fourth and final quiz
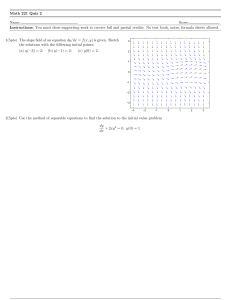
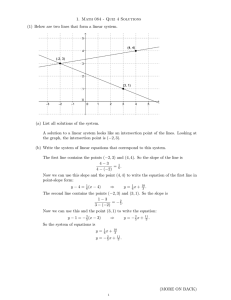
... 1. Math 084 - Quiz 4 Solutions (1) Below are two lines that form a linear system. ...
... 1. Math 084 - Quiz 4 Solutions (1) Below are two lines that form a linear system. ...
Name________________________ Student I.D.___________________ Math 2250−1 Quiz 7
... 1c) Use your work in (1a) to solve the initial value problem y 5 y 6 y=0 y 0 = 1 y 0 =4 . (3 points) y x = c1 e ...
... 1c) Use your work in (1a) to solve the initial value problem y 5 y 6 y=0 y 0 = 1 y 0 =4 . (3 points) y x = c1 e ...
test one
... S(t) when 0 ≤ t < 100, and solve it. (b) After the first 100 seconds, the tank overflows. Write a differential equation for S(t) for t ≥ 100, and solve it. ...
... S(t) when 0 ≤ t < 100, and solve it. (b) After the first 100 seconds, the tank overflows. Write a differential equation for S(t) for t ≥ 100, and solve it. ...
Mon, Mar 17
... A differential equation is an equation which contains derivatives within it. More specifically, it is an equation which may contain an independent variable x (or t) and/or a dependent variable y (or some other variable name), but definitely contains a derivative y ' = dy/dx (or dy/dt). It may also c ...
... A differential equation is an equation which contains derivatives within it. More specifically, it is an equation which may contain an independent variable x (or t) and/or a dependent variable y (or some other variable name), but definitely contains a derivative y ' = dy/dx (or dy/dt). It may also c ...
x,
... Using the method of reduction of order, find another linear independent solution. 2. Using Laplace transform solve the boundary value problem y"- 2yf+ y(x) = x, ...
... Using the method of reduction of order, find another linear independent solution. 2. Using Laplace transform solve the boundary value problem y"- 2yf+ y(x) = x, ...
Math 2250-10 Quiz 2 SOLUTIONS January 17, 2014
... Since y t is differentiable it's also continuous, so y t K 4 also is - and is never zero. Thus y K 4 = CeK2 x C ...
... Since y t is differentiable it's also continuous, so y t K 4 also is - and is never zero. Thus y K 4 = CeK2 x C ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.