MAIN SEQUENCE STARS, Red Giants and White Dwarfs
... Supergiants for Higher Mass Stars • For more massive stars the same thing happens, but the star starts way up on the H-R diagram, and it enters the SUPERGIANT phase. • The ESCAPE VELOCITY from such big stars gets low: Vesc = (2 G M / R)1/2 as R increases while M stays the same. • They lose a lot of ...
... Supergiants for Higher Mass Stars • For more massive stars the same thing happens, but the star starts way up on the H-R diagram, and it enters the SUPERGIANT phase. • The ESCAPE VELOCITY from such big stars gets low: Vesc = (2 G M / R)1/2 as R increases while M stays the same. • They lose a lot of ...
Planetary Fact Sheet – Metric
... 1. If the shape of the Earth’s orbit was unaltered but its rotation axis was shifted so that it had no tilt with respect to the orbit, how would the seasons be affected? This requires you understand the relationship between the tilt of the Earth and its seasons. This is summarized in unit 6.3 on pag ...
... 1. If the shape of the Earth’s orbit was unaltered but its rotation axis was shifted so that it had no tilt with respect to the orbit, how would the seasons be affected? This requires you understand the relationship between the tilt of the Earth and its seasons. This is summarized in unit 6.3 on pag ...
The Helium Flash • When the temperature of a stellar core reaches T
... and are called RR Lyr stars. Because the structure of the horizontal branch can differ dramatically from cluster to cluster, the (luminosity specific) number of RR Lyr stars in a globular cluster can change by an order of magnitude, or more. • In the observable HR digram (i.e., V vs. B−V ), the extre ...
... and are called RR Lyr stars. Because the structure of the horizontal branch can differ dramatically from cluster to cluster, the (luminosity specific) number of RR Lyr stars in a globular cluster can change by an order of magnitude, or more. • In the observable HR digram (i.e., V vs. B−V ), the extre ...
Ground-Based Astrometry 2010-2020
... 0.3′′ pixels to magnitude 24 (single visit). • SkyMapper: Based at Siding Spring Observatory, SkyMapper achieved first light in 2008. During the planned Southern Sky Survey, 20000 square degrees will be imaged in six optical filters on 0.5′′ pixels to magnitude 21 (single visit). A shorter-integrati ...
... 0.3′′ pixels to magnitude 24 (single visit). • SkyMapper: Based at Siding Spring Observatory, SkyMapper achieved first light in 2008. During the planned Southern Sky Survey, 20000 square degrees will be imaged in six optical filters on 0.5′′ pixels to magnitude 21 (single visit). A shorter-integrati ...
Galileo
... countless more which have never before been seen, exposing these plainly to the eye in numbers ten times exceeding the old and familiar stars. It is a very beautiful thing, and most gratifying to the sight, to behold the body of the moon, distant from us almost sixty earthly radii, 4 as if it were n ...
... countless more which have never before been seen, exposing these plainly to the eye in numbers ten times exceeding the old and familiar stars. It is a very beautiful thing, and most gratifying to the sight, to behold the body of the moon, distant from us almost sixty earthly radii, 4 as if it were n ...
The Sun and Stars 4.1 Energy formation and layers of the Sun 4.2
... Prominences and Solar Flares. It is important for us to follow the Sunspot cycle to know when there is going to be an increase in Sunspots, because they cause Solar Flares and Prominences. Although the Earth’s magnetic field can deflect or pull in much of the energy that is carried in a solar flare, ...
... Prominences and Solar Flares. It is important for us to follow the Sunspot cycle to know when there is going to be an increase in Sunspots, because they cause Solar Flares and Prominences. Although the Earth’s magnetic field can deflect or pull in much of the energy that is carried in a solar flare, ...
When we look at a neighboring galaxy (such as M31, the
... supergiants from foreground stars—and that is through measuring the radial velocities of the stars. M31 is barreling towards us at -300 km/sec (about -670,000 miles/hr), where the minus sign serves as a reminder that the velocity is towards us. (Truth be told: most of this apparent motion is actuall ...
... supergiants from foreground stars—and that is through measuring the radial velocities of the stars. M31 is barreling towards us at -300 km/sec (about -670,000 miles/hr), where the minus sign serves as a reminder that the velocity is towards us. (Truth be told: most of this apparent motion is actuall ...
2_ISM - UCT Astronomy Department
... interstellar medium (dust and gas) in this section Why? The history review of history of determining shape and size of galaxies have shown the importance of dust absorption and scattering, and Rayleigh scattering in the determination of the true size of the Galaxy • distances to object in the Galaxy ...
... interstellar medium (dust and gas) in this section Why? The history review of history of determining shape and size of galaxies have shown the importance of dust absorption and scattering, and Rayleigh scattering in the determination of the true size of the Galaxy • distances to object in the Galaxy ...
Project Icarus: Astronomical Considerations Relating to the Choice
... select the choice of target stars(s) for Icarus, we propose here that the above areas of scientific investigation be considered as listed in order of increasing priority. Thus, scientific investigations conducted en route are a low priority when it comes to the choice of target, not because such inv ...
... select the choice of target stars(s) for Icarus, we propose here that the above areas of scientific investigation be considered as listed in order of increasing priority. Thus, scientific investigations conducted en route are a low priority when it comes to the choice of target, not because such inv ...
