Ch. 21 notes-1
... There are billions of galaxies in the universe. Astronomers have classified most galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. Spiral Galaxies A spiral galaxy is a galaxy that has the shape of twin spirals. They have arms that spiral outward, like pinwheels. The Milky Way ...
... There are billions of galaxies in the universe. Astronomers have classified most galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. Spiral Galaxies A spiral galaxy is a galaxy that has the shape of twin spirals. They have arms that spiral outward, like pinwheels. The Milky Way ...
PHYSICS 113 Assignment #9 SOLUTIONS Chapter 17 13. Starting
... clusters all have approximately the same absolute brightness (i.e. luminosity). These methods work up to distances of nearly one Gpc (= 1,000 Mpc). (vii) The distances to the most remote objects in the universe (e.g. quasars) are found by measuring the redshift of those objects and then by convertin ...
... clusters all have approximately the same absolute brightness (i.e. luminosity). These methods work up to distances of nearly one Gpc (= 1,000 Mpc). (vii) The distances to the most remote objects in the universe (e.g. quasars) are found by measuring the redshift of those objects and then by convertin ...
hubble amazing universe worksheet
... 16. The gravitational field around a Black Hole is so large, that _________________ cannot even escape. 17. Most stars revolve at relatively slow speeds, but Hubble detected ones going too _______________. They must be going around a BH. 18. Hubble provided actual evidence that ______________ colli ...
... 16. The gravitational field around a Black Hole is so large, that _________________ cannot even escape. 17. Most stars revolve at relatively slow speeds, but Hubble detected ones going too _______________. They must be going around a BH. 18. Hubble provided actual evidence that ______________ colli ...
The Runaway Universe - Astronomy & Astrophysics Group
... “I have observed the nature and the material of the Milky Way. With the aid of the telescope this has been scrutinized so directly and with such ocular certainty that all the disputes which have vexed philosophers through so many ages have been resolved, and we are at last freed from wordy debates a ...
... “I have observed the nature and the material of the Milky Way. With the aid of the telescope this has been scrutinized so directly and with such ocular certainty that all the disputes which have vexed philosophers through so many ages have been resolved, and we are at last freed from wordy debates a ...
Study Guide 4 Part A Outline
... o The Hubble Law implies Universe is expanding The expansion started at some definite time in the past (the Big Bang)Universe expands away from every galaxy. Every galaxy would see its own version of the Hubble Law. Quasars & Active Galactic Nuclei o Quasars and other active galaxies emit large ...
... o The Hubble Law implies Universe is expanding The expansion started at some definite time in the past (the Big Bang)Universe expands away from every galaxy. Every galaxy would see its own version of the Hubble Law. Quasars & Active Galactic Nuclei o Quasars and other active galaxies emit large ...
Lecture 12
... The light from the Andromeda galaxy left it about 1.5Myr ago, and the light from something in the Virgo Cluster about 65 Myr ago (about when the dinosaurs were killed). We’ll see we think the Universe is ~14Gyr old, so light from an object >14Glyr (5000Mpc) away will not have had enough time to reac ...
... The light from the Andromeda galaxy left it about 1.5Myr ago, and the light from something in the Virgo Cluster about 65 Myr ago (about when the dinosaurs were killed). We’ll see we think the Universe is ~14Gyr old, so light from an object >14Glyr (5000Mpc) away will not have had enough time to reac ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
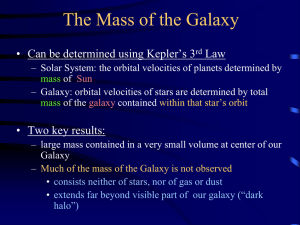
... – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
... – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
Big Bang Theory Scientific origin of the Universe
... pitch as the train passes by and recedes. The effect arises because the sound waves arrive at the listener's ear closer together as the source approaches, and further apart as it recedes. ...
... pitch as the train passes by and recedes. The effect arises because the sound waves arrive at the listener's ear closer together as the source approaches, and further apart as it recedes. ...
Science 9: Unit 4 Review
... 23. Astronomers believe that the universe is expanding. What does this ...
... 23. Astronomers believe that the universe is expanding. What does this ...
Stars and galaxies Intro
... • Uses a series of lenses to focus visible light • Limited by how large lenses can be made FYI: The largest is the 40-inch Yerkes telescope, built in 1895 in Wisconsin (40 inch lens in a sixty-foot long telescope) Pictured right – can you spot the famous scientist in the ...
... • Uses a series of lenses to focus visible light • Limited by how large lenses can be made FYI: The largest is the 40-inch Yerkes telescope, built in 1895 in Wisconsin (40 inch lens in a sixty-foot long telescope) Pictured right – can you spot the famous scientist in the ...
Our Galaxy and the Universe
... planets form from this rotating disk of dust and gases because of gravity. ...
... planets form from this rotating disk of dust and gases because of gravity. ...
