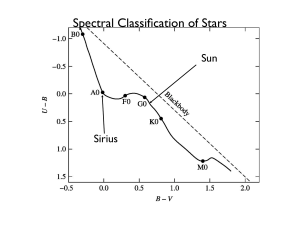
Astronomy 252: Short Project 2 Stellar Spectra: Their Classification
... show absorption lines due to ionized helium (He II), and doubly and even triply ionized carbon, oxygen and silicon. On the other hand, the coolest stars (the M-type stars) show lines due to molecules in their spectra. Morgan and Keenan (and their predecessors) based their spectral classification sys ...
... show absorption lines due to ionized helium (He II), and doubly and even triply ionized carbon, oxygen and silicon. On the other hand, the coolest stars (the M-type stars) show lines due to molecules in their spectra. Morgan and Keenan (and their predecessors) based their spectral classification sys ...
Application Exercise: Distances to Stars Using Measured Parallax
... of the measured parallax method to determine distances to nearby stars, those within about 650 light years from the Sun. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are still just points of light. Although we may be able to tell a lot about a star through its light, these observations do n ...
... of the measured parallax method to determine distances to nearby stars, those within about 650 light years from the Sun. Even when observed with the largest telescopes, stars are still just points of light. Although we may be able to tell a lot about a star through its light, these observations do n ...
FREE Sample Here
... Astronomical unit: The average distance between Earth and Sun, which is about 1.496 108 km. Ecliptic plane: The two-dimensional plane in which Earth orbits around the Sun. Most of the other planets orbit nearly in this same plane. Axis tilt: The amount that a planet’s rotation axis is tipped relat ...
... Astronomical unit: The average distance between Earth and Sun, which is about 1.496 108 km. Ecliptic plane: The two-dimensional plane in which Earth orbits around the Sun. Most of the other planets orbit nearly in this same plane. Axis tilt: The amount that a planet’s rotation axis is tipped relat ...
Astrophysics Pristine CNO abundances from Magellanic Cloud B stars
... Key words. stars: abundances – stars: atmospheres – stars: early type – galaxies: Magellanic Clouds – galaxies: clusters: individual: NGC 2004 ...
... Key words. stars: abundances – stars: atmospheres – stars: early type – galaxies: Magellanic Clouds – galaxies: clusters: individual: NGC 2004 ...
Bluffer`s Guide to Sirius
... another billion years or so. Since the 1840s we have known that Sirius has an unseen companion. By observing the position of Sirius very carefully, astronomers noticed that the star was moving slightly in a predictable manner. It was clear that Sirius was being tugged by the gravitational pull of an ...
... another billion years or so. Since the 1840s we have known that Sirius has an unseen companion. By observing the position of Sirius very carefully, astronomers noticed that the star was moving slightly in a predictable manner. It was clear that Sirius was being tugged by the gravitational pull of an ...
PDF
... Space astrometry has been a long dream that started officially in 1967 when Pierre Lacroute proposed a space telescope for astrometric measurements during a talk in Prague. But as explained by Eric Høg in his 2001 Miraculous approval of Hipparcos, the key idea of using slits and photo cells to measu ...
... Space astrometry has been a long dream that started officially in 1967 when Pierre Lacroute proposed a space telescope for astrometric measurements during a talk in Prague. But as explained by Eric Høg in his 2001 Miraculous approval of Hipparcos, the key idea of using slits and photo cells to measu ...
ASPEN WORKSHOP 2003
... Asymmetry index is another way to identify mergers (subtract flipped image), zero in ellipticals, larger in bluer galaxies, up to few tenths. AI(Red), or AI(Blue) >0.3 suggests interaction, as in half of ULIRGS [as long as they are identified as “single galaxy”!] Simulations show that AI stays above ...
... Asymmetry index is another way to identify mergers (subtract flipped image), zero in ellipticals, larger in bluer galaxies, up to few tenths. AI(Red), or AI(Blue) >0.3 suggests interaction, as in half of ULIRGS [as long as they are identified as “single galaxy”!] Simulations show that AI stays above ...
Gilmore - Astrometry and Astrophysics in the Gaia sky
... distances to 1% for 18 million stars to 2.5 kpc distances to 10% for 150 million stars to 25 kpc rare stellar types and rapid evolutionary phases in large numbers parallax calibration of all distance indicators e.g. Cepheids and RR Lyrae to LMC/SMC ...
... distances to 1% for 18 million stars to 2.5 kpc distances to 10% for 150 million stars to 25 kpc rare stellar types and rapid evolutionary phases in large numbers parallax calibration of all distance indicators e.g. Cepheids and RR Lyrae to LMC/SMC ...
ies la arboleda – centro tic - plurilingüe
... Edwin Hubble discovered that galaxies are moving away from Earth and the distances between galaxies are bigger and bigger, so the universe is expanding. Hubble thought that these galaxies were together in a common point in the past. This idea is the origin of the Big Bang theory, which is represente ...
