Stars and Universe Test Review - Garnet Valley School District
... 21. _________________________ uses a curved surface to reflect radio waves from space 22. _________________________ a graph that plots a star’s temperature (x axis) verses its brightness (y-axis) 23. _________________________ irregular shaped galaxies 24. _________________________ the distance from ...
... 21. _________________________ uses a curved surface to reflect radio waves from space 22. _________________________ a graph that plots a star’s temperature (x axis) verses its brightness (y-axis) 23. _________________________ irregular shaped galaxies 24. _________________________ the distance from ...
Research proposal uploaded for ESO fellowship
... of galaxies or how much energy is being released by supernovae. This is a fundamental issue in galaxy formation models, given the importance of supernova feedback in determining the star formation history of galaxies. What have we learned from observations? Spectroscopic campaigns of distant galaxie ...
... of galaxies or how much energy is being released by supernovae. This is a fundamental issue in galaxy formation models, given the importance of supernova feedback in determining the star formation history of galaxies. What have we learned from observations? Spectroscopic campaigns of distant galaxie ...
Our Place In the Universe
... Galaxies may exist at that distance, but their light would be too faint for our telescopes to see. Because looking 15 billion light-years away means looking to a time before the universe existed. ...
... Galaxies may exist at that distance, but their light would be too faint for our telescopes to see. Because looking 15 billion light-years away means looking to a time before the universe existed. ...
Lecture9 - Physics
... The percentage of radiation that can penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere at different wavelengths. Regions in which the curve is high are called “windows,” because the atmosphere is relatively transparent at those wavelengths. There are also three wavelength ranges in which the atmosphere is opaque a ...
... The percentage of radiation that can penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere at different wavelengths. Regions in which the curve is high are called “windows,” because the atmosphere is relatively transparent at those wavelengths. There are also three wavelength ranges in which the atmosphere is opaque a ...
STARS In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and
... What are Galaxies? l. Galaxies are classified according to their----------2. The Milky Way belongs to a small cluster of galaxies called the group. 3. What is a quasar? 4. Name these types of galaxies. ...
... What are Galaxies? l. Galaxies are classified according to their----------2. The Milky Way belongs to a small cluster of galaxies called the group. 3. What is a quasar? 4. Name these types of galaxies. ...
Galaxies have different sizes and shapes.
... 26,000 light-years from the Sun. A large but very faint layer of stars surrounds the disk and bulge. In addition to stars, the Milky Way contains clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. The stars and nebulae in the Milky Way orbit the galaxy’s center at very high speeds. However, the galaxy is so lar ...
... 26,000 light-years from the Sun. A large but very faint layer of stars surrounds the disk and bulge. In addition to stars, the Milky Way contains clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. The stars and nebulae in the Milky Way orbit the galaxy’s center at very high speeds. However, the galaxy is so lar ...
Document
... There are two types of Cepheids, with two different period-luminosity relationships. Hubble had unknowingly used the wrong relationship. Like measuring with a Yardstick when he should have used ...
... There are two types of Cepheids, with two different period-luminosity relationships. Hubble had unknowingly used the wrong relationship. Like measuring with a Yardstick when he should have used ...
Galaxy Hunters Article, Cosmology Information, First Star Facts
... largest meetings ever devoted to the origin of galaxies. The first star was born about 14 billion years ago, Abel believes, in a universe that was more mysterious but also far simpler than our own. Smaller and denser than today, the universe was pitch-black and contained mostly hydrogen and helium w ...
... largest meetings ever devoted to the origin of galaxies. The first star was born about 14 billion years ago, Abel believes, in a universe that was more mysterious but also far simpler than our own. Smaller and denser than today, the universe was pitch-black and contained mostly hydrogen and helium w ...
Science 9 Unit 5: Space Name:
... Bigger telescopes enable astronomers to discover new bodies in space. Sir William Herschel built a huge reflecting telescope and discovered the planet Uranus with it in 1773. The largest refracting telescope was built at the Yerkes Observatory near the end of the nineteenth century. With it, Gerald ...
