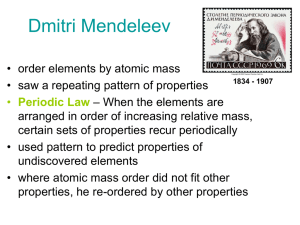
Dmitri Mendeleev
... Naturally occurring neon contains three different isotopes: Ne-20 (with 10 protons and 10 neutrons), Ne-21 (with 10 protons and 11 neutrons), and Ne-22 (with 10 protons and 12 neutrons). ...
... Naturally occurring neon contains three different isotopes: Ne-20 (with 10 protons and 10 neutrons), Ne-21 (with 10 protons and 11 neutrons), and Ne-22 (with 10 protons and 12 neutrons). ...
Ch. 4 Slides
... system) does each of the following elements belong? If the group has a name, indicate that as well. ...
... system) does each of the following elements belong? If the group has a name, indicate that as well. ...
Getting to Know: Periodic Table
... element do not have the same number of neutrons. For example, most atoms of the element carbon, C, have 6 neutrons in their nucleus. There are some atoms of carbon that have 7 or even 8 neutrons in their nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
... element do not have the same number of neutrons. For example, most atoms of the element carbon, C, have 6 neutrons in their nucleus. There are some atoms of carbon that have 7 or even 8 neutrons in their nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. ...
atomic number - geraldinescience
... • The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. • All atoms of any given element have the same atomic number. An element’s atomic number sets the atoms of that element apart from the atoms of all other elements. • Elements on the periodic table are ordered according to ...
... • The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. • All atoms of any given element have the same atomic number. An element’s atomic number sets the atoms of that element apart from the atoms of all other elements. • Elements on the periodic table are ordered according to ...
Pre-AP Chemistry
... Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. (1a) Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. (1e) Students know some naturally occurring isotopes of elements are radioa ...
... Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. (1a) Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. (1e) Students know some naturally occurring isotopes of elements are radioa ...
Isotope
... 5. How many protons do I have (in the isotope)? 6. How many neutrons do I have (in isotope)? 7. How many electrons do I have if I am neutral(in isotope)? 8. (Pick an ion of the right side of the card) How many protons and electrons do I have? 9. (Consider that I am the previous chosen isotope in que ...
... 5. How many protons do I have (in the isotope)? 6. How many neutrons do I have (in isotope)? 7. How many electrons do I have if I am neutral(in isotope)? 8. (Pick an ion of the right side of the card) How many protons and electrons do I have? 9. (Consider that I am the previous chosen isotope in que ...
Unit 2 Notes Atomic
... Electrons travel around the nucleus in welldefined paths called ___________ (like planets in a solar system). ! Electrons in different orbits have different amounts of _____________. ! The further from the nucleus, the more __________ an electron has. ...
... Electrons travel around the nucleus in welldefined paths called ___________ (like planets in a solar system). ! Electrons in different orbits have different amounts of _____________. ! The further from the nucleus, the more __________ an electron has. ...
Miss Turner`s Chemistry Notes – Foundation Chemistry – Atomic
... Electrons - Electrons are tiny electrically charged particles. They have a negative charge, very little mass and they exist in the empty space surrounding the nucleus of the atom, which contains all the other particles. In their elemental states, atoms are not charged, and will have the same number ...
... Electrons - Electrons are tiny electrically charged particles. They have a negative charge, very little mass and they exist in the empty space surrounding the nucleus of the atom, which contains all the other particles. In their elemental states, atoms are not charged, and will have the same number ...
build your own atom - brittany
... 2. To be very simple today, we are making a neutrally charged atom, so we will be using equal amounts of protons, neutrons and electrons. Previous art projects have depleted our pom-pom supply, so the two examples we show will have very small atomic numbers. 3. The wire represents the electron path. ...
