q8sol.pdf
... Show all work. How you get your answer is just as important, if not more important, than the answer itself. If you think it, write it! Find the general solution to the system of equations x0 = 3x − y y 0 = 2x + y ...
... Show all work. How you get your answer is just as important, if not more important, than the answer itself. If you think it, write it! Find the general solution to the system of equations x0 = 3x − y y 0 = 2x + y ...
Supplementary Information
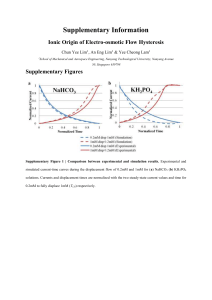
... Zeta potential ζ of the experimental solutions were measured via the current monitoring technique (see Fig. 7 in main article). For the case of 1mM potassium chloride (KCl), the microcapillary and reservoir connecting to the cathode were filled with 1mM KCl while the reservoir connecting to the anod ...
... Zeta potential ζ of the experimental solutions were measured via the current monitoring technique (see Fig. 7 in main article). For the case of 1mM potassium chloride (KCl), the microcapillary and reservoir connecting to the cathode were filled with 1mM KCl while the reservoir connecting to the anod ...
Muthuvel, R.
... Calculator: TI-83 or TI-84 Graphics Calculator is required. (If you already have a TI-85 or TI-86, you do not need to buy a TI-83 or TI-84.) TI-89 and TI-92 will not be allowed on exams and quizzes. Bring your calculator to class every day. Course Description: In this course, we will cover topics in ...
... Calculator: TI-83 or TI-84 Graphics Calculator is required. (If you already have a TI-85 or TI-86, you do not need to buy a TI-83 or TI-84.) TI-89 and TI-92 will not be allowed on exams and quizzes. Bring your calculator to class every day. Course Description: In this course, we will cover topics in ...
Two-Year Algebra 2 A Semester Exam Review 2015–2016
... There are four functions represented by tables below. They are either exponential or logarithmic. For each table, write a function equation. ...
... There are four functions represented by tables below. They are either exponential or logarithmic. For each table, write a function equation. ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.