The Galilean Moons of Jupiter
... The parallactic angle is a phenomena of diurnal motion, negative before meridian transit and positive after. At meridian transit the angle is 0 while the Jupiter system is drawn tilted only by the amount of its rotation axis inclination. In Egde Mode you can select four different optical instruments ...
... The parallactic angle is a phenomena of diurnal motion, negative before meridian transit and positive after. At meridian transit the angle is 0 while the Jupiter system is drawn tilted only by the amount of its rotation axis inclination. In Egde Mode you can select four different optical instruments ...
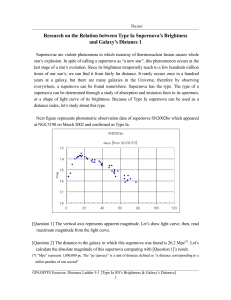
Absolute magnitude of type Ia supernovae
... last stage of a star’s evolution. Since its brightness temporarily reach to a few hundreds million times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supe ...
... last stage of a star’s evolution. Since its brightness temporarily reach to a few hundreds million times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supe ...
Living with a Red Dwarf - Center for Space and Habitability (CSH)
... • Very shortwave ultraviolet (EUV) and X-rays are absorbed high up in the atmosphere, and heat it to the point where the atmosphere can escape to space. • i.e. it’s the rocket fuel that brings molecules up to escape velocity and can launch atmosphere out of the gravity well. • Shorter wave ultraviol ...
... • Very shortwave ultraviolet (EUV) and X-rays are absorbed high up in the atmosphere, and heat it to the point where the atmosphere can escape to space. • i.e. it’s the rocket fuel that brings molecules up to escape velocity and can launch atmosphere out of the gravity well. • Shorter wave ultraviol ...
Solutions to End-of-Chapter Problems (Chapter 2)
... 6. Circumpolar stars are stars that never appear to rise or set from a given location, but are always visible on any clear night. From the North Pole, every visible star is circumpolar, as all circle the horizon at constant altitudes. In contrast, a much smaller portion of the sky is circumpolar fro ...
... 6. Circumpolar stars are stars that never appear to rise or set from a given location, but are always visible on any clear night. From the North Pole, every visible star is circumpolar, as all circle the horizon at constant altitudes. In contrast, a much smaller portion of the sky is circumpolar fro ...
The Milky Way - The Independent School
... • Do other galaxies contain supermassive black holes and dark matter, as does our galaxy? ...
... • Do other galaxies contain supermassive black holes and dark matter, as does our galaxy? ...
IAU-Perraut-2013 - Putting A Stars into Context
... Coupled with spectroscopy, optical interferometry can allow kinematics studies of A stars’ environments. Going beyong angular diameter measurements allows limbdarkening to be derived and besides surfaces of fast rotators to be ...
... Coupled with spectroscopy, optical interferometry can allow kinematics studies of A stars’ environments. Going beyong angular diameter measurements allows limbdarkening to be derived and besides surfaces of fast rotators to be ...
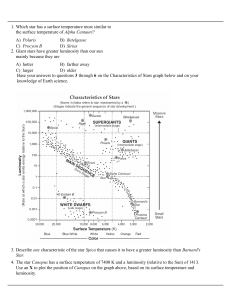
2-star-life-cycle-and-star-classification
... A) Barnard's Star B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sun 78. When a star less massive than our sun consumes all of its nuclear fuel it will then become a A) white dwarf B) nova C) supernova D) black hole 79. Which of the following stars is least bright? A) the sun B) a blue supergiant C) a white dwarf D) ...
... A) Barnard's Star B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sun 78. When a star less massive than our sun consumes all of its nuclear fuel it will then become a A) white dwarf B) nova C) supernova D) black hole 79. Which of the following stars is least bright? A) the sun B) a blue supergiant C) a white dwarf D) ...
A6 - Vicphysics
... with an altitude-azimuth coordinate system (alt-az), the other using the right ascension-declination system. Students can determine the location of one or more identified stars using the two different coordinate systems. Having done this you could then issue a second pair of charts, this time for an ...
... with an altitude-azimuth coordinate system (alt-az), the other using the right ascension-declination system. Students can determine the location of one or more identified stars using the two different coordinate systems. Having done this you could then issue a second pair of charts, this time for an ...
Labeling the HR Diagram - Mastering Physics Answers
... Hint 1. How does the HR diagram show surface temperature? On the HR diagram, surface temperature increases __________. ANSWER: upward, so stars low on the luminosity axis have lower surface temperature than stars higher up right to left, so stars farther to the left along the spectral type axis ha ...
