UNIT 5 Lecture 16 CONTROL SYSTEMS
... energy to counteract stress. Exhaustion can result from changes during alarm and resistance reactions. If stress causing exhaustion is too great, it may lead to death. Stress and disease Stress can lead to diseases such as gastritis, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, peptic ulcers, hyper ...
... energy to counteract stress. Exhaustion can result from changes during alarm and resistance reactions. If stress causing exhaustion is too great, it may lead to death. Stress and disease Stress can lead to diseases such as gastritis, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, peptic ulcers, hyper ...
The Endocrine System
... • Hormones: Chemical messengers used produces and released by the endocrine system to regulates physiologically processes of the human body. • Release and distributed to work on specific cells (target cells) that respond to there presence. • The hormones of the endocrine system are divided into thre ...
... • Hormones: Chemical messengers used produces and released by the endocrine system to regulates physiologically processes of the human body. • Release and distributed to work on specific cells (target cells) that respond to there presence. • The hormones of the endocrine system are divided into thre ...
Endocrine System
... Endocrine activity of the Adrenal Cortex • Hyper-secretion: Aldosteronism: Hypokalemia, increase in extracellular fluid and blood volume,and hypertension, may also have period of muscular paralysis • Hypo-secretion: Addison’s disease Mineralocorticoids deficiency, death occurs in four days to two w ...
... Endocrine activity of the Adrenal Cortex • Hyper-secretion: Aldosteronism: Hypokalemia, increase in extracellular fluid and blood volume,and hypertension, may also have period of muscular paralysis • Hypo-secretion: Addison’s disease Mineralocorticoids deficiency, death occurs in four days to two w ...
File
... a condition characterized by a visibly enlarged thyroid gland in the neck; overactive thyroid gland hypothyroidism a condition caused by an underachieve thyroid gland insulin resistance a condition common in type II diabetes in which the pancreas secretes insulin, but they body's insulin receptors a ...
... a condition characterized by a visibly enlarged thyroid gland in the neck; overactive thyroid gland hypothyroidism a condition caused by an underachieve thyroid gland insulin resistance a condition common in type II diabetes in which the pancreas secretes insulin, but they body's insulin receptors a ...
Hormone Replacement Therapy– Will it make me gain
... significant number of chronic health problems such as cardiovascular disease and breast cancer to name a few. Menopause in general is associated with a decrease in the resting metabolism that reduces our ability to efficiently burn calories and hence increases body weight. A number of studies have s ...
... significant number of chronic health problems such as cardiovascular disease and breast cancer to name a few. Menopause in general is associated with a decrease in the resting metabolism that reduces our ability to efficiently burn calories and hence increases body weight. A number of studies have s ...
Essentials for Hormone Balance
... Statements with claims have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat or prevent any disease ...
... Statements with claims have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat or prevent any disease ...
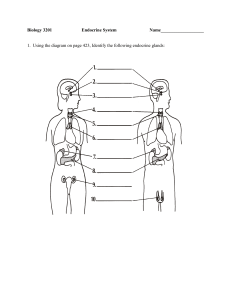
Biology 232
... nervous control – signals from neurons control the secretion of hormones hormonal control – one hormone controls the secretion of another hormone negative feedback – secretion of most hormones is controlled by feedback of its product or a product of its action eg. high blood glucose causes release o ...
... nervous control – signals from neurons control the secretion of hormones hormonal control – one hormone controls the secretion of another hormone negative feedback – secretion of most hormones is controlled by feedback of its product or a product of its action eg. high blood glucose causes release o ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... Accelerates the original process, either to ensure that the pathway continues to run or to speed up its ...
... Accelerates the original process, either to ensure that the pathway continues to run or to speed up its ...
The Endocrine System
... Permissive effect: enhancement of a target organ’s responsiveness to a hormone from prior exposure to a different hormone Synergistic effect: effect of two or more hormones acting on an organ Antagonistic effect: occurs when the effect of one hormone opposes the effect of another on a target organ ...
... Permissive effect: enhancement of a target organ’s responsiveness to a hormone from prior exposure to a different hormone Synergistic effect: effect of two or more hormones acting on an organ Antagonistic effect: occurs when the effect of one hormone opposes the effect of another on a target organ ...
Endocrinology-general physiolofy of hormone, hormonal feed
... = growth hormone-induced “insulin resistance” attenuates insulin’s actions, such as: ...
... = growth hormone-induced “insulin resistance” attenuates insulin’s actions, such as: ...
Endocrine work book
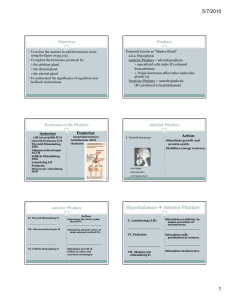
... The pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate the hormone production of many other endocrine glands in the body. Such substances are referred to as tropic hormones. It is referred to as the “master gland” of the endocrine system and is composed of two glands - the anterior and posterior pituit ...
