* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Galaxies - Wallkill Valley Regional High School
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
History of the telescope wikipedia , lookup
Dark matter wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Open cluster wikipedia , lookup
Andromeda Galaxy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies wikipedia , lookup
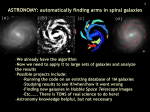
How We See Ourselves In The Universe: A Look At The Galaxies That Surround Us How High Can You Count? Our solar system contains the following items: 1 star (the sun) 8 planets 1-3 dwarf planetoids a few hundred natural satellites (moons) gases, asteroids, dust, etc. Well, Guess What? Our solar system is only one of billions of star systems that make up the Milky Way Galaxy, which is only one of several dozen galaxies that makes up our Local Cluster, and our Local Cluster group is only one of many in a collection called superclusters… Welcome to the Universe! What are galaxies? Galaxies contain millions or billions of stars held together by gravity Gravity holds galaxies together in clusters Clusters of galaxies can form even larger groups called superclusters How do we see galaxies? We can see our own Milky Way without the use of a telescope Spyglasses let us see further at sea and into the skies Telescopes (far-seeing) allow us to see distant galaxies With new technology comes new discovery Optical Telescopes Radio Telescopes Very Large Array (VLA) New Mexico Refracting Telescope Nice, France Reflecting Telescope, Los Angeles, CA - Uses combinations of - Uses combinations of lenses to see distant light sources mirrors to see distant light sources - Detects radio signals from space Infrared Telescopes Hubble Telescope (1990) Hubble repairs (2001) X-Ray Telescopes Chandra Observatory (1999) Messier 100 Tarantula Nebula in Large Magellanic Cloud Pillars of Creation, Eagle Nebula Crab Nebula caused by 1054 supernova Supernova 1604 Spiral Galaxies Milky Way NGC 7331 “Pinwheel” - A flat, rotating disc of mainly young (blue) stars and interstellar matter - A central “bulge” of mainly older (red) stars - A spherical “halo” of stars, including many in globular clusters - A super-massive black hole at the center of the central bulge NGC 1672 Andromeda NGC 1365 Elliptical Galaxies ESO-325 M 59 NGC 4125 - Have no spiral arms and are spherical or egg shaped - Contain mostly older (red) stars and little interstellar matter - Range from dwarf to giant galaxies based on number of stars M 32 M 105 M 87 Irregular Galaxies IC 10 M 82 “The Cigar” NGC 1569 - Lack regular shapes and do not have well-defined structure - Some contain large amounts of interstellar matter, others do not - More dwarf irregular galaxies than large ones - Most irregular galaxies found near spiral or elliptical galaxies, so gravity may affect shapes Large Magellanic Cloud NGC 4449 NGC 1427A Are galaxies stationary? - Galaxies are on the move, due to gravity, inertia and early forces at the time of the Big Bang - If the spectral lines in light from a galaxy shift toward the red end of the spectrum, the galaxy is moving away from us (red shift) - If the spectral lines in light from a galaxy shift toward the blue end of the spectrum, the galaxy is moving toward us (blue shift) Hubble Deep Field, 13 million years ago Artistic depiction of a quasar; a new galaxy?