History of the Atom - Oak Park Unified School District
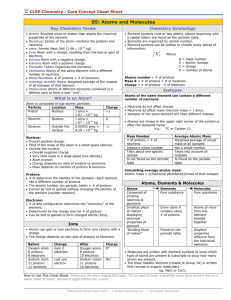
... > Mass of 1.0073 amu (2000x bigger than electron) > Atomic number: (Z) # of protons in nucleus, identifies elements • Neutron: neutral particle found in the nucleus > Mass of 1.0087 amu (about the same as a proton) > Number of neutrons determines isotopes ...
... > Mass of 1.0073 amu (2000x bigger than electron) > Atomic number: (Z) # of protons in nucleus, identifies elements • Neutron: neutral particle found in the nucleus > Mass of 1.0087 amu (about the same as a proton) > Number of neutrons determines isotopes ...
Matter and Atoms - davis.k12.ut.us
... element is made up of one kind of atom. Atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still have the properties of that element. Molecule is two or more atoms put together that still have the properties of a particular substance. ...
... element is made up of one kind of atom. Atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still have the properties of that element. Molecule is two or more atoms put together that still have the properties of a particular substance. ...
CHEMISTRY FALL FINAL PRACTICE 2016
... a. Get the atomic number _________ b. Identify the element __________________ c. Find the mass number of the most common isotope of an element _________ d. Get how many neutrons the most common isotope has _________ e. How many valence electrons an element has _________ f. What is its charge/oxidati ...
... a. Get the atomic number _________ b. Identify the element __________________ c. Find the mass number of the most common isotope of an element _________ d. Get how many neutrons the most common isotope has _________ e. How many valence electrons an element has _________ f. What is its charge/oxidati ...
chemistry i - surrattchemistry
... nucleuselectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus b. The atom is a hard sphereelectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleusmost of the atom is empty space with a small dense nucleus. c. Most of the atom is empty space with a small, dense nucleuselectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucl ...
... nucleuselectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus b. The atom is a hard sphereelectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleusmost of the atom is empty space with a small dense nucleus. c. Most of the atom is empty space with a small, dense nucleuselectrons exist in orbitals outside the nucl ...
The Periodic Table
... development of the Periodic Table. Objective: use the Periodic Table to identify and explain periodic trends, including atomic and ionic radii, electronegativity, and ionization energy. ...
... development of the Periodic Table. Objective: use the Periodic Table to identify and explain periodic trends, including atomic and ionic radii, electronegativity, and ionization energy. ...
The Periodic Table HL Page 1 of 3 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... -derive the electronic configurations of ions of s- and p-block elements only -describe the arrangement of electrons in individual orbitals of p-block atoms ...
... -derive the electronic configurations of ions of s- and p-block elements only -describe the arrangement of electrons in individual orbitals of p-block atoms ...
Atomic Structure PPT
... configurations so different levels of bonding 2) Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer most shell. 3) Valence electrons are important because they affect how the element reacts with other elements. ...
... configurations so different levels of bonding 2) Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer most shell. 3) Valence electrons are important because they affect how the element reacts with other elements. ...
2010 Physical Science Comprehensive Test REVIEW Ch 0.3 Sig
... 38. Be able to identify the atomic number, mass number, and stable isotopes. Your periodic table will not have a key on it. Such as: What is the atomic number of phosphorus? Such as: What is the mass number of K-41? Such as: K-41 is stable, but K-40 is not 42. Many models have been developed to expl ...
... 38. Be able to identify the atomic number, mass number, and stable isotopes. Your periodic table will not have a key on it. Such as: What is the atomic number of phosphorus? Such as: What is the mass number of K-41? Such as: K-41 is stable, but K-40 is not 42. Many models have been developed to expl ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Metalloid – A metalloid is any chemical element which has properties in between those of metals and nonmetals, or that has a mixture of them. Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical comb ...
... Metalloid – A metalloid is any chemical element which has properties in between those of metals and nonmetals, or that has a mixture of them. Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical comb ...
Introduction to atoms
... • Democritus (ancient Greek) -- (atomos); indivisible particle of a ...
... • Democritus (ancient Greek) -- (atomos); indivisible particle of a ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Metalloid – A metalloid is any chemical element which has properties in between those of metals and nonmetals, or that has a mixture of them. Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical comb ...
... Metalloid – A metalloid is any chemical element which has properties in between those of metals and nonmetals, or that has a mixture of them. Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical comb ...
O 2 (g)
... • Consider the three metals Li, Na, and K – All 3 metals are soft – All 3 metals are less dense than water – All 3 metals have similar appearance and low melting points – The most interesting feature is that all 3 metals react with the same elements in a nearly identical manner • As you see in the p ...
... • Consider the three metals Li, Na, and K – All 3 metals are soft – All 3 metals are less dense than water – All 3 metals have similar appearance and low melting points – The most interesting feature is that all 3 metals react with the same elements in a nearly identical manner • As you see in the p ...
