Learning PP 1
... “Education is what survives when what has been learned has been forgotten.” B.F. Skinner ...
... “Education is what survives when what has been learned has been forgotten.” B.F. Skinner ...
Psych Ch 7 Typed Notes
... Chapter 7 - Learning A) Classical Conditioning Associations made between a natural stimulus and a learned stimulus Ivan Pavlov – Dogs associated various items with food (Ringing Bell, A Feeder). They responded by salivating, or become excitable. Demo – rubber bands; clapping Role of Punishment and R ...
... Chapter 7 - Learning A) Classical Conditioning Associations made between a natural stimulus and a learned stimulus Ivan Pavlov – Dogs associated various items with food (Ringing Bell, A Feeder). They responded by salivating, or become excitable. Demo – rubber bands; clapping Role of Punishment and R ...
Chapter 7 - Learning
... C) Social Learning • Learning from the behavior of others. Could be either positive or negative behaviors. Ex? • Related to “Observational Learning” • Examples from “my” home life: ...
... C) Social Learning • Learning from the behavior of others. Could be either positive or negative behaviors. Ex? • Related to “Observational Learning” • Examples from “my” home life: ...
Commentary on slides Lecture 16
... 3. These connections are carried via 3 large fiber bundles, the superior, middle and inferior cerebellar peduncles. In cross section (here mid-saggital) the cerebellum can be see to consist of a number of leaflets or folia. 4. The midline portion of the cerebellum is called the vermis and is flanked ...
... 3. These connections are carried via 3 large fiber bundles, the superior, middle and inferior cerebellar peduncles. In cross section (here mid-saggital) the cerebellum can be see to consist of a number of leaflets or folia. 4. The midline portion of the cerebellum is called the vermis and is flanked ...
Lateral Zone
... • It has connections with motor cortex. It also called as cerebrocerebellum. It is concerned with palnning and programming of movements. Cerebellum does not initiate movement but controls sequence and timing of successive movements that lead to smooth progression from one movement to next. • Lateral ...
... • It has connections with motor cortex. It also called as cerebrocerebellum. It is concerned with palnning and programming of movements. Cerebellum does not initiate movement but controls sequence and timing of successive movements that lead to smooth progression from one movement to next. • Lateral ...
STUDY GUIDE Module 15 Define: Taste Aversion Spontaneous
... when an organism produces the same response to similar stimuli. ...
... when an organism produces the same response to similar stimuli. ...
Behavioral Learning Theory
... learning as nothing more than the achievement of new behavior based on environmental conditions. This theory is more concerned with the response generated. Input is stimulus and output is response that produces behavioral changes. This theory was pioneered by Pavlov, Edward Lee and Skinner. They des ...
... learning as nothing more than the achievement of new behavior based on environmental conditions. This theory is more concerned with the response generated. Input is stimulus and output is response that produces behavioral changes. This theory was pioneered by Pavlov, Edward Lee and Skinner. They des ...
Slide ()
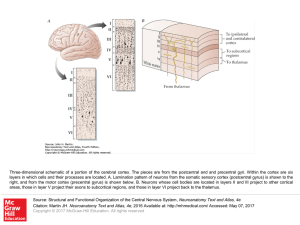
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
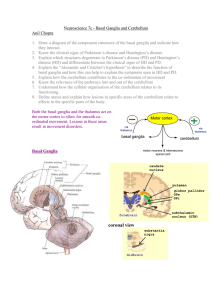
Neuroscience 7c – Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum
... The cerebellum is involved in the co-ordination of movement. It compares what you thought you were going to do (according to the motor cortex) with what you are actually about to do (according to proprioceptive feedback). The Basic Circuit is the same in all parts of the cerebellum and has 3 parts t ...
... The cerebellum is involved in the co-ordination of movement. It compares what you thought you were going to do (according to the motor cortex) with what you are actually about to do (according to proprioceptive feedback). The Basic Circuit is the same in all parts of the cerebellum and has 3 parts t ...