... Bigger telescopes enable astronomers to discover new bodies in space. Sir William Herschel built a huge reflecting telescope and discovered the planet Uranus with it in 1773. The largest refracting telescope was built at the Yerkes Observatory near the end of the nineteenth century. With it, Gerald ...
exploring the solar system, the galaxies, and the
... Open the Amazing Space web site at http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/ in preparation for lab activities during which you will find resources to address specific Georgia Performance Standards related to Astronomy for grades 2, 4, and 6. Read these standards below, and select at least two topics for whic ...
... Open the Amazing Space web site at http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/ in preparation for lab activities during which you will find resources to address specific Georgia Performance Standards related to Astronomy for grades 2, 4, and 6. Read these standards below, and select at least two topics for whic ...
The Components and Origin of the Universe
... single raison and so it appears you are sitting still The ...
... single raison and so it appears you are sitting still The ...
Chapter 25 - OG
... Every chemical element produces a unique pattern of dark lines ~ just like a finger print. ** Can also tell energy level Low energy: newer stars emit radio & infrared waves. Higher energy: exploding stars emit ultraviolet & x-rays. ...
... Every chemical element produces a unique pattern of dark lines ~ just like a finger print. ** Can also tell energy level Low energy: newer stars emit radio & infrared waves. Higher energy: exploding stars emit ultraviolet & x-rays. ...
Galaxy and Beyond
... • Falling space rock/particle that emits light as it streaks through • Heated by immense friction through Earth’s atmosphere • Video ...
... • Falling space rock/particle that emits light as it streaks through • Heated by immense friction through Earth’s atmosphere • Video ...
AMUSE-Virgo Super-massive black holes vs. nuclear star clusters: the X-ray view
... X-ray luminosity function of globular clusters + Ultra-luminous X-ray sources in early type galaxies (Chandra+Hubble) ...
... X-ray luminosity function of globular clusters + Ultra-luminous X-ray sources in early type galaxies (Chandra+Hubble) ...
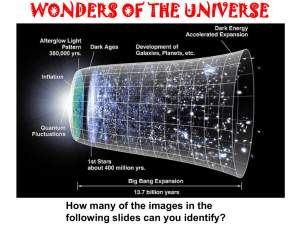
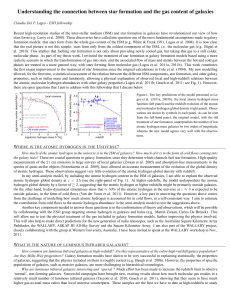
cosmology[1] - KarenConnerEnglishIV
... Although Fred’s theory is probably not correct, he did help us figure out something else extremely important- how elements heavier than helium were created. He also came up with the name- Big Bang. He didn’t mean it nicely. ...
... Although Fred’s theory is probably not correct, he did help us figure out something else extremely important- how elements heavier than helium were created. He also came up with the name- Big Bang. He didn’t mean it nicely. ...
solar system formation and gal
... • Over time it flattens into a disc-like shape while spinning in one direction • Astronomers theorize that any planets forming during this phase would form in the same flat plane and would rotate and revolve around the star in the same way • Using technology, astronomers have discovered flattening n ...
... • Over time it flattens into a disc-like shape while spinning in one direction • Astronomers theorize that any planets forming during this phase would form in the same flat plane and would rotate and revolve around the star in the same way • Using technology, astronomers have discovered flattening n ...
Chapter 25 Beyond Our Solar System
... • White dwarfs are the remains of low-mass and medium-mass stars. • Neutron stars, which are smaller and more massive than white dwarfs, are thought to be the remnants of supernova events. • A spinning neutron star that appears to give off pulses of radio waves is called a pulsar. • Dense objects wi ...
... • White dwarfs are the remains of low-mass and medium-mass stars. • Neutron stars, which are smaller and more massive than white dwarfs, are thought to be the remnants of supernova events. • A spinning neutron star that appears to give off pulses of radio waves is called a pulsar. • Dense objects wi ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.


















![cosmology[1] - KarenConnerEnglishIV](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002375580_1-efbe19cf7c791439d3765f11461d68f5-300x300.png)