05: Atoms and Molecules
... • Atom: Smallest piece of matter that retains the chemical properties of the element. • Nucleus: Center of the atom—contains the protons and neutrons. • amu: Atomic Mass Unit (1.66 × 10-27 kg) • Ion: Atom with a charge, resulting from the loss or gain of electrons. • Anion: Atom with a negative char ...
... • Atom: Smallest piece of matter that retains the chemical properties of the element. • Nucleus: Center of the atom—contains the protons and neutrons. • amu: Atomic Mass Unit (1.66 × 10-27 kg) • Ion: Atom with a charge, resulting from the loss or gain of electrons. • Anion: Atom with a negative char ...
Topic 1 - Periodic Table
... has a different number of neutrons. Some isotopes are radioactive; many are not. Half-life is the length of time required for half of a given sample of a radioactivy isotope to decay Electrons have little mass and a negative charge. They are located in electron clouds or probability clouds outside t ...
... has a different number of neutrons. Some isotopes are radioactive; many are not. Half-life is the length of time required for half of a given sample of a radioactivy isotope to decay Electrons have little mass and a negative charge. They are located in electron clouds or probability clouds outside t ...
NAME - Partners4results
... ____ 23. The atomic mass of an atom of carbon is 12, and the atomic mass of an atom of oxygen is 16. To produce CO, 16g of oxygen can be combined with 12g of carbon. According to the Law of Multiple Proportions, the ratio of oxygen to carbon when 32g of oxygen combine with 12g of carbon is a. 1:1 b. ...
... ____ 23. The atomic mass of an atom of carbon is 12, and the atomic mass of an atom of oxygen is 16. To produce CO, 16g of oxygen can be combined with 12g of carbon. According to the Law of Multiple Proportions, the ratio of oxygen to carbon when 32g of oxygen combine with 12g of carbon is a. 1:1 b. ...
Chapter 8 and 10: Structure of the Atom
... 4. What specific information did Thompson include in his model of the atom that was different from Dalton? 5. Describe Millikan’s oil-drop experiment, the observations he made and the inductive reasoning he used to further the developing model of the atom. 6. Describe Rutherford’s gold foil experime ...
... 4. What specific information did Thompson include in his model of the atom that was different from Dalton? 5. Describe Millikan’s oil-drop experiment, the observations he made and the inductive reasoning he used to further the developing model of the atom. 6. Describe Rutherford’s gold foil experime ...
File - Ms. Gutierrez`s Chemistry Website
... • Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. • The atoms of each element differ from the atom of the element before it by one proton. • In atoms that are electrically neutral, atomic number also is the number of electrons. ...
... • Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. • The atoms of each element differ from the atom of the element before it by one proton. • In atoms that are electrically neutral, atomic number also is the number of electrons. ...
Topic 7. 1 Atomic Structure
... Rutherford’s model didn’t explain why atoms emitted or absorbed only light at certain wavelengths. 1885 JJ Balmer showed that hydrogen’s four emission lines fit a mathematical formula. This “Balmer series” also show the pattern continued into non-visible ultra-violet and infra-red. Bohr call ...
... Rutherford’s model didn’t explain why atoms emitted or absorbed only light at certain wavelengths. 1885 JJ Balmer showed that hydrogen’s four emission lines fit a mathematical formula. This “Balmer series” also show the pattern continued into non-visible ultra-violet and infra-red. Bohr call ...
Semester Exam Review Guide
... 18. Which of the statement about the periodic table is true: a. elements are arranged by atomic number. b. metallic elements are placed on the right-hand side. c. elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. d. both a and c. 19. __________ brought back the concept of the ato ...
... 18. Which of the statement about the periodic table is true: a. elements are arranged by atomic number. b. metallic elements are placed on the right-hand side. c. elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. d. both a and c. 19. __________ brought back the concept of the ato ...
Greek philosophers (300 BC)
... Why e-s (usually) don’t fly off of atoms: they have enough attraction to the nucleus to keep them in “orbit.” (Kind of like planets in orbit around the sun.) ...
... Why e-s (usually) don’t fly off of atoms: they have enough attraction to the nucleus to keep them in “orbit.” (Kind of like planets in orbit around the sun.) ...
atoms
... foil which was only a few atoms thick. They found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit. ...
... foil which was only a few atoms thick. They found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit. ...
Physical and Chemical Properties
... • Compounds are substances that form when two or more elements combine from a chemical change. • Ex. NaCl (Sodium Chloride) • The properties of compounds are different from the properties of the elements that make up the compound • A molecule is the smallest particle of a substance with the same pro ...
... • Compounds are substances that form when two or more elements combine from a chemical change. • Ex. NaCl (Sodium Chloride) • The properties of compounds are different from the properties of the elements that make up the compound • A molecule is the smallest particle of a substance with the same pro ...
History of the Atomic Model
... Element Block from periodic table • 17 ---- atomic number Cl ---- Symbol Chlorine –Name 35.45 --- atomic mass or mass number ...
... Element Block from periodic table • 17 ---- atomic number Cl ---- Symbol Chlorine –Name 35.45 --- atomic mass or mass number ...