Minireview Embarrassed, but Not Depressed: Eye Opening Lessons
... paired with complex spikes, the receptive fields shrank back to normal size. Opposite effects were observed in inhibitory interneurons—conjunctive activation of climbing fibers and parallel fibers led to an expansion, not shrinkage, of interneuron receptive fields. Since these in vivo experiments me ...
... paired with complex spikes, the receptive fields shrank back to normal size. Opposite effects were observed in inhibitory interneurons—conjunctive activation of climbing fibers and parallel fibers led to an expansion, not shrinkage, of interneuron receptive fields. Since these in vivo experiments me ...
The Cerebellum
... Spinocerebellum (Vermis + Intermed. Hem) Control of limbs and trunk Cerebrocerebellum ...
... Spinocerebellum (Vermis + Intermed. Hem) Control of limbs and trunk Cerebrocerebellum ...
Gross Appearance of Cerebellum
... → vestibular nuclei, reticular formation and red nucleus → vestibulospinal tract, reticulospinal tract and rubrospinal tract → motor neurons of anterior horn ...
... → vestibular nuclei, reticular formation and red nucleus → vestibulospinal tract, reticulospinal tract and rubrospinal tract → motor neurons of anterior horn ...
neurology_lab6_13_4_2011 - Post-it
... ☻Function: play an important role in control of muscle tone and coordination of muscle movement on the same side of the body (3)- Cerebrocerebellum ☻latral zone ...
... ☻Function: play an important role in control of muscle tone and coordination of muscle movement on the same side of the body (3)- Cerebrocerebellum ☻latral zone ...
An adult is experiencing inferior alternating hemiplegia. Which
... B) Muscles of the lower face are weak on the right side. C) The protruded tongue deviates to the right side. D) Brisk DTRs are present in the right arm. E) Stroking the left foot produces a Babinski response. DTRs = deep tendon reflexes = muscle stretch reflexes ...
... B) Muscles of the lower face are weak on the right side. C) The protruded tongue deviates to the right side. D) Brisk DTRs are present in the right arm. E) Stroking the left foot produces a Babinski response. DTRs = deep tendon reflexes = muscle stretch reflexes ...
Purkinje cells
... arises from certain diseases that selectively affect alpha motor neurons (such as polio) Muscle atrophy. (decrease in the mass of the muscle) Weakness. Fasciculation. spontaneous action potentials, visible twitch (called a fasciculation) Fibrillation. generate spontaneous action potentials; causing ...
... arises from certain diseases that selectively affect alpha motor neurons (such as polio) Muscle atrophy. (decrease in the mass of the muscle) Weakness. Fasciculation. spontaneous action potentials, visible twitch (called a fasciculation) Fibrillation. generate spontaneous action potentials; causing ...
Organization of Behavior
... act on central pattern generators changes in activity in brainstem "command" circuits directed by sensory input + or klinotaxis (single receptor compares stimulus over time) tropotaxis (paired receptors--simultaneous comparison) telotaxis (toward a goal--e.g. swim toward shore) not well studied in v ...
... act on central pattern generators changes in activity in brainstem "command" circuits directed by sensory input + or klinotaxis (single receptor compares stimulus over time) tropotaxis (paired receptors--simultaneous comparison) telotaxis (toward a goal--e.g. swim toward shore) not well studied in v ...
Basic Forms of Learning Classical Conditioning Evidence of Learning
... Basic Forms of Learning • Learning – a relatively enduring change in behavior as a result of previous experience • The most basic forms of learning occur automatically, subconsciously – without any particular effort on our part. • 2 forms of basic learning or “conditioning” involve learning associat ...
... Basic Forms of Learning • Learning – a relatively enduring change in behavior as a result of previous experience • The most basic forms of learning occur automatically, subconsciously – without any particular effort on our part. • 2 forms of basic learning or “conditioning” involve learning associat ...
OverviewCerebellum
... B. In some cases the CS does not overlap the US; this is trace conditioning. The cerebellum is essential for learning this conditioned response. ...
... B. In some cases the CS does not overlap the US; this is trace conditioning. The cerebellum is essential for learning this conditioned response. ...