... Edwin Hubble discovered that galaxies are moving away from Earth and the distances between galaxies are bigger and bigger, so the universe is expanding. Hubble thought that these galaxies were together in a common point in the past. This idea is the origin of the Big Bang theory, which is represente ...
The Evolution of Stars - a More Detailed Picture (Chapter 8
... luminosity (Fig. 1). These are called Hayashi-tracks. In time, as the internal temperature continues to rise, ionisation is completed and the opacity drops. The convective zone recedes from the centre, and the star moves to higher effective temperatures. Slowly nuclear burning starts in the core. As ...
... luminosity (Fig. 1). These are called Hayashi-tracks. In time, as the internal temperature continues to rise, ionisation is completed and the opacity drops. The convective zone recedes from the centre, and the star moves to higher effective temperatures. Slowly nuclear burning starts in the core. As ...
Activities
... continuous cycle in the number of sunspots, which are the most visible tracer of the magnetic fields that cause all forms of solar activity. The solar cycle seems to be linked to changes in the Sun’s global magnetic field. At one solar activity maximum, the magnetic field is aligned so that a compas ...
... continuous cycle in the number of sunspots, which are the most visible tracer of the magnetic fields that cause all forms of solar activity. The solar cycle seems to be linked to changes in the Sun’s global magnetic field. At one solar activity maximum, the magnetic field is aligned so that a compas ...
Archaeoastronomical Study of the Main Pyramids of Giza
... are possible; it is only a matter of conventions. For example in the Medieval map known as the Hereford Mappa Mundi (dating to XIII century) East is at the top. According to Bauval (2006), for ancient Egyptians it was more logical to put South, and not North, on the top of their maps. South was “up” ...
... are possible; it is only a matter of conventions. For example in the Medieval map known as the Hereford Mappa Mundi (dating to XIII century) East is at the top. According to Bauval (2006), for ancient Egyptians it was more logical to put South, and not North, on the top of their maps. South was “up” ...
Chapter 30: Stars
... GROUPS OF STARS Long ago, many civilizations looked at the brightest stars and named groups of them after animals, mythological characters, or everyday objects. These groups of stars are called constellations. Today, we group stars by the 88 constellations named by ancient peoples. Some constellatio ...
... GROUPS OF STARS Long ago, many civilizations looked at the brightest stars and named groups of them after animals, mythological characters, or everyday objects. These groups of stars are called constellations. Today, we group stars by the 88 constellations named by ancient peoples. Some constellatio ...
Stellar Structure and Evolution II
... burning ends with a pulse that ejects the H and He into space as a planetary nebula • The core left behind becomes a white dwarf ...
... burning ends with a pulse that ejects the H and He into space as a planetary nebula • The core left behind becomes a white dwarf ...
Chemical Evolution
... accretion to have occurred > 8Gyr ago. Perhaps more stringent limits come from the different elemental abundances, since timescale for Type Ia SNe only a few Gyr, but need detailed chemical evolution models. Halo can be formed from any system that formed stars early on, for only brief period , an ...
... accretion to have occurred > 8Gyr ago. Perhaps more stringent limits come from the different elemental abundances, since timescale for Type Ia SNe only a few Gyr, but need detailed chemical evolution models. Halo can be formed from any system that formed stars early on, for only brief period , an ...
Studying the Universe Studying the Universe
... Each color of visible light represents a different wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. Visible light is just a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum, as shown in Figure 11. The electromagnetic spectrum is made of all of the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. Most of the electromagne ...
... Each color of visible light represents a different wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. Visible light is just a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum, as shown in Figure 11. The electromagnetic spectrum is made of all of the wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. Most of the electromagne ...
PSU/TCfA search for planets around evolved stars
... 2Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pennsylvania State University, 525 Davey Laboratory, University Park, PA 16802 ...
... 2Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Pennsylvania State University, 525 Davey Laboratory, University Park, PA 16802 ...
Determination of kinetic energies of stars using Hipparcos data *
... As is well known, the stars of late spectral types have larger proper motions than the stars of early spectral types. There is a good deal of different hypotheses that aim to explain this phenomenon. One of them asserts that the late type stars have smaller masses, which is why their velocities are ...
... As is well known, the stars of late spectral types have larger proper motions than the stars of early spectral types. There is a good deal of different hypotheses that aim to explain this phenomenon. One of them asserts that the late type stars have smaller masses, which is why their velocities are ...
Direct Detection of Galactic Halo Dark Matter
... luminous matter, primarily stars, cannot explain the observed rotational characteristics of the galaxy’s spiral disk. A substantial portion of this unseen matter may be old, very cool white dwarfs (1–4). A white dwarf is the extremely dense end-state in the evolution of stars with masses less than a ...
... luminous matter, primarily stars, cannot explain the observed rotational characteristics of the galaxy’s spiral disk. A substantial portion of this unseen matter may be old, very cool white dwarfs (1–4). A white dwarf is the extremely dense end-state in the evolution of stars with masses less than a ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.