Does size matter (in the SFRs)?
... the same locations of the graph, and have very similar values of the SFRs. On the contrary of course, UGC 5296 is not the only quiescent galaxy in the Universe, but the caveat is that 2/3 of the 18 galaxies we have observed common among the are quiescent. As they were selected because of their small ...
... the same locations of the graph, and have very similar values of the SFRs. On the contrary of course, UGC 5296 is not the only quiescent galaxy in the Universe, but the caveat is that 2/3 of the 18 galaxies we have observed common among the are quiescent. As they were selected because of their small ...
Page 25 - Types of Galaxies
... • Edwin Hubble classified galaxies into four major types: A) spiral B) barred spiral C) elliptical D) irregular • Most galaxies are spirals, barred spirals, or ellipticals. • Earth can be found in the Milky Way Galaxy, which is a spiral galaxy ...
... • Edwin Hubble classified galaxies into four major types: A) spiral B) barred spiral C) elliptical D) irregular • Most galaxies are spirals, barred spirals, or ellipticals. • Earth can be found in the Milky Way Galaxy, which is a spiral galaxy ...
Galaxy Zoo: Pre and post‐workshop information
... Hubble analysed the light from very distant galaxies and found that their spectra were all redshifted. This Doppler effect whereby wavelengths of spectral lines are affected by the motion of the light source indicates all distant galaxies are receding from us. This was a huge discovery as previously ...
... Hubble analysed the light from very distant galaxies and found that their spectra were all redshifted. This Doppler effect whereby wavelengths of spectral lines are affected by the motion of the light source indicates all distant galaxies are receding from us. This was a huge discovery as previously ...
The galaxies that host powerful radio sources
... • Faint at radio and IR wavelengths. These facts suggest they are distant and dusty. ...
... • Faint at radio and IR wavelengths. These facts suggest they are distant and dusty. ...
ONLINE practice exam
... 4. Most of the Lithium in the universe was formed: a.) in the first few minutes after the Big Bang b.) in the cores of stars with masses similar to the sun c.) in the cores of stars less massive than the sun d.) in the cores of stars more massive than the sun e.) in supernova explosions 5. Because o ...
... 4. Most of the Lithium in the universe was formed: a.) in the first few minutes after the Big Bang b.) in the cores of stars with masses similar to the sun c.) in the cores of stars less massive than the sun d.) in the cores of stars more massive than the sun e.) in supernova explosions 5. Because o ...
Studying Space Chapter 26 Notes
... 2d. Students know that stars differ in their life cycles, and visual, radio, and x-ray telescopes may be used to collect data that reveal those differences. ...
... 2d. Students know that stars differ in their life cycles, and visual, radio, and x-ray telescopes may be used to collect data that reveal those differences. ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
Astronomy 114 Problem Set # 7 Due: 30 Apr 2007 SOLUTIONS 1
... [Alternatively, we could use the M(r) relationship from Newton’s Laws that we derived earlier.] This mass is much larger than determined from the luminous matter, so there should be a lot of invisible “dark” mass in the NGC 4378. ...
... [Alternatively, we could use the M(r) relationship from Newton’s Laws that we derived earlier.] This mass is much larger than determined from the luminous matter, so there should be a lot of invisible “dark” mass in the NGC 4378. ...
HighRedshiftGalaxies
... faint counts and searches for primaeval galaxies in the late 1970's and early 1980's faint galaxy redshift surveys made possible by multi-object spectrographs in the late 1980's and early 1990's the launch of Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and its revelation of resolved galaxy images to significan ...
... faint counts and searches for primaeval galaxies in the late 1970's and early 1980's faint galaxy redshift surveys made possible by multi-object spectrographs in the late 1980's and early 1990's the launch of Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and its revelation of resolved galaxy images to significan ...
Guide to Deep Space Poster PDF
... In the constellation of Serpens lies the Eagle Nebula, (right) a giant cloud of interstellar gas and dust. Here new stars are being born, condensing out of the nebula. The radiation from these stellar infants is energizing the gas, causing it to glow. A closer look at the Eagle Nebula reveals intrig ...
... In the constellation of Serpens lies the Eagle Nebula, (right) a giant cloud of interstellar gas and dust. Here new stars are being born, condensing out of the nebula. The radiation from these stellar infants is energizing the gas, causing it to glow. A closer look at the Eagle Nebula reveals intrig ...
Document
... The Hubble Space Telescope is the direct solution to a problem that telescopes have faced since the very earliest days of their invention: the atmosphere. The quandary is twofold: Shifting air pockets in Earth's atmosphere distort the view of telescopes on the ground, no matter how large or scientif ...
... The Hubble Space Telescope is the direct solution to a problem that telescopes have faced since the very earliest days of their invention: the atmosphere. The quandary is twofold: Shifting air pockets in Earth's atmosphere distort the view of telescopes on the ground, no matter how large or scientif ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.