Predicting Sky Dome Appearance on Earth
... Attempting to imagine the inhabitants and appearance of alien lands that no man had yet set foot in is an effort probably as old as our species. It certainly dates as far back as antiquity, with Pliny the Elder writing, apparently not from first hand knowledge, about the strange inhabitants of faraw ...
... Attempting to imagine the inhabitants and appearance of alien lands that no man had yet set foot in is an effort probably as old as our species. It certainly dates as far back as antiquity, with Pliny the Elder writing, apparently not from first hand knowledge, about the strange inhabitants of faraw ...
Word Document - Montana State University Extended
... Scientists generally agree that the Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago yet complex life has existed on the Earth for about the last 500 million years. It is still unclear exactly what chain of events lead up to the emergence of complex life on this planet. One of the factors that scientists be ...
... Scientists generally agree that the Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago yet complex life has existed on the Earth for about the last 500 million years. It is still unclear exactly what chain of events lead up to the emergence of complex life on this planet. One of the factors that scientists be ...
Carbon Stars - The OzSky Star Safari
... – Near the end of their life, they become a red giant star. – Then they leave the initial Red Giant phase via the Horizontal Branch as the helium ignites to form carbon. – On the Asymptotic Giant Branch, they become Carbon Stars and Red Giants again and eventually blow off their ...
... – Near the end of their life, they become a red giant star. – Then they leave the initial Red Giant phase via the Horizontal Branch as the helium ignites to form carbon. – On the Asymptotic Giant Branch, they become Carbon Stars and Red Giants again and eventually blow off their ...
Starburst Galaxies Under the Microscope: High
... several episodes of violent star formation, of which the last one is probably still ongoing. The resulting star clusters have been studied extensively. Radio and mid-IR observations show that the region between the two remnant nuclei (usually referred to as the overlap region) hosts spectacular obsc ...
... several episodes of violent star formation, of which the last one is probably still ongoing. The resulting star clusters have been studied extensively. Radio and mid-IR observations show that the region between the two remnant nuclei (usually referred to as the overlap region) hosts spectacular obsc ...
night watch - Warren Astronomical Society
... Pluto, the outermost known planet, is a deviant. It has the most eccentric orbit: an eccentricity of .25 compared with Mercury’s .21 and a maximum of .09 for the other planets. Its orbit has the greatest inclination with respect to the ecliptic plane. Pluto’s orbit is inclined by 17 degrees while Me ...
... Pluto, the outermost known planet, is a deviant. It has the most eccentric orbit: an eccentricity of .25 compared with Mercury’s .21 and a maximum of .09 for the other planets. Its orbit has the greatest inclination with respect to the ecliptic plane. Pluto’s orbit is inclined by 17 degrees while Me ...
Chapter15- Our Galaxy-pptx - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... The Milky Way Galaxy appears in our sky as a faint band of light. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... The Milky Way Galaxy appears in our sky as a faint band of light. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
PPT presentation
... luminosity functions, indistinguishable from those observed in the spiral galaxies M31 and M81. The invariance with galaxy type and metallicity demonstrated the PNLF to be an excellent standard candle. Model simulations indicated a central star mass distribution highly peaked at ~0.6 Msun, similar t ...
... luminosity functions, indistinguishable from those observed in the spiral galaxies M31 and M81. The invariance with galaxy type and metallicity demonstrated the PNLF to be an excellent standard candle. Model simulations indicated a central star mass distribution highly peaked at ~0.6 Msun, similar t ...
Family of stars - Inside Mines
... band across diagram from hot, bluish, bright stars (top left) to cool, dim, reddish stars (bottom right) – Our Sun is a typical MS star: spectral class G2, absolute magnitude +4.83 • Outside of MS: stages in the stellar evolution of the MS stars. ...
... band across diagram from hot, bluish, bright stars (top left) to cool, dim, reddish stars (bottom right) – Our Sun is a typical MS star: spectral class G2, absolute magnitude +4.83 • Outside of MS: stages in the stellar evolution of the MS stars. ...
STC-Scripting Guide for Celestia
... This guide takes a detailed look at the STC-file that is needed to tell Celestia the position and further characteristics of the star. If you want to know more about creating planetary systems and thus SSC-files then take a look at the excellent guide from Ulrich Dickmann and Bob Hegwood (English ve ...
... This guide takes a detailed look at the STC-file that is needed to tell Celestia the position and further characteristics of the star. If you want to know more about creating planetary systems and thus SSC-files then take a look at the excellent guide from Ulrich Dickmann and Bob Hegwood (English ve ...
Entropy Production of Main-Sequence Stars
... herein. This is connected with the fact that in order to determine a star’s mass, some theoretical stellar model is required, and therefore, additional assumptions are necessary. As a result, the calculation of ΣM turns out to be combined rather than based on experimental data only. This complicates ...
... herein. This is connected with the fact that in order to determine a star’s mass, some theoretical stellar model is required, and therefore, additional assumptions are necessary. As a result, the calculation of ΣM turns out to be combined rather than based on experimental data only. This complicates ...
Understanding the Astrophysics of Galaxy Evolution: the role of
... correlated with dark matter halo mass and so the best link to the underlying cosmological model. A survey must be large (∼ few ×105 galaxies) in order to disentangle covariances in the physical properties of galaxies. One reason it is so difficult to understand how galaxies form is because almost al ...
... correlated with dark matter halo mass and so the best link to the underlying cosmological model. A survey must be large (∼ few ×105 galaxies) in order to disentangle covariances in the physical properties of galaxies. One reason it is so difficult to understand how galaxies form is because almost al ...
Entropy
... death of the Universe and until now, the papers related to entropy have always been in the centre of attention among astrophysicists and cosmologists. Currently, this quantity and its derivatives are used to discuss mysteries of black holes, questions connected with the accelerated expansion of the ...
... death of the Universe and until now, the papers related to entropy have always been in the centre of attention among astrophysicists and cosmologists. Currently, this quantity and its derivatives are used to discuss mysteries of black holes, questions connected with the accelerated expansion of the ...
Lecture 20: Formation of Planets, Exoplanets 3/30
... • heavier elements (metals, silicates) condense first, at higher temperatures, then molecules like water H and He remain gases • density and temperature falls with distance from star. Planet formation occurs when not too far and not too close • “snow line” separates type of planets being formed ...
... • heavier elements (metals, silicates) condense first, at higher temperatures, then molecules like water H and He remain gases • density and temperature falls with distance from star. Planet formation occurs when not too far and not too close • “snow line” separates type of planets being formed ...
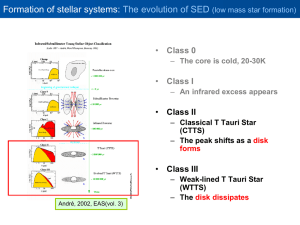
Chapter 7 Formation of Stars
... this image is about one light year. The Herbig–Haro objects are designated HH-1 and HH-2, and correspond to the nebulosity at the ends of the jets. In the bottom image, a complex jet about a half light year long emerges from a star hidden in a dust cloud near the left edge of the image. The twisted ...
... this image is about one light year. The Herbig–Haro objects are designated HH-1 and HH-2, and correspond to the nebulosity at the ends of the jets. In the bottom image, a complex jet about a half light year long emerges from a star hidden in a dust cloud near the left edge of the image. The twisted ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.