... The pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate the hormone production of many other endocrine glands in the body. Such substances are referred to as tropic hormones. It is referred to as the “master gland” of the endocrine system and is composed of two glands - the anterior and posterior pituit ...
BSC 2086 Class Notes Chapter 16 – Part 1 Summer 2010
... Please name the three corticosteroids produced by the Adrenal Cortex. Mineralocorticoids regulate ___________________ primarily _________ and ____________ in the extracellular fluid (ECF). _________________________ is the most important mineralocorticoid that stimulates Na+ _______________________ a ...
... Please name the three corticosteroids produced by the Adrenal Cortex. Mineralocorticoids regulate ___________________ primarily _________ and ____________ in the extracellular fluid (ECF). _________________________ is the most important mineralocorticoid that stimulates Na+ _______________________ a ...
File
... 2. The ___thyroid gland_____ is located inside the neck and helps to regulate metabolism. 3. This so-called master gland, the ___pituitary gland____, secretes growth hormone, among other things. 4. The ___pineal gland_______ helps to regulate the sleep-wake cycle. 5. ___Hormones________ (from the Gr ...
... 2. The ___thyroid gland_____ is located inside the neck and helps to regulate metabolism. 3. This so-called master gland, the ___pituitary gland____, secretes growth hormone, among other things. 4. The ___pineal gland_______ helps to regulate the sleep-wake cycle. 5. ___Hormones________ (from the Gr ...
Lesson 3 | The Endocrine System
... Directions: In this word search puzzle, find and circle the four terms listed below. Then put the terms that match each definition on the lines provided. ...
... Directions: In this word search puzzle, find and circle the four terms listed below. Then put the terms that match each definition on the lines provided. ...
Typical disorders of the endocrine system 1. Choose the correct
... a) myxedema; + b) diffuse toxic goiter; c) endemic cretinism; d) acromegaly; e) insulinoma. 32. Specify the possible causes of hyperthyroidism + a) the excess of TSH; b) an excess of insulin. 33. Enlargement of the thyroid gland, exophthalmus, increase of basal metabolism and heat production, tachyc ...
... a) myxedema; + b) diffuse toxic goiter; c) endemic cretinism; d) acromegaly; e) insulinoma. 32. Specify the possible causes of hyperthyroidism + a) the excess of TSH; b) an excess of insulin. 33. Enlargement of the thyroid gland, exophthalmus, increase of basal metabolism and heat production, tachyc ...
Endocrine System Notes 1
... Secretion: response to lowered blood calcium levels Hormone: Parathyroid hormone (PTH), nonsteroidal ...
... Secretion: response to lowered blood calcium levels Hormone: Parathyroid hormone (PTH), nonsteroidal ...
Ch 9 Hypothalamus and Pituitary
... Some are purely endocrine glands (ductless) Hormones Anterior ...
... Some are purely endocrine glands (ductless) Hormones Anterior ...
Lecture 25 - The Endocrine System
... homeostatic functions including water balance People with adrenal insufficiency: these stresses can cause hypotension, shock and death: must give glucocorticoids, eg for surgery or if have infection, etc.18 ...
... homeostatic functions including water balance People with adrenal insufficiency: these stresses can cause hypotension, shock and death: must give glucocorticoids, eg for surgery or if have infection, etc.18 ...
The Endocrine System
... Permissive effect: enhancement of a target organ’s responsiveness to a hormone from prior exposure to a different hormone Synergistic effect: effect of two or more hormones acting on an organ Antagonistic effect: occurs when the effect of one hormone opposes the effect of another on a target organ ...
... Permissive effect: enhancement of a target organ’s responsiveness to a hormone from prior exposure to a different hormone Synergistic effect: effect of two or more hormones acting on an organ Antagonistic effect: occurs when the effect of one hormone opposes the effect of another on a target organ ...
Endocrine System
... Hypophysectomy- radiation or surgery to remove all or part of the pituitary ...
... Hypophysectomy- radiation or surgery to remove all or part of the pituitary ...
The Endocrine System - respiratorytherapyfiles.net
... Glucagon: promotes movement of glucose into the blood by breaking down glycogen stored in liver cells ...
... Glucagon: promotes movement of glucose into the blood by breaking down glycogen stored in liver cells ...
releasing hormones
... • Nonsteroid Hormones • Usually proteins or peptides that are not fat soluble • Relies on two messengers to produce an effect • First messenger (hormone) binds to the plasma membrane • Binding triggers the release of membrane enzymes that lead to cAMP (second messenger) formation • cAMP activates ...
... • Nonsteroid Hormones • Usually proteins or peptides that are not fat soluble • Relies on two messengers to produce an effect • First messenger (hormone) binds to the plasma membrane • Binding triggers the release of membrane enzymes that lead to cAMP (second messenger) formation • cAMP activates ...