stars concept review
... smashed together to form neutrons b. a large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars are born c. a shrinking, spinning region in space with a central concentration of matter d. a large explosion on a star that makes it brighter e. an object so dense that even light cannot escape its gravity ...
... smashed together to form neutrons b. a large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars are born c. a shrinking, spinning region in space with a central concentration of matter d. a large explosion on a star that makes it brighter e. an object so dense that even light cannot escape its gravity ...
Using the D810A DSLR for Deep Space Astrophotography
... Unlike cameras that must be modified, you can shoot H-alpha nebulae photographs right out of the box with the D810A. The cost savings to using a DSLR designed specifically for astrophotography versus using a CCD Cooled camera—which is one of the other options that photographers serious about photogr ...
... Unlike cameras that must be modified, you can shoot H-alpha nebulae photographs right out of the box with the D810A. The cost savings to using a DSLR designed specifically for astrophotography versus using a CCD Cooled camera—which is one of the other options that photographers serious about photogr ...
Script - ESA/Hubble
... …while the smallest stars burn slowly enough to be virtually immortal: their expected lifespan is much longer than the present age of the Universe, meaning we’ve never seen one die. [Narrator] ...
... …while the smallest stars burn slowly enough to be virtually immortal: their expected lifespan is much longer than the present age of the Universe, meaning we’ve never seen one die. [Narrator] ...
lecture 32 orbits
... outermost shell. There are 7 concentric spherical shells, each containing one object: Sun, Moon, or a planet (5 planets were known then). The shells rotate uniformly around Earth. ...
... outermost shell. There are 7 concentric spherical shells, each containing one object: Sun, Moon, or a planet (5 planets were known then). The shells rotate uniformly around Earth. ...
Chapter 25 Study guide Answer Key
... Compare and contrast apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. Apparent is how bright a star appears to us and absolute is how bright it actually is. ...
... Compare and contrast apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. Apparent is how bright a star appears to us and absolute is how bright it actually is. ...
Lecture 1
... Observational astronomers refer to any massive component too dim to be detected (stellar remnants such as white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes) as dark matter. A more stringent definition is any massive component of the universe which doesn’t emit, absorb, or scatter light at all. The usual ...
... Observational astronomers refer to any massive component too dim to be detected (stellar remnants such as white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes) as dark matter. A more stringent definition is any massive component of the universe which doesn’t emit, absorb, or scatter light at all. The usual ...
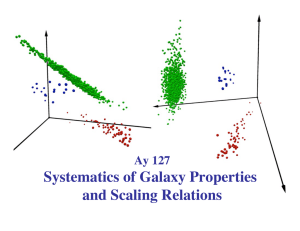
Systematics of Galaxy Properties and Scaling Relations Ay 127
... Virial Theorem connects mass, density, and kinetic temperature, and is thus an equation of a plane in that (theoretical) parameter space. Assumptions about the dynamical structure of ellipticals and their (M/ L) ratios then map the VT into the tilted FP in the observable parameter space of measured ...
... Virial Theorem connects mass, density, and kinetic temperature, and is thus an equation of a plane in that (theoretical) parameter space. Assumptions about the dynamical structure of ellipticals and their (M/ L) ratios then map the VT into the tilted FP in the observable parameter space of measured ...
Space ppt
... Space…and Beyond! S6E1. Students will explore current scientific views of the universe and how those views evolved. a. Relate the Nature of Science to the progression of basic historical scientific models (geocentric, heliocentric) as they describe our solar system, and the Big Bang as it describes ...
... Space…and Beyond! S6E1. Students will explore current scientific views of the universe and how those views evolved. a. Relate the Nature of Science to the progression of basic historical scientific models (geocentric, heliocentric) as they describe our solar system, and the Big Bang as it describes ...
Slide 1
... •Ellipticals have lots of globular clusters (about twice that of disk galaxies) •these fall into two groups based on color •color determined by metallicity, with more metal-rich GCs (redder) possibly the result of galaxy mergers •Ellipticals have much less cool, atomic gas than spiral galaxies •< 1 ...
... •Ellipticals have lots of globular clusters (about twice that of disk galaxies) •these fall into two groups based on color •color determined by metallicity, with more metal-rich GCs (redder) possibly the result of galaxy mergers •Ellipticals have much less cool, atomic gas than spiral galaxies •< 1 ...
Things to know: This meant as a guide to what you should know. I
... How do you measure distances to stars? What are the definitions of parallax and light year? Know the concept of the cosmic calendar and the basic sequence of events including the formation of the Milky Way, the formation of the Sun and the busy events of December 31st. Your cosmic address What are t ...
... How do you measure distances to stars? What are the definitions of parallax and light year? Know the concept of the cosmic calendar and the basic sequence of events including the formation of the Milky Way, the formation of the Sun and the busy events of December 31st. Your cosmic address What are t ...
Galaxies - cloudfront.net
... billions of stars. Galaxies are divided into three types according to shape: spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies. • Spiral galaxies spin and appear as a rotating disk of stars and dust, with a bulge in the middle. Several spiral arms reach outward from the central bulge like the arms of a pin ...
... billions of stars. Galaxies are divided into three types according to shape: spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies. • Spiral galaxies spin and appear as a rotating disk of stars and dust, with a bulge in the middle. Several spiral arms reach outward from the central bulge like the arms of a pin ...
1201 Discussion Notes
... Remember, the orbits in an elliptical galaxy are fairly random, so even if we focus on one area there will be a range of Doppler shifted lines from the stars that are moving towards and away from us at different speeds. These all combine (they sort of add together) to make a broadened line. The broa ...
... Remember, the orbits in an elliptical galaxy are fairly random, so even if we focus on one area there will be a range of Doppler shifted lines from the stars that are moving towards and away from us at different speeds. These all combine (they sort of add together) to make a broadened line. The broa ...
Sample Exam Questions
... Sample Exam Questions for ASTR 1023.001 The purpose of this sampling is to acquaint you with the way I ask questions. These specific questions will not be used this semester. Math questions like those at the end may appear on all exams. Sample Questions for Exam 1: 1. One light year can be defined a ...
... Sample Exam Questions for ASTR 1023.001 The purpose of this sampling is to acquaint you with the way I ask questions. These specific questions will not be used this semester. Math questions like those at the end may appear on all exams. Sample Questions for Exam 1: 1. One light year can be defined a ...
Spiral Galaxies - Astronomy Centre
... • This difference is seen in colour: • Spiral disks are relatively blue due to light from hot, massive, young stars • Elliptical galaxies are relatively red due to the dominant population of older, lower-mass stars ...
... • This difference is seen in colour: • Spiral disks are relatively blue due to light from hot, massive, young stars • Elliptical galaxies are relatively red due to the dominant population of older, lower-mass stars ...
Lesson 1, The Earth
... in space with an infrared telescope? An astronomer would study objects in space with an infrared telescope to collect data not obtainable with visible light, such as the heat being produced by a sun or planet. ...
... in space with an infrared telescope? An astronomer would study objects in space with an infrared telescope to collect data not obtainable with visible light, such as the heat being produced by a sun or planet. ...
Spiral galaxies: Spiral galaxies: Inclination Spiral galaxies: Internal
... • HI gas mass is directly proportional to 21 cm line intensity • HI disk is much more extended than optical light, typically out to 2R25 sometimes farther • The radial motion of the 21 cm line can be used to measure rotation in spiral galaxies ...
... • HI gas mass is directly proportional to 21 cm line intensity • HI disk is much more extended than optical light, typically out to 2R25 sometimes farther • The radial motion of the 21 cm line can be used to measure rotation in spiral galaxies ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.