... 2. To be very simple today, we are making a neutrally charged atom, so we will be using equal amounts of protons, neutrons and electrons. Previous art projects have depleted our pom-pom supply, so the two examples we show will have very small atomic numbers. 3. The wire represents the electron path. ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND MOLECULAR BONDING
... Atoms and molecules are small. If a bb was an atom and a marble was a small molecule then you would be the size of North America! Atoms (and molecules, atoms bonded together by their electrons) are about 10-10 meters. But what do they look like? Although we’ll never actually see them, the structure ...
... Atoms and molecules are small. If a bb was an atom and a marble was a small molecule then you would be the size of North America! Atoms (and molecules, atoms bonded together by their electrons) are about 10-10 meters. But what do they look like? Although we’ll never actually see them, the structure ...
Teaching notes - Teachit Science
... A substance that cannot be split into another by any chemical means. (7) ...
... A substance that cannot be split into another by any chemical means. (7) ...
9.3 Atoms and Elements notes
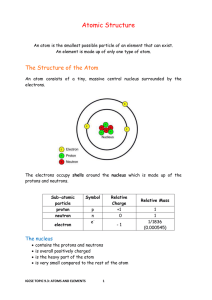
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
... number of electrons in an atom = number of protons Electrons are arranged in energy levels (also known as shells) around the nucleus. The lowest energy levels are always filled first. These are closer to the nucleus and hold the least numbers of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 el ...
The Atom - TeacherWeb
... Neutrons maintain stability. If you change the number of neutrons, you have an ISOTOPE. ...
... Neutrons maintain stability. If you change the number of neutrons, you have an ISOTOPE. ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE Text Book Chapters 2, 4, 5 OBJECTIVES
... dense nucleus separated from electrons located outside The difference is that Electrons do not stay in definite fixed orbits – rather they are probably found in a region around the nucleus called an _________________ Picture of current model: ...
... dense nucleus separated from electrons located outside The difference is that Electrons do not stay in definite fixed orbits – rather they are probably found in a region around the nucleus called an _________________ Picture of current model: ...
chpt 11 and 12 notes with answers
... ◦ Plum-Pudding Model: electrons are located all around an atom ...
... ◦ Plum-Pudding Model: electrons are located all around an atom ...
8b Isotopes and Ions2
... What happens if the number of neutrons change??? If an atom gains neutrons… 1. The mass increases by 1 for every neutron added. 2. The number of protons and electrons stay the same. 3. The charge remains neutral. (Neutrons don’t have a charge.) 4. The identity of the atom does not change ...
... What happens if the number of neutrons change??? If an atom gains neutrons… 1. The mass increases by 1 for every neutron added. 2. The number of protons and electrons stay the same. 3. The charge remains neutral. (Neutrons don’t have a charge.) 4. The identity of the atom does not change ...
Ch. 5 notes
... particles called atoms (atomos) ‘indivisible’ – Hypothesized without using experiments ...
... particles called atoms (atomos) ‘indivisible’ – Hypothesized without using experiments ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... particular orbital an electron has the same energy, regardless how far from the nucleus it happens to be. Things to remember about orbitals: Orbitals have defined shape and size Electron in an particular orbital has the same energy regardless where within the orbital it is “found” Orbitals of ...
... particular orbital an electron has the same energy, regardless how far from the nucleus it happens to be. Things to remember about orbitals: Orbitals have defined shape and size Electron in an particular orbital has the same energy regardless where within the orbital it is “found” Orbitals of ...
Chapter 3 - mrgoosby
... Name 5 things that are matter and five things that are not matter What is the difference between atomic mass and atomic number? Name and describe the Isotopes of ...
... Name 5 things that are matter and five things that are not matter What is the difference between atomic mass and atomic number? Name and describe the Isotopes of ...
PPT - kimscience.com
... All atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties; they differ from atoms of every other element Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds (can form more than one compound together) Chemical reactions consist of the comb ...
... All atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties; they differ from atoms of every other element Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds (can form more than one compound together) Chemical reactions consist of the comb ...