What is learned?
... grp 1 shows NO fear conditioning to tone grp 2 shows some fear, but less than grp 3 grp 3 shows strong conditioned fear of tone what does tone say to grp 3? "your 10% now goes up to 40%, so BE SCARED!" what does tone say to grp 1? "your 40% stays the same; sure, life sucks, but it's ...
... grp 1 shows NO fear conditioning to tone grp 2 shows some fear, but less than grp 3 grp 3 shows strong conditioned fear of tone what does tone say to grp 3? "your 10% now goes up to 40%, so BE SCARED!" what does tone say to grp 1? "your 40% stays the same; sure, life sucks, but it's ...
Ch 6 Learning Notes
... • Trial = pairing of UCS and CS… (How many times have the tone and the meat powder been paired?) Some behaviors are learned after only one trial or pairing, while others take many trials. • Acquisition = initial stage in learning, acquiring the response • Stimulus contiguity = Conditioning has been ...
... • Trial = pairing of UCS and CS… (How many times have the tone and the meat powder been paired?) Some behaviors are learned after only one trial or pairing, while others take many trials. • Acquisition = initial stage in learning, acquiring the response • Stimulus contiguity = Conditioning has been ...
Learning - Mr. Hunsaker`s Classes
... Classical Conditioning • Although classical conditioning happens quite easily, there are a few basic principles that researchers have discovered: – The UR (unconditioned response) and CR (conditioned response) are essentially the same – salivation. – The CS (conditioned stimulus) must precede the U ...
... Classical Conditioning • Although classical conditioning happens quite easily, there are a few basic principles that researchers have discovered: – The UR (unconditioned response) and CR (conditioned response) are essentially the same – salivation. – The CS (conditioned stimulus) must precede the U ...
PSYCH CLASSICAL-CONDITIONING
... Classical conditioning theory of phobic disorder: individuals learn to discriminate between a CS that is followed reliably by a fear-inducing UCS & stimuli that, although similar, are rarely or never followed by the UCS. For example, in the case of the dog that is fearful of all men because it has b ...
... Classical conditioning theory of phobic disorder: individuals learn to discriminate between a CS that is followed reliably by a fear-inducing UCS & stimuli that, although similar, are rarely or never followed by the UCS. For example, in the case of the dog that is fearful of all men because it has b ...
Unit 6 Notes
... -Acquisition - in classical conditioning, the initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. In operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response. -Higher-order conditioning - a pr ...
... -Acquisition - in classical conditioning, the initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus begins triggering the conditioned response. In operant conditioning, the strengthening of a reinforced response. -Higher-order conditioning - a pr ...
Chapter06 - J. Randall Price, Ph.D.
... • Both behavior and cognitive learning occurs in humans. • Human behavior more influenced by learning than instincts than other animals. • Human learning ranges from simple to complex. ...
... • Both behavior and cognitive learning occurs in humans. • Human behavior more influenced by learning than instincts than other animals. • Human learning ranges from simple to complex. ...
ICANN2006web
... Patterns in {N_i,p & N_i,n} are backbones of the Hopfield model. They form the backbone structure of the model. ...
... Patterns in {N_i,p & N_i,n} are backbones of the Hopfield model. They form the backbone structure of the model. ...
Modern neuroscience is based on ideas derived
... methods, and offered exciting new possibilities. No other technique has comparable power and flexibility to show at once the spectrum of inputs and outputs of small or large brain areas, a column, layer, or single neurons. Using tracers we learned, for example, that connections between any two struc ...
... methods, and offered exciting new possibilities. No other technique has comparable power and flexibility to show at once the spectrum of inputs and outputs of small or large brain areas, a column, layer, or single neurons. Using tracers we learned, for example, that connections between any two struc ...
Sparse coding in the primate cortex
... neurons’ breadth of tuning across various stimulus sets than about sparseness per se. Coding across stimuli and across cells are, however, closely related (Table 2). For instance, the sparseness averaged across stimuli and narrowness of tuning averaged across units must be equal. What evidence is th ...
... neurons’ breadth of tuning across various stimulus sets than about sparseness per se. Coding across stimuli and across cells are, however, closely related (Table 2). For instance, the sparseness averaged across stimuli and narrowness of tuning averaged across units must be equal. What evidence is th ...
Unit 5, Learning
... Intrinsic motivation- the desire to perform a behavior for its own sake- self fulfillment or self enjoyment are the driving factors- practicing a sport because you love the sport Extrinsic motivation- the desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishment- going ...
... Intrinsic motivation- the desire to perform a behavior for its own sake- self fulfillment or self enjoyment are the driving factors- practicing a sport because you love the sport Extrinsic motivation- the desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishment- going ...
Occular Dominance Columns
... • Adjacent columns have similar response properties. • Same orientation is repeated at approx. 1 mm horizontal intervals (orientation preference). ...
... • Adjacent columns have similar response properties. • Same orientation is repeated at approx. 1 mm horizontal intervals (orientation preference). ...
deep learning with different types of neurons
... D EEP LEARNING hypothesizes that in order to learn high-level representations of data a hierarchy of intermediate representations are needed. In the vision case the first level of representation could be gabor-like filters, the second level could be line and corner detectors, and higher level repres ...
