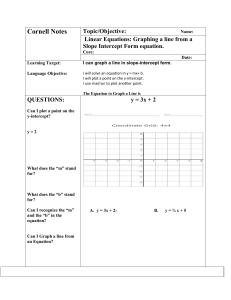
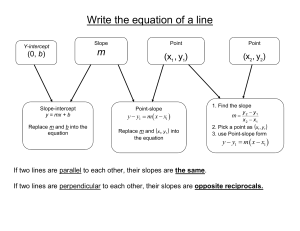
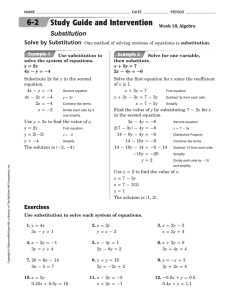
Class 7 - shilepsky.net
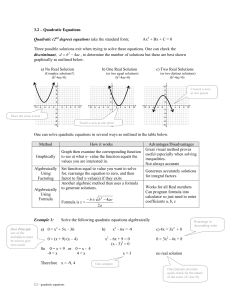
... Zero-Factor Property: If a and b are real numbers and ab=0, then a=0 or b=0 or both equal zero. Example: Solve the equation (2x-3)(x+5) = 0. By the Zero-Factor property either 2x-3 or x+5 must be 0. If 2x-3=0 then 2x=3 and x=2/3. If x+5=0 then x=-5. Therefore, the solutions are 2/3 and -5. We might ...
... Zero-Factor Property: If a and b are real numbers and ab=0, then a=0 or b=0 or both equal zero. Example: Solve the equation (2x-3)(x+5) = 0. By the Zero-Factor property either 2x-3 or x+5 must be 0. If 2x-3=0 then 2x=3 and x=2/3. If x+5=0 then x=-5. Therefore, the solutions are 2/3 and -5. We might ...
Full text
... If we had chosen a r b i t r a r y initial conditions for the B. T s, then the numerator (1) on the lefthand side would have been replaced by some polynomial entailing a further calculation subsequently. This procedure is analogous to solving linear non-homogeneous differential equations. One first ...
... If we had chosen a r b i t r a r y initial conditions for the B. T s, then the numerator (1) on the lefthand side would have been replaced by some polynomial entailing a further calculation subsequently. This procedure is analogous to solving linear non-homogeneous differential equations. One first ...
Hw2.pdf
... a.- Obtain, plot and tabulate the exact solution of the problem. b.- Use the method of finite differences with central diferences throughout to obtain a discrete analogue of the convection-diffusion equation, create a mesh of uniformly spaced nodes (spacing h) and solve the resulting set of algebrai ...
... a.- Obtain, plot and tabulate the exact solution of the problem. b.- Use the method of finite differences with central diferences throughout to obtain a discrete analogue of the convection-diffusion equation, create a mesh of uniformly spaced nodes (spacing h) and solve the resulting set of algebrai ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.