Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties. A periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element (or a group of elements) to another element (or group of elements). Each horizontal row of the periodic table is called a perio ...
... elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties. A periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element (or a group of elements) to another element (or group of elements). Each horizontal row of the periodic table is called a perio ...
4.1Atoms and Isotopes
... Carbon has three isotopes: C-12 (most abundant), C-13 (used in medical imagingMRI), and C-14 (used for dating fossils) Tin (Sn) has the most isotopes of any element at 10 Many isotopes are radioactive (unstable nucleus that will eventually break apart and release energy in sometimes harmful forms – ...
... Carbon has three isotopes: C-12 (most abundant), C-13 (used in medical imagingMRI), and C-14 (used for dating fossils) Tin (Sn) has the most isotopes of any element at 10 Many isotopes are radioactive (unstable nucleus that will eventually break apart and release energy in sometimes harmful forms – ...
Discussion Notes (cont.)
... Nucleus: The dense, positively charged structure found in the center of the atom. It is composed of protons and neutrons. Proton: A particle with a positive charge, found in the nucleus of atoms. Electron: A particle with a negative charge. Electrons move very fast around the outside of the nucleus ...
... Nucleus: The dense, positively charged structure found in the center of the atom. It is composed of protons and neutrons. Proton: A particle with a positive charge, found in the nucleus of atoms. Electron: A particle with a negative charge. Electrons move very fast around the outside of the nucleus ...
LBC1_Sec3_Unit01_Alchemy
... Nucleus: The dense, positively charged structure found in the center of the atom. It is composed of protons and neutrons. Proton: A particle with a positive charge, found in the nucleus of atoms. Electron: A particle with a negative charge. Electrons move very fast around the outside of the nucleus ...
... Nucleus: The dense, positively charged structure found in the center of the atom. It is composed of protons and neutrons. Proton: A particle with a positive charge, found in the nucleus of atoms. Electron: A particle with a negative charge. Electrons move very fast around the outside of the nucleus ...
File - docstover.org
... Write out the electron distribution for the elementPhosphorus according to Hund’s rule. Use arrows to represent electrons. 1s2 ____ 2s2 _____ 2p6 _____ _____ ____ 3s2 _____ 3p6 _____ _____ _____ Write the electron configuration for the following elements: Calcium Iodine Vandium Emission (or brig ...
... Write out the electron distribution for the elementPhosphorus according to Hund’s rule. Use arrows to represent electrons. 1s2 ____ 2s2 _____ 2p6 _____ _____ ____ 3s2 _____ 3p6 _____ _____ _____ Write the electron configuration for the following elements: Calcium Iodine Vandium Emission (or brig ...
1 - WordPress.com
... Use the following data table on the isotopes of element “X” to answer Questions A&B listed below: ...
... Use the following data table on the isotopes of element “X” to answer Questions A&B listed below: ...
The Modern Theory of Atomic Structure
... If a single element is subjected to a high voltage, it has a spectrum too, but it is different! ...
... If a single element is subjected to a high voltage, it has a spectrum too, but it is different! ...
Carbon Isotopes
... The mass of an atom is mainly in the nucleus. Protons and neutrons have an approximately equal mass of one atomic mass unit. Electrons have negligible mass. Therefore, the mass of an atom is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. This number is called the atomic mass number of the a ...
... The mass of an atom is mainly in the nucleus. Protons and neutrons have an approximately equal mass of one atomic mass unit. Electrons have negligible mass. Therefore, the mass of an atom is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. This number is called the atomic mass number of the a ...
Unit 2 -- Atomic Structure, Periodic Table, and
... Semi-Metals (metalloids) • Divides metals from nonmetals • properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals • Ex: Si, Ge, ... • “stair case” on right Side of periodic table ...
... Semi-Metals (metalloids) • Divides metals from nonmetals • properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals • Ex: Si, Ge, ... • “stair case” on right Side of periodic table ...
2 periodic table pd9
... protons increases necessarily have a larger atomic radius and outermost energy level stays the same, the attractive force between elecs. and pros. pulls the atom tighter (closer to nucleus) ...
... protons increases necessarily have a larger atomic radius and outermost energy level stays the same, the attractive force between elecs. and pros. pulls the atom tighter (closer to nucleus) ...
8th Grade Chapter 3 Study Guide
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ...
... Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ ...
Yr11 Chemistry Title Page:TourismContents
... Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple (whole number) ratios to form compounds. ...
... Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple (whole number) ratios to form compounds. ...
