Hwk 1 (Due THURSDAY 22 Jan)
... Terminology: Let L be a differential operator, mapping functions to functions. d [For example, L = dx , in which case L(f ) = f 0 .] We say L is linear if L(u + v) = L(u) + L(v) and L(cu) = cL(u), for all functions u, v, and all constants, c. An equation of the form L(u) = 0 is called a homogeneous ...
... Terminology: Let L be a differential operator, mapping functions to functions. d [For example, L = dx , in which case L(f ) = f 0 .] We say L is linear if L(u + v) = L(u) + L(v) and L(cu) = cL(u), for all functions u, v, and all constants, c. An equation of the form L(u) = 0 is called a homogeneous ...
MAT 0024 5
... 5.7 Solving Polynomial Equations by Factoring A quadratic or second degree equation (highest power of x is 2) is one that may be written in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a 0. Example: x2 – 2x + 4 = 0 Get 0 on one side. 1. x2 –5x = 8 ...
... 5.7 Solving Polynomial Equations by Factoring A quadratic or second degree equation (highest power of x is 2) is one that may be written in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a 0. Example: x2 – 2x + 4 = 0 Get 0 on one side. 1. x2 –5x = 8 ...
13_5elimination method by multiolication
... Previously, we learned how to solve systems of equations by using addition or subtraction which eliminated one of the variables. ...
... Previously, we learned how to solve systems of equations by using addition or subtraction which eliminated one of the variables. ...
Lesson 32 - Math @ Purdue
... Addition Method: As with the substitution method, the goal of the addition method is to eliminate one of the variables. 1. Write both equations in general form ( Ax By C ) . 2. If necessary, multiply one or both of the equations by appropriate nonzero numbers so that the sum of the x-coefficient ...
... Addition Method: As with the substitution method, the goal of the addition method is to eliminate one of the variables. 1. Write both equations in general form ( Ax By C ) . 2. If necessary, multiply one or both of the equations by appropriate nonzero numbers so that the sum of the x-coefficient ...
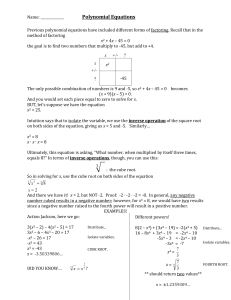
Previous polynomial equations have included
... on both sides of the equation, giving us x = 5 and -5. Similarly… x3 = 8 x∙x∙x=8 Ultimately, this equation is asking, “What number, when multiplied by itself three times, equals 8?” In terms of inverse operations, though, you can use this: ...
... on both sides of the equation, giving us x = 5 and -5. Similarly… x3 = 8 x∙x∙x=8 Ultimately, this equation is asking, “What number, when multiplied by itself three times, equals 8?” In terms of inverse operations, though, you can use this: ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.