elimination method
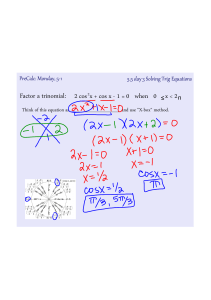
... * Tip - When there are fractions in the equations, clear the fractions first! When to use which method????? Graph: to approximate a solution, check a solution or show visual. Substitution or combination: for exact solutions. Substitution: when one variable has 1 or –1 for the coefficient. Combinati ...
... * Tip - When there are fractions in the equations, clear the fractions first! When to use which method????? Graph: to approximate a solution, check a solution or show visual. Substitution or combination: for exact solutions. Substitution: when one variable has 1 or –1 for the coefficient. Combinati ...
Math 11 - BigEngine
... Section 5.1: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by GRAPHING When you are asked to solve a system of equations, you are being asked to determine all the ordered pairs (x, y) that satisfy EACH equation in the system. For example: Is (5, -2) a solution to either of the following systems? a) ...
... Section 5.1: Solving Systems of Linear Equations by GRAPHING When you are asked to solve a system of equations, you are being asked to determine all the ordered pairs (x, y) that satisfy EACH equation in the system. For example: Is (5, -2) a solution to either of the following systems? a) ...
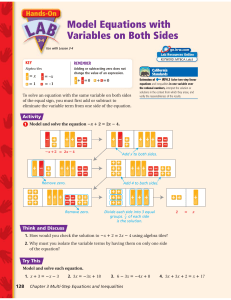
Lesson 12-2 Check Your Understanding ACTIVITY 12
... 15. Attend to precision. In Lesson 12-1, Item 8, you wrote an equation for this situation: Brynn needs to save $125 to build a doghouse for her new puppy. She has saved $68. How much more does she need to save? Now use this set of possible solutions and substitution to solve the equation. ...
... 15. Attend to precision. In Lesson 12-1, Item 8, you wrote an equation for this situation: Brynn needs to save $125 to build a doghouse for her new puppy. She has saved $68. How much more does she need to save? Now use this set of possible solutions and substitution to solve the equation. ...
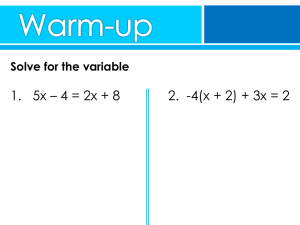
Name___________________________________________ Date_________________________ Algebra I – Pd ____ Complex Equations
... Name___________________________________________ Date_________________________ Algebra I – Pd ____ Complex Equations 2A ...
... Name___________________________________________ Date_________________________ Algebra I – Pd ____ Complex Equations 2A ...
Ph.D. QUALIFYING EXAM DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Spring II, 2009
... (b) Use (a) to write down a general solution u = u(x, y, a, b). (Hint: Use the fact that the PDE is invariant under rotations in the xy) (c) Find the solution of the PDE satisfying the condition u(x, x) = 2. 4. Let B+ = {(x,y) I x~ +Y~ < 1,y > 0} be the open half disk. Suppose u(x, y) ~ C~ ( B+ ) ~ ...
... (b) Use (a) to write down a general solution u = u(x, y, a, b). (Hint: Use the fact that the PDE is invariant under rotations in the xy) (c) Find the solution of the PDE satisfying the condition u(x, x) = 2. 4. Let B+ = {(x,y) I x~ +Y~ < 1,y > 0} be the open half disk. Suppose u(x, y) ~ C~ ( B+ ) ~ ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.