Chapter 31 Galaxies & the Universe
... These groups of galaxies may have from a few to hundreds of member galaxies and may range in sizes up to 30 million ly. In a cluster, most of the inner region galaxies are ellipticals. Galaxies in the outer portions are a mix of ellipticals and spirals. The galaxies often ...
... These groups of galaxies may have from a few to hundreds of member galaxies and may range in sizes up to 30 million ly. In a cluster, most of the inner region galaxies are ellipticals. Galaxies in the outer portions are a mix of ellipticals and spirals. The galaxies often ...
Galaxies
... • Spiral galaxies are denoted by “S”, and barred spirals by “SB”. Letters “a”, “b”, “c” denote how tightly the spiral arms are wound, with “a” being most tightly wound. The Andromeda Galaxy is an Sb. • Elliptical galaxies are denoted by “E”, with a number from 0-7 indicating how circular it appears. ...
... • Spiral galaxies are denoted by “S”, and barred spirals by “SB”. Letters “a”, “b”, “c” denote how tightly the spiral arms are wound, with “a” being most tightly wound. The Andromeda Galaxy is an Sb. • Elliptical galaxies are denoted by “E”, with a number from 0-7 indicating how circular it appears. ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... temperature of the stars on the x-axis and the absolute brightness on the y-axis. ...
... temperature of the stars on the x-axis and the absolute brightness on the y-axis. ...
Review Day
... The H-R Diagram show the relationship between temperature and brightness. Identifies four characteristics of stars Temperature Brightness Color Category ...
... The H-R Diagram show the relationship between temperature and brightness. Identifies four characteristics of stars Temperature Brightness Color Category ...
Benchmark lesson
... How are stars grouped together? Did you ever look into the sky and imagine that the stars made a picture? Many ancient people thought they saw patterns in the stars. They named the stars after the patterns they saw—animals or other figures that had special meanings to them. These groups of stars are ...
... How are stars grouped together? Did you ever look into the sky and imagine that the stars made a picture? Many ancient people thought they saw patterns in the stars. They named the stars after the patterns they saw—animals or other figures that had special meanings to them. These groups of stars are ...
September 3 and 5 slides
... • What are the distances to the spirals? • Are the spirals composed of gas or stars? • Why do the spirals avoid the plane of the Milky Way? • Harlow Shapley (Mt. Wilson Observatory; “establishment”) and Heber Curtis (Lick Observatory; “youngster”) • Curtis argued for the spirals being “island univer ...
... • What are the distances to the spirals? • Are the spirals composed of gas or stars? • Why do the spirals avoid the plane of the Milky Way? • Harlow Shapley (Mt. Wilson Observatory; “establishment”) and Heber Curtis (Lick Observatory; “youngster”) • Curtis argued for the spirals being “island univer ...
answers
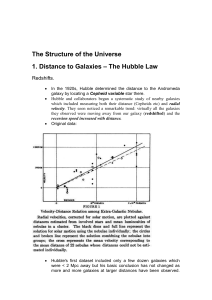
... c) Convert the units of the slope to years. It should be around 14 x 109 years. d) What is the meaning of the slope? The age of the universe! Edwin discovered this relationship 80 years ago. However, he graphed the speed on the vertical axis. This has switched to make it easier for the students. The ...
... c) Convert the units of the slope to years. It should be around 14 x 109 years. d) What is the meaning of the slope? The age of the universe! Edwin discovered this relationship 80 years ago. However, he graphed the speed on the vertical axis. This has switched to make it easier for the students. The ...
Lecture Eleven (Powerpoint format)
... The Question of the “Nebulae” -How Big is the Universe?? For hundreds of years astronomers observed fuzzy “nebulae” (literally “clouds” from Latin) in their telescopes. The precise nature of these nebulae was the subject of intense speculation and debate. Since no one could see any individual ...
... The Question of the “Nebulae” -How Big is the Universe?? For hundreds of years astronomers observed fuzzy “nebulae” (literally “clouds” from Latin) in their telescopes. The precise nature of these nebulae was the subject of intense speculation and debate. Since no one could see any individual ...
red giant - Teacher Pages
... a. This is supported by a phenomenon called the Doppler shift 1). Stars are moving away from Earth and their light becomes dimmer. This is called the red shift. This gives support of the expanding universe 2). If stars move toward Earth, we see a blue shift – light becomes brighter ...
... a. This is supported by a phenomenon called the Doppler shift 1). Stars are moving away from Earth and their light becomes dimmer. This is called the red shift. This gives support of the expanding universe 2). If stars move toward Earth, we see a blue shift – light becomes brighter ...
Star formation in galaxies over the last 10 billion
... The emission lines are at longer wavelengths than measured in the lab: They are “redshifted”. This is because distant galaxies move away from us (“Doppler effect”, expansion of the Universe). wavelength ...
... The emission lines are at longer wavelengths than measured in the lab: They are “redshifted”. This is because distant galaxies move away from us (“Doppler effect”, expansion of the Universe). wavelength ...
PH607lec08
... that cluster galaxies commonly interact. Over time, the galaxy interactions are likely to affect the content of the cluster itself. Researchers believe that the Hercules Cluster is significantly similar to young galaxy clusters in the distant, early Universe and that exploring galaxy types and their ...
... that cluster galaxies commonly interact. Over time, the galaxy interactions are likely to affect the content of the cluster itself. Researchers believe that the Hercules Cluster is significantly similar to young galaxy clusters in the distant, early Universe and that exploring galaxy types and their ...
Polarimetry & Star
... Gravitational collapse of some of these “structures” produces the first stars and galaxies. ...
... Gravitational collapse of some of these “structures” produces the first stars and galaxies. ...
General Astrophysical Concepts: Astronomical length scales
... nucleus of a quasar is about five million times the mass of our Sun The light-emitting region of a typical quasar is comparable in size to our Solar System Quasars and AGNs can be 100 to 1000 times more luminous than our Milky Way galaxy Most galaxies have massive black holes at their centers ...
... nucleus of a quasar is about five million times the mass of our Sun The light-emitting region of a typical quasar is comparable in size to our Solar System Quasars and AGNs can be 100 to 1000 times more luminous than our Milky Way galaxy Most galaxies have massive black holes at their centers ...
It is now recognized that the vast majority of ellipticals are of
... Colour: Large automated imaging surveys are better at defining a galaxy's colour rather than morphology. it is more natural to describe a galaxy as being on the ‘red sequence’ or ‘blue sequence’ rather than being an ‘early type’ or ‘late type’. This interpretation also has the advantage that galaxy ...
... Colour: Large automated imaging surveys are better at defining a galaxy's colour rather than morphology. it is more natural to describe a galaxy as being on the ‘red sequence’ or ‘blue sequence’ rather than being an ‘early type’ or ‘late type’. This interpretation also has the advantage that galaxy ...
Hubble’s Law & Black Holes at a Galaxy’s Center
... Simplicio: You tell me the universe is expanding, and some things do move away but other things do not. How does a thing know what to do? 3. Sagredo explains: The fundamental reason is a. Galaxies move away; other things do not. b. Big objects move away; little objects do not. c. If the force holdin ...
... Simplicio: You tell me the universe is expanding, and some things do move away but other things do not. How does a thing know what to do? 3. Sagredo explains: The fundamental reason is a. Galaxies move away; other things do not. b. Big objects move away; little objects do not. c. If the force holdin ...
Lecture Eleven (Powerpoint format)
... Kip went to work on the problem and actually worked out the details using relativity theory. He suggested that wormholes might work. Intringued, Thorne picked up the wormhole problem over the next several years and began pursuing it as an active research project. Inspired by his bold lead on s ...
... Kip went to work on the problem and actually worked out the details using relativity theory. He suggested that wormholes might work. Intringued, Thorne picked up the wormhole problem over the next several years and began pursuing it as an active research project. Inspired by his bold lead on s ...
Astronomers Demonstrate the Global Internet Telescope
... "monster in the middle" of a galaxy far away from our Milky Way. For this, they have used the world's research computer networks to create a giant virtual telescope. This allows imaging of the objects with unprecedented detail, and in real-time, which would have been impossible only a few years ago. ...
... "monster in the middle" of a galaxy far away from our Milky Way. For this, they have used the world's research computer networks to create a giant virtual telescope. This allows imaging of the objects with unprecedented detail, and in real-time, which would have been impossible only a few years ago. ...
jodrell_bank_wms - Faulkes Telescope Project
... green and red filters in turn. The three images are then combined to produce the colour image. ...
... green and red filters in turn. The three images are then combined to produce the colour image. ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.