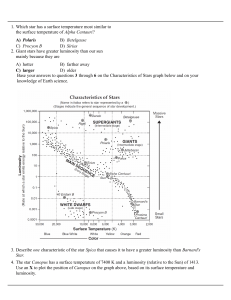
A) Polaris B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sirius 1. Which star has a
... A) Barnard's Star B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sun 78. When a star less massive than our sun consumes all of its nuclear fuel it will then become a A) white dwarf B) nova C) supernova D) black hole 79. Which of the following stars is least bright? A) the sun B) a blue supergiant C) a white dwarf D) ...
... A) Barnard's Star B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sun 78. When a star less massive than our sun consumes all of its nuclear fuel it will then become a A) white dwarf B) nova C) supernova D) black hole 79. Which of the following stars is least bright? A) the sun B) a blue supergiant C) a white dwarf D) ...
ph507rev1
... parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Before 1990, fewer than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 1012 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations made by the European Space Agency with the Hipparcos mission (1989-1993) accurately determin ...
... parallax accuracy to 0.001” within a few years. Before 1990, fewer than 10,000 stellar parallaxes had been measured (and only 500 known well), but there are about 1012 stars in our Galaxy. Space observations made by the European Space Agency with the Hipparcos mission (1989-1993) accurately determin ...
Astronomy Astrophysics NGC 7419 as a template for red supergiant clusters &
... spectroscopy around the Hα line for most of the candidate Be stars, confirming their nature. A second peculiarity of NGC 7419 is the presence of five red supergiants (RSGs) as confirmed radial velocity members of the cluster (Beauchamp et al. 1994). Until recently, this was the highest number of RSG ...
... spectroscopy around the Hα line for most of the candidate Be stars, confirming their nature. A second peculiarity of NGC 7419 is the presence of five red supergiants (RSGs) as confirmed radial velocity members of the cluster (Beauchamp et al. 1994). Until recently, this was the highest number of RSG ...
Seeds of a Tychonic Revolution: Telescopic Observations of the
... must be two thousand or more AU distant. Very faint stars, seen only with his telescope, must be still more distant. Mareo has a keen mind. He quickly realizes that this hypothesis is not just another speculation that can be backed only by assertions. This hypothesis is testable. Mareo’s telescopic ...
... must be two thousand or more AU distant. Very faint stars, seen only with his telescope, must be still more distant. Mareo has a keen mind. He quickly realizes that this hypothesis is not just another speculation that can be backed only by assertions. This hypothesis is testable. Mareo’s telescopic ...
Lab 7
... along the celestial equator of an object (think of it as sort of a space longitude). By tradition, the RA is measured counterclockwise in units of hours and minutes, starting at 0 hours and coming back, after one full circle, to 24 hours. To determine the angle above or below the celestial equator y ...
... along the celestial equator of an object (think of it as sort of a space longitude). By tradition, the RA is measured counterclockwise in units of hours and minutes, starting at 0 hours and coming back, after one full circle, to 24 hours. To determine the angle above or below the celestial equator y ...
The ultra-luminous x-ray sources near center of M82
... accretion disks orbiting the stellar-mass black hole binaries Stellar-mass black hole binaries with anisotropic X-ray emission (mechanical beaming) Micro-blazars observed along the direction of their relativistically beamed jet Young supernova remnants in a high-density medium or hypernova rem ...
... accretion disks orbiting the stellar-mass black hole binaries Stellar-mass black hole binaries with anisotropic X-ray emission (mechanical beaming) Micro-blazars observed along the direction of their relativistically beamed jet Young supernova remnants in a high-density medium or hypernova rem ...
Life Stages of High
... • This double-shell burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses ...
... • This double-shell burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses ...
PDF - Interactive Stars
... These twenty two lost star signs reconnect us to the ancient vision of a sacred, living cosmos, and to the great celestial sphere around us. Your Sign Beyond the Zodiac Linked to your Sun Sign These star signs are the ancient constellations which lie to the North and South of the zodiac band of star ...
... These twenty two lost star signs reconnect us to the ancient vision of a sacred, living cosmos, and to the great celestial sphere around us. Your Sign Beyond the Zodiac Linked to your Sun Sign These star signs are the ancient constellations which lie to the North and South of the zodiac band of star ...
PDF - Interactive Stars
... These twenty two lost star signs reconnect us to the ancient vision of a sacred, living cosmos, and to the great celestial sphere around us. Your Sign Beyond the Zodiac Linked to your Sun Sign These star signs are the ancient constellations which lie to the North and South of the zodiac band of star ...
... These twenty two lost star signs reconnect us to the ancient vision of a sacred, living cosmos, and to the great celestial sphere around us. Your Sign Beyond the Zodiac Linked to your Sun Sign These star signs are the ancient constellations which lie to the North and South of the zodiac band of star ...
direct contact among galactic civilizations by relativistic
... magnitude less than this figure, and the rate of star formation in early galactic history is possibly several orders of ma~itude more @). According to present views of stellar nucleogenesis@@,stars (and, by implication, planets) formed in the early history of the Galaxy are extremely poor in heavy e ...
... magnitude less than this figure, and the rate of star formation in early galactic history is possibly several orders of ma~itude more @). According to present views of stellar nucleogenesis@@,stars (and, by implication, planets) formed in the early history of the Galaxy are extremely poor in heavy e ...
Atoms and Stars IST 3360 and IST 1990
... • Normally counter-clockwise from above north pole • All planets exhibited this sometimes • Plato’s theory had extra spheres and features to handle retrograde motion ...
... • Normally counter-clockwise from above north pole • All planets exhibited this sometimes • Plato’s theory had extra spheres and features to handle retrograde motion ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.