Section 3 – 5 Solving Equations with Variable on
... should not exceed a certain limit, which depends on his or her age. This maximum rate is represented by the expression 0.8(220 – a), where a is age in years. Find the age of a person whose maximum pulse is 152. ...
... should not exceed a certain limit, which depends on his or her age. This maximum rate is represented by the expression 0.8(220 – a), where a is age in years. Find the age of a person whose maximum pulse is 152. ...
Chapter 2
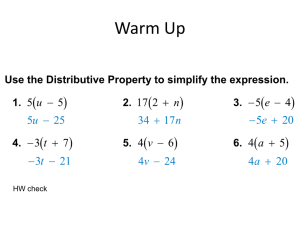
... Solving Equations Example: Solve the equation 3(4 – x) + 5x = 9. 12 – 3x + 5x = 9 (Distributive property) 12 + 2x = 9 (Combine like terms.) 12 - 12 + 2x = 9 - 12 (Add –12 to both sides.) 2x = -3 (Divide both sides by 2.) x 3 ...
... Solving Equations Example: Solve the equation 3(4 – x) + 5x = 9. 12 – 3x + 5x = 9 (Distributive property) 12 + 2x = 9 (Combine like terms.) 12 - 12 + 2x = 9 - 12 (Add –12 to both sides.) 2x = -3 (Divide both sides by 2.) x 3 ...
1.3 Solving Linear Equations
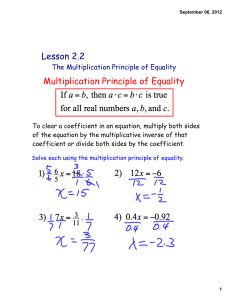
... sides of an equation by the same term. • Division prop of = - can divide both sides of an equation by the same term. ** So basically, whatever you do to one side of an equation, you MUST do to the other! ...
... sides of an equation by the same term. • Division prop of = - can divide both sides of an equation by the same term. ** So basically, whatever you do to one side of an equation, you MUST do to the other! ...
Systems of Equations
... Example: The ordered pair (4, 1) is a solution of the system since 3(4) + 2(1) = 14 and 2(4) – 5(1) = 3. Example: The ordered pair (0, 7) is not a solution of the system since 3(0) + 2(7) = 14 but 2(0) – 5(7) = – 35, not 3. ...
... Example: The ordered pair (4, 1) is a solution of the system since 3(4) + 2(1) = 14 and 2(4) – 5(1) = 3. Example: The ordered pair (0, 7) is not a solution of the system since 3(0) + 2(7) = 14 but 2(0) – 5(7) = – 35, not 3. ...
Chapter 7 Notes
... A) Algebraic Expression – A group of number or variables connected by +, -, *, / (Except by Zero), Raising to power or roots. B) Equation – A statement where two Algebraic Expressions are Equal. C) Theorem – Linear Equations in one variable: An equation is Linear if and only if it can be written in ...
... A) Algebraic Expression – A group of number or variables connected by +, -, *, / (Except by Zero), Raising to power or roots. B) Equation – A statement where two Algebraic Expressions are Equal. C) Theorem – Linear Equations in one variable: An equation is Linear if and only if it can be written in ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.