Algebra 2
... If any vertical line passes through two or more points on the graph of a relation, then it does not define a function. If any horizontal line passes through two or more points on the graph of a relation, then its inverse does not define a function. a function where each range element has a unique do ...
... If any vertical line passes through two or more points on the graph of a relation, then it does not define a function. If any horizontal line passes through two or more points on the graph of a relation, then its inverse does not define a function. a function where each range element has a unique do ...
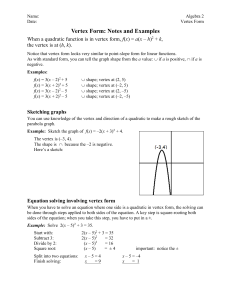
Vertex Form
... 2. Below are several quadratic functions written in vertex form. Without using your calculator, sketch a graph for each function, and label the vertex with its coordinates. (See the previous page for an example.) a. f(x) = 2(x – 1)2 + 3 ...
... 2. Below are several quadratic functions written in vertex form. Without using your calculator, sketch a graph for each function, and label the vertex with its coordinates. (See the previous page for an example.) a. f(x) = 2(x – 1)2 + 3 ...
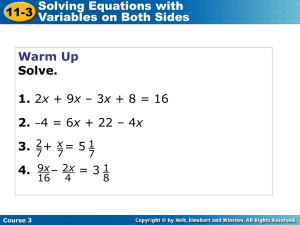
Course 3
... variables on both sides of the equal sign. Solving an equation with variables on both sides is similar to solving an equation with a variable on only one side. You can add or subtract a term containing a variable on both sides of an equation. ...
... variables on both sides of the equal sign. Solving an equation with variables on both sides is similar to solving an equation with a variable on only one side. You can add or subtract a term containing a variable on both sides of an equation. ...
9-1 Quadratic Equations & Functions
... Unless a specific domain is given, the domain of a quadratic function is all real numbers. One way to find the range of a quadratic function is by looking at its graph. For the graph of y = x2 – 4x + 5, the range begins at the minimum value of the function, where y = 1. All y-values greater than or ...
... Unless a specific domain is given, the domain of a quadratic function is all real numbers. One way to find the range of a quadratic function is by looking at its graph. For the graph of y = x2 – 4x + 5, the range begins at the minimum value of the function, where y = 1. All y-values greater than or ...
CalcWSInvFunctions WS 8
... 1. a. Sketch the graph of y e x . State its domain and range. b. Sketch the inverse onto the same axes. c. Solve algebraically for the inverse of y e x . d. Graph both the function and inverse on the TI-Nspire and examine the symmetry to check that it is in fact the equation of the inverse. ...
... 1. a. Sketch the graph of y e x . State its domain and range. b. Sketch the inverse onto the same axes. c. Solve algebraically for the inverse of y e x . d. Graph both the function and inverse on the TI-Nspire and examine the symmetry to check that it is in fact the equation of the inverse. ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.