... Hint 1. How does the HR diagram show surface temperature? On the HR diagram, surface temperature increases __________. ANSWER: upward, so stars low on the luminosity axis have lower surface temperature than stars higher up right to left, so stars farther to the left along the spectral type axis ha ...
The APEX Telescope Large Area Survey of the Galaxy (ATLASGAL)
... and with the Herschel Hi-GAL data when they become available. Star formation triggered by expanding H ii regions The Spitzer–GLIMPSE images at 8 µm have unveiled a “bubbling Galactic disc”. More than 600 bubbles with diameters of a few arcminutes have been catalogued by Churchwell et al. (2006, 2007 ...
... and with the Herschel Hi-GAL data when they become available. Star formation triggered by expanding H ii regions The Spitzer–GLIMPSE images at 8 µm have unveiled a “bubbling Galactic disc”. More than 600 bubbles with diameters of a few arcminutes have been catalogued by Churchwell et al. (2006, 2007 ...
Girardi
... CMDs of galaxies at a known distance. Worth mentioning: IAC-Star (Aparicio & Gallart 2004), with a web interface and implementing Teramo and Padova tracks MATCH-related codes by Dolphin (2002?), now implemented with several sets of ...
... CMDs of galaxies at a known distance. Worth mentioning: IAC-Star (Aparicio & Gallart 2004), with a web interface and implementing Teramo and Padova tracks MATCH-related codes by Dolphin (2002?), now implemented with several sets of ...
Chapter 2. Discovering the Universe for Yourself
... 6. Circumpolar stars are stars that never appear to rise or set from a given location, but are always visible on any clear night. From the North Pole, every visible star is circumpolar, as all circle the horizon at constant altitudes. In contrast, a much smaller portion of the sky is circumpolar fro ...
... 6. Circumpolar stars are stars that never appear to rise or set from a given location, but are always visible on any clear night. From the North Pole, every visible star is circumpolar, as all circle the horizon at constant altitudes. In contrast, a much smaller portion of the sky is circumpolar fro ...
OBJXlab-JCU_Alt
... Most of the things in the sky look like dots or smudges of light. Even through the biggest telescopes only a few objects, like the large planets, a few galaxies and nebulae, show distinguishing details. It takes careful observation—with spectrometers, photometers, imaging cameras at a wide range of ...
... Most of the things in the sky look like dots or smudges of light. Even through the biggest telescopes only a few objects, like the large planets, a few galaxies and nebulae, show distinguishing details. It takes careful observation—with spectrometers, photometers, imaging cameras at a wide range of ...
Neistein_dekel60
... The history of one galaxy We follow all the particles, and check which got heated/cooled/SF/accreted ...
... The history of one galaxy We follow all the particles, and check which got heated/cooled/SF/accreted ...
21_Testbank
... clouds with higher angular momentum would have collapsed to a more disklike form (spiral galaxies). Such differences in the initial conditions is an example of the role of nature in galaxy evolution. An example of nurture is a collision between two spiral galaxies that randomizes the ordered stellar ...
... clouds with higher angular momentum would have collapsed to a more disklike form (spiral galaxies). Such differences in the initial conditions is an example of the role of nature in galaxy evolution. An example of nurture is a collision between two spiral galaxies that randomizes the ordered stellar ...
epsilon Aur
... The primary star in the system is a yellow-white supergiant, whose diameter is comparable in size with that of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. The secondary object is a mystery. It orbits the primary star every 27 years, at a distance similar to that of Neptune from our Sun. These eclipses last fo ...
... The primary star in the system is a yellow-white supergiant, whose diameter is comparable in size with that of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. The secondary object is a mystery. It orbits the primary star every 27 years, at a distance similar to that of Neptune from our Sun. These eclipses last fo ...
ISP205L, Week 13 Computer Lab Activity The Distance to the Pleiades
... showing the relative amounts of light emitted at different wavelengths by thermal emitters (such as the photospheres of stars) which have different temperatures. The ratio of the fluxes at the B and V wavelengths is a sensitive measure of which one of these curves describes the spectrum. ...
... showing the relative amounts of light emitted at different wavelengths by thermal emitters (such as the photospheres of stars) which have different temperatures. The ratio of the fluxes at the B and V wavelengths is a sensitive measure of which one of these curves describes the spectrum. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.