Distant galaxies and quasars The ages of things Light
... By adding up starlight from blue stars / IR from deep samples, we can now estimate the total rate of star formation in the Universe (regardless which galaxies it is taking place in ... This, like the quasar evolution, shows a dramatic peak at earlier times ... but somewhat later than the quasars ...
... By adding up starlight from blue stars / IR from deep samples, we can now estimate the total rate of star formation in the Universe (regardless which galaxies it is taking place in ... This, like the quasar evolution, shows a dramatic peak at earlier times ... but somewhat later than the quasars ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... from objects in space making it observable. • Optical Telescopes – The most common type of telescope it is designed to collect and focus visible light for close observation. • Refracting Optical Telescope – The simplest type uses two lenses to magnify light. Cannot perfectly focus and their size is ...
... from objects in space making it observable. • Optical Telescopes – The most common type of telescope it is designed to collect and focus visible light for close observation. • Refracting Optical Telescope – The simplest type uses two lenses to magnify light. Cannot perfectly focus and their size is ...
Earth - Capital High School
... The Hubble Ultra Deep Field, or HUDF, is an image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax, composited from Hubble Space Telescope data accumulated over a period from September 3, 2003 through January 16, 2004. It is the deepest image of the universe ever taken in visible light, lookin ...
... The Hubble Ultra Deep Field, or HUDF, is an image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax, composited from Hubble Space Telescope data accumulated over a period from September 3, 2003 through January 16, 2004. It is the deepest image of the universe ever taken in visible light, lookin ...
Galaxies - Wallkill Valley Regional High School
... - Range from dwarf to giant galaxies based on number of stars ...
... - Range from dwarf to giant galaxies based on number of stars ...
cosmological horizon
... where the force of gravity is stronger than the expansion pressure, a gravitationally bound object is formed for example, the stars in our Galaxy are bound together by gravity, so it does ...
... where the force of gravity is stronger than the expansion pressure, a gravitationally bound object is formed for example, the stars in our Galaxy are bound together by gravity, so it does ...
Sky News – March 2015 The Realm of the Galaxies
... Coma Bernices. With our night sky pointing away from the hustle and bustle of the plane of the Milky Way, we can see deep into the sky without objects being obscured or dimmed by looking through our galaxy. In spring skies we are treated to views of the closest cluster of galaxies in Virgo of which ...
... Coma Bernices. With our night sky pointing away from the hustle and bustle of the plane of the Milky Way, we can see deep into the sky without objects being obscured or dimmed by looking through our galaxy. In spring skies we are treated to views of the closest cluster of galaxies in Virgo of which ...
AGN-Hubble
... The Hubble Constant and the Age of the Universe If you plot the scale of the Universe vs time, the Hubble constant is the slope of the line now. If it’s really constant, then the age of the Universe is just 1/H [since H=v/D=(d/t)/d]. That’s because if you know how fast we are expanding, you can run ...
... The Hubble Constant and the Age of the Universe If you plot the scale of the Universe vs time, the Hubble constant is the slope of the line now. If it’s really constant, then the age of the Universe is just 1/H [since H=v/D=(d/t)/d]. That’s because if you know how fast we are expanding, you can run ...
The Earth in Perspective
... Now, THIS is really fascinating It's rather dazzling to see it presented this way. ...
... Now, THIS is really fascinating It's rather dazzling to see it presented this way. ...
Galaxies and the Big Bang Theory
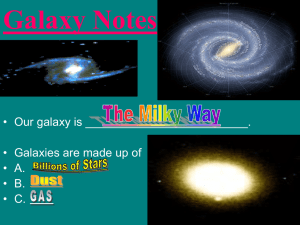
... Spiral Galaxies The shape of a spiral galaxy is a bulge in the middle and arms that spiral outward like ______________. •Many bright, young stars •Spiral galaxies contain ____________ and _____________. Elliptical Galaxies •Look like _______________ or __________________ ______________. •Billions of ...
... Spiral Galaxies The shape of a spiral galaxy is a bulge in the middle and arms that spiral outward like ______________. •Many bright, young stars •Spiral galaxies contain ____________ and _____________. Elliptical Galaxies •Look like _______________ or __________________ ______________. •Billions of ...
Origins of the Universe
... in the universe that cannot • planets be seen, but its effects on other things can be detected? ...
... in the universe that cannot • planets be seen, but its effects on other things can be detected? ...
Hubblecast Episode 68: The Hubble time machine Visual notes 00
... 10. Hubble is still searching the distant Universe for clues about how the Universe formed, and how it has evolved. Several of Hubble’s surveys, for example CANDELS, CLASH, and GOODS, are scanning for distant supernova explosions, objects that are good celestial distance markers. Observations of dis ...
... 10. Hubble is still searching the distant Universe for clues about how the Universe formed, and how it has evolved. Several of Hubble’s surveys, for example CANDELS, CLASH, and GOODS, are scanning for distant supernova explosions, objects that are good celestial distance markers. Observations of dis ...
10.1 PPT
... • Early astronomers were able to observe outer space by using the best instruments of the time, early telescopes. • With the development of more powerful telescopes in the 1920’s, suddenly more celestial bodies were discovered. • Celestial bodies is a general term for all the objects in the sky, in ...
... • Early astronomers were able to observe outer space by using the best instruments of the time, early telescopes. • With the development of more powerful telescopes in the 1920’s, suddenly more celestial bodies were discovered. • Celestial bodies is a general term for all the objects in the sky, in ...
Astronomy Quiz #1 Answers
... 7. What are the two important discoveries made by Edwin Hubble? -many galaxies existed beyond the Milky Way -almost all galaxies are moving away from each other ...
... 7. What are the two important discoveries made by Edwin Hubble? -many galaxies existed beyond the Milky Way -almost all galaxies are moving away from each other ...
Slide 1
... • There are about 100 billion galaxies in our universe. • If we plot all the visible galaxies on a graph, we will see something like this. ...
... • There are about 100 billion galaxies in our universe. • If we plot all the visible galaxies on a graph, we will see something like this. ...
WFPC2
... •WFPC 2 replaced the original WFPC, and contained corrective optics to compensate for the spherical aberration caused by the flawed main mirror •WFPC 2 remained in orbit for 15 years, until replaced by WFPC 3 in May of 2009 ...
... •WFPC 2 replaced the original WFPC, and contained corrective optics to compensate for the spherical aberration caused by the flawed main mirror •WFPC 2 remained in orbit for 15 years, until replaced by WFPC 3 in May of 2009 ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.