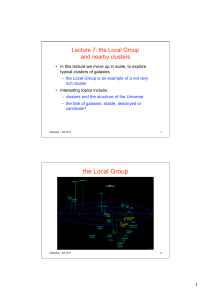
the Local Group - Simon P Driver
... each other – with some exceptions like satellite galaxies – the three spirals are easily the biggest – dwarf galaxies are on the outskirts of the group • how typical is this of other galaxy groups? – turns out that the Local group is not very rich in galaxies ...
... each other – with some exceptions like satellite galaxies – the three spirals are easily the biggest – dwarf galaxies are on the outskirts of the group • how typical is this of other galaxy groups? – turns out that the Local group is not very rich in galaxies ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.