... D EEP LEARNING hypothesizes that in order to learn high-level representations of data a hierarchy of intermediate representations are needed. In the vision case the first level of representation could be gabor-like filters, the second level could be line and corner detectors, and higher level repres ...
What is Learning? - The Psychology Deck
... 4. In classical conditioning, learning is evident when a a. stimulus automatically produces a response without a prior history of experience. b. stimulus which did not initially produce a response now elicits that response. c. spontaneously emitted response increases in frequency as a result of its ...
... 4. In classical conditioning, learning is evident when a a. stimulus automatically produces a response without a prior history of experience. b. stimulus which did not initially produce a response now elicits that response. c. spontaneously emitted response increases in frequency as a result of its ...
Chapter 4 Learning - Western Washington University
... • between the shock and the tone. The tone comes to predict the shock. Anxiety is high before tone is on. • Panel 2 the dog comes to jump, before the shock when it hears the tone. Anxiety starts to drop as the dog starts to jump. Note the shock has not appeared. • Panel 3 Dog is jumping, shock appe ...
... • between the shock and the tone. The tone comes to predict the shock. Anxiety is high before tone is on. • Panel 2 the dog comes to jump, before the shock when it hears the tone. Anxiety starts to drop as the dog starts to jump. Note the shock has not appeared. • Panel 3 Dog is jumping, shock appe ...
Module 10: Operant & Cognitive Approaches
... ▪ Examples: $$ for good grades, praise for performing well in a game ▪ Other Examples: ...
... ▪ Examples: $$ for good grades, praise for performing well in a game ▪ Other Examples: ...
Learned Movements Elicited by Direct Stimulation of Cerebellar
... were given. After testing for responses to MCP stimulation, the animal was subjected to 100 presentations of the forelimb CS alone, which caused extinction of forelimb-elicited CRs. When MCP stimulation was then applied, no CRs were present. Thus, the responses elicited by MCP stimulation were depen ...
... were given. After testing for responses to MCP stimulation, the animal was subjected to 100 presentations of the forelimb CS alone, which caused extinction of forelimb-elicited CRs. When MCP stimulation was then applied, no CRs were present. Thus, the responses elicited by MCP stimulation were depen ...
Objectives 34
... - Babinski sign infers a release from inhibition; usually Babinski is suppressed - During normal volitional movement some muscles need to be activated, but others need to be inhibited; An individual muscle needs to be active during part of a movement and inhibited during another part; stimulation of ...
... - Babinski sign infers a release from inhibition; usually Babinski is suppressed - During normal volitional movement some muscles need to be activated, but others need to be inhibited; An individual muscle needs to be active during part of a movement and inhibited during another part; stimulation of ...
Gamma band activity in the nuclei of the Reticular Activating System
... characterized by low amplitude, high frequency oscillatory activity in the gamma band range (~20-100 Hz). Gamma frequency oscillations have been proposed to participate in conscious perception, problem solving, memory, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. It has been suggested that such coherent acti ...
... characterized by low amplitude, high frequency oscillatory activity in the gamma band range (~20-100 Hz). Gamma frequency oscillations have been proposed to participate in conscious perception, problem solving, memory, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. It has been suggested that such coherent acti ...
Tsuda et al NeurosciRes
... Berglund et al., 2006; Li and Tsien, 2012; Looger and Griesbeck, 2012; Zhao et al., 2011b; ...
... Berglund et al., 2006; Li and Tsien, 2012; Looger and Griesbeck, 2012; Zhao et al., 2011b; ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
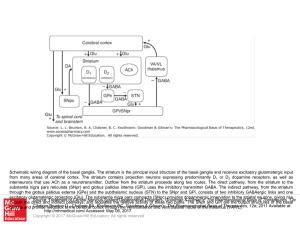
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
ECE-453 Lecture 1
... a lot while the object (cause) remains the same Thus, learning persistent patterns on the retina would correspond to learning objects in the visual world Associating patterns with their causes corresponds to invariant pattern recognition ...
... a lot while the object (cause) remains the same Thus, learning persistent patterns on the retina would correspond to learning objects in the visual world Associating patterns with their causes corresponds to invariant pattern recognition ...
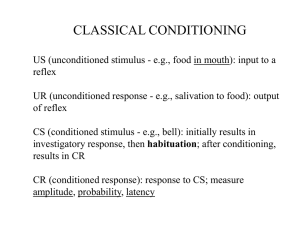
Classical Conditioning
... a behavior occurs it is reinforced. The problem with this is that if the creature gets used to being rewarded and then is not, it will quit doing the behavior To avoid the problem with continuous reinforcement, there can be different schedules of reinforcement (different methods of reinforcing) used ...
... a behavior occurs it is reinforced. The problem with this is that if the creature gets used to being rewarded and then is not, it will quit doing the behavior To avoid the problem with continuous reinforcement, there can be different schedules of reinforcement (different methods of reinforcing) used ...
Learning Theory and Development of Social
... dentist for the first time. The dentist, the office, the receptionist, the smells and sounds of the place are essentially neutral stimuli for the child, so will have no particular emotional effect on behaviour. Then the child sits in the dentist's chair and experiences pain (UCS) which in turn elici ...
... dentist for the first time. The dentist, the office, the receptionist, the smells and sounds of the place are essentially neutral stimuli for the child, so will have no