The Milky Way - Department of Physics
... which are contained inside others. In other words, this chapter will give us perspective for all of our exploration to follow. It is easy to learn a few facts, but it is the relationships between facts that are interesting. The relationships illustrated in this chapter will give us a perspective on ...
... which are contained inside others. In other words, this chapter will give us perspective for all of our exploration to follow. It is easy to learn a few facts, but it is the relationships between facts that are interesting. The relationships illustrated in this chapter will give us a perspective on ...
24.1 Hubble`s Galaxy Classification
... Elliptical galaxies have no spiral arms and no disk. They come in many sizes, from giant ellipticals of trillions of stars, down to dwarf ellipticals of less than a million stars. Ellipticals also contain very little, if any, cool gas and dust, and they show no evidence of ongoing star formation. Ma ...
... Elliptical galaxies have no spiral arms and no disk. They come in many sizes, from giant ellipticals of trillions of stars, down to dwarf ellipticals of less than a million stars. Ellipticals also contain very little, if any, cool gas and dust, and they show no evidence of ongoing star formation. Ma ...
Ch. 27 Stars & Galaxies
... • Constellations: Star groups that shift in fixed patterns as viewed from Earth ...
... • Constellations: Star groups that shift in fixed patterns as viewed from Earth ...
Galaxies
... 5. Limitations of the model There are several limitations of our computer model. First, it is only a two-dimensional demonstration of the galactic collision, but actually, the stars in the galaxies do not completely lie on the same plane. As a result, the model does not consider the 3-D component of ...
... 5. Limitations of the model There are several limitations of our computer model. First, it is only a two-dimensional demonstration of the galactic collision, but actually, the stars in the galaxies do not completely lie on the same plane. As a result, the model does not consider the 3-D component of ...
ASTR 101 Scale of the Universe: an Overview
... What are the dark areas we see in the images of galaxies. What are the largest structures in the universe? How old is the universe? What is the observable universe? From the information in page 23 (Hubble deep field) make a rough estimate of the total number of galaxies in the universe. How realisti ...
... What are the dark areas we see in the images of galaxies. What are the largest structures in the universe? How old is the universe? What is the observable universe? From the information in page 23 (Hubble deep field) make a rough estimate of the total number of galaxies in the universe. How realisti ...
Astro 6590: Galaxies and the Universe Astro
... and gas are about 70% hydrogen by mass and 25% helium, the rest being heavier elements (called "metals"). • Typical scales are: masses between 106 to 1012 M (1 solar mass is 2 x 1030 kg), and sizes ~ 1-100 kpc (1 pc = 3.1 x 1016 m). Galaxies that rotate have Prot ~ 10-100 Myr at about 100 km/s. The ...
... and gas are about 70% hydrogen by mass and 25% helium, the rest being heavier elements (called "metals"). • Typical scales are: masses between 106 to 1012 M (1 solar mass is 2 x 1030 kg), and sizes ~ 1-100 kpc (1 pc = 3.1 x 1016 m). Galaxies that rotate have Prot ~ 10-100 Myr at about 100 km/s. The ...
How do the most massive galaxies constrain theories of
... AGN feedback model too much scatter in red sequence at high redshift…formation time too late or too spread out ...
... AGN feedback model too much scatter in red sequence at high redshift…formation time too late or too spread out ...
has occurred over the past 14 billion years COSMIC DOWNSIZING
... sensitive optical views of the universe come from the Hubble Space Telescope. In the Hubble Deep Field studies — 10day exposures of two tiny regions of the sky observed through four different wavelength filters — researchers have found thousands of distant galaxies, with the oldest dating back to ab ...
... sensitive optical views of the universe come from the Hubble Space Telescope. In the Hubble Deep Field studies — 10day exposures of two tiny regions of the sky observed through four different wavelength filters — researchers have found thousands of distant galaxies, with the oldest dating back to ab ...
Wavelength
... thousands of years for light from some stars in our galaxy to reach us. For stars that we can see in nearby galaxies it can take millions of years. The farthest objects we can see are quasars. They are so distant that the light we see from them today left billions of years ago. ...
... thousands of years for light from some stars in our galaxy to reach us. For stars that we can see in nearby galaxies it can take millions of years. The farthest objects we can see are quasars. They are so distant that the light we see from them today left billions of years ago. ...
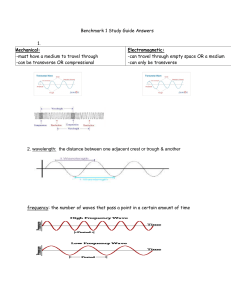
Benchmark 1 Study Guide Answers 1. mMechanical: m-
... Spectroscopes collect and separate light from stars into color bands & uses those bands to identify star elements Satellites are in orbit around Earth & use special instruments & telescopes to collect data to be sent back to Earth to be interpreted Space Probes travel out of Earth's orbit to dangero ...
... Spectroscopes collect and separate light from stars into color bands & uses those bands to identify star elements Satellites are in orbit around Earth & use special instruments & telescopes to collect data to be sent back to Earth to be interpreted Space Probes travel out of Earth's orbit to dangero ...