Problem Set 4
... how they change, what changes about them and how humans have tried to understand and organize nature. 29) Why do you think we are starting with the history of the atom? Again answers will vary, but the historical evidence allows you a perspective of how humans have improved what we understand to be ...
... how they change, what changes about them and how humans have tried to understand and organize nature. 29) Why do you think we are starting with the history of the atom? Again answers will vary, but the historical evidence allows you a perspective of how humans have improved what we understand to be ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
ScienceHelpNotes-UnitB3 - JA Williams High School
... One of the most common examples of covalently bonded molecular compound is water, H O . Table sugar, ...
... One of the most common examples of covalently bonded molecular compound is water, H O . Table sugar, ...
Atomic Structure Notes Blank
... c. Very dense (Extremely small % of total volume of atom, BUT 99.97% of its _________) 2. Outside nucleus a. 99.9% of atom is this empty space through which the _____________ travel. b. Overall __________________ charge C. How they fit together 1. Electrons are held within the atom due to their attr ...
... c. Very dense (Extremely small % of total volume of atom, BUT 99.97% of its _________) 2. Outside nucleus a. 99.9% of atom is this empty space through which the _____________ travel. b. Overall __________________ charge C. How they fit together 1. Electrons are held within the atom due to their attr ...
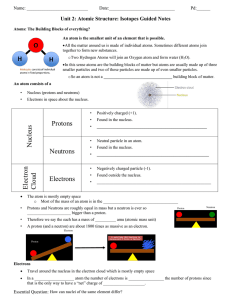
Nucleus Protons Neutrons Electron Cloud Electrons
... An atom is the smallest unit of an element that is possible. All the matter around us is made of individual atoms. Sometimes different atoms join together to form new substances. o Two Hydrogen Atoms will join an Oxygen atom and form water (H2O). In this sense atoms are the building blocks of ma ...
... An atom is the smallest unit of an element that is possible. All the matter around us is made of individual atoms. Sometimes different atoms join together to form new substances. o Two Hydrogen Atoms will join an Oxygen atom and form water (H2O). In this sense atoms are the building blocks of ma ...
Makeup of Atoms - chemmybear.com
... • the nucleus is tiny - because most of the alpha’s missed the nucleus and went straight through the foil • the nucleus is positively charged - because the (+) charged alpha was repelled by the (+) charged nucleus • the nucleus is incredibly dense - because the nucleus was able to bounce back at a v ...
... • the nucleus is tiny - because most of the alpha’s missed the nucleus and went straight through the foil • the nucleus is positively charged - because the (+) charged alpha was repelled by the (+) charged nucleus • the nucleus is incredibly dense - because the nucleus was able to bounce back at a v ...
PROFESSIONAL LEARNING COMMUNITY MODEL FOR ENTRY
... periodic table. Mendeleev overcame sickness and strife in his youth to become a professor at Saint Petersburg State University. After becoming a teacher, he wrote the Principles of Chemistry (18681870). "By attempting to classify the elements according to their chemical properties, he noticed patter ...
... periodic table. Mendeleev overcame sickness and strife in his youth to become a professor at Saint Petersburg State University. After becoming a teacher, he wrote the Principles of Chemistry (18681870). "By attempting to classify the elements according to their chemical properties, he noticed patter ...
Chapter 10 - Department Of Computer Science
... An element is defined as a substance in which all the atoms have the same number of protons The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element The atomic number also represents the number of electrons in a neutral atom ...
... An element is defined as a substance in which all the atoms have the same number of protons The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element The atomic number also represents the number of electrons in a neutral atom ...
A Guided Tour of the Periodic Table
... within energy levels. (s, p, d, and f ) ▫a region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons. ...
... within energy levels. (s, p, d, and f ) ▫a region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons. ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... Name: _________________________________ Period: ____ Date: ___ / ___ / ___ ...
... Name: _________________________________ Period: ____ Date: ___ / ___ / ___ ...
Introduction to Atoms - Mother Teresa Regional School
... Electrons move rapidly around the nucleus and have a negative electric charge. ...
... Electrons move rapidly around the nucleus and have a negative electric charge. ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents
... 4. Spontaneous decay can involve the release of different particles from the nucleus. The types of particles, as well as their masses and charges, can be found on Table O. 5. Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial decay, nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. Nuclear fission occurs when t ...
... 4. Spontaneous decay can involve the release of different particles from the nucleus. The types of particles, as well as their masses and charges, can be found on Table O. 5. Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial decay, nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. Nuclear fission occurs when t ...