Our place in the Universe
... You have to imagine that this is our entire 3-dimensional view of the sky flattened into a map. EVERY 3-dimensional direction we look we see CBR (cosmic ...
... You have to imagine that this is our entire 3-dimensional view of the sky flattened into a map. EVERY 3-dimensional direction we look we see CBR (cosmic ...
Ch 28 Vocab cnp
... Chapter 28: Stars and Galaxies A halo of gases that is formed by the expelled layers of a star’s atmosphere The brightness of a star The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth A group of millions, or even billions of stars held together by gravity A unit of me ...
... Chapter 28: Stars and Galaxies A halo of gases that is formed by the expelled layers of a star’s atmosphere The brightness of a star The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth A group of millions, or even billions of stars held together by gravity A unit of me ...
Big Bang Theory
... away from us (red-shift) at a speed that is proportional to their distance the more distant the galaxy, the greater the velocity (moving away at faster speeds) ...
... away from us (red-shift) at a speed that is proportional to their distance the more distant the galaxy, the greater the velocity (moving away at faster speeds) ...
Messier Galaxies of #202541
... Rho Virginis and 4 dim stars near 6 Coma Berenicis. Rho and 6 Coma will be important guide stars. These stars have been plotted in figure 1. Notice that the dimmers stars have not been designated by their common names, but by their magnitudes. The decimal has been left out to avoid mistaking it for ...
... Rho Virginis and 4 dim stars near 6 Coma Berenicis. Rho and 6 Coma will be important guide stars. These stars have been plotted in figure 1. Notice that the dimmers stars have not been designated by their common names, but by their magnitudes. The decimal has been left out to avoid mistaking it for ...
solar.gmu.edu
... •A quasar’s luminosity can be calculated from its apparent brightness and the distance using the inverse-square law •Even though small, the luminosity of a quasar (1038 to 1042 Watts) can be very larger, i.e., several thousand times more than the entire Milly Way Galaxies (1037). •A quasar has emiss ...
... •A quasar’s luminosity can be calculated from its apparent brightness and the distance using the inverse-square law •Even though small, the luminosity of a quasar (1038 to 1042 Watts) can be very larger, i.e., several thousand times more than the entire Milly Way Galaxies (1037). •A quasar has emiss ...
Science 9 Unit 5: Space Name:
... The technique of using a number of telescopes in combination is called interferometry. When working together, these telescopes can detect objects in space with better clarity and at greater distances than any current Earth-based observatory. The Hubble Space Telescope ( HST ) The HST makes one com ...
... The technique of using a number of telescopes in combination is called interferometry. When working together, these telescopes can detect objects in space with better clarity and at greater distances than any current Earth-based observatory. The Hubble Space Telescope ( HST ) The HST makes one com ...
Astronomy Final Exam Review
... • Supernova- how massive and supermassive stars begin the end of their lives (after red giant or supergiant phase) • Quasar- rare, starlike object that gives off radio waves as material is sucked toward a black hole • Light year- the distance light travels in a year • AU-(astronomical unit)- 1AU= di ...
... • Supernova- how massive and supermassive stars begin the end of their lives (after red giant or supergiant phase) • Quasar- rare, starlike object that gives off radio waves as material is sucked toward a black hole • Light year- the distance light travels in a year • AU-(astronomical unit)- 1AU= di ...
PH607lec12
... Though many astronomers agree that hierarchical formation seems to be occurring, there are still some wrinkles to the theory. For example, the very most massive galaxies don't seem to be growing at as high a rate as middle-mass galaxies. When astronomers look at the brightest galaxies now compared t ...
... Though many astronomers agree that hierarchical formation seems to be occurring, there are still some wrinkles to the theory. For example, the very most massive galaxies don't seem to be growing at as high a rate as middle-mass galaxies. When astronomers look at the brightest galaxies now compared t ...
Astronomy Final Exam Review
... • Supernova- how massive and supermassive stars begin the end of their lives (after red giant or supergiant phase) • Quasar- rare, starlike object that gives off radio waves as material is sucked toward a black hole • Light year- the distance light travels in a year • AU-(astronomical unit)- 1AU= di ...
... • Supernova- how massive and supermassive stars begin the end of their lives (after red giant or supergiant phase) • Quasar- rare, starlike object that gives off radio waves as material is sucked toward a black hole • Light year- the distance light travels in a year • AU-(astronomical unit)- 1AU= di ...
imaging science in astronomy - RIT CIS
... contact with the universe. It is interesting to ponder how humans would conceive of the universe if we had nothing more in the way of imaging apparatus at our disposal, as was the case for astronomers before Galileo. In contrast to the complex cosmologies currently pondered in modern physics, most o ...
... contact with the universe. It is interesting to ponder how humans would conceive of the universe if we had nothing more in the way of imaging apparatus at our disposal, as was the case for astronomers before Galileo. In contrast to the complex cosmologies currently pondered in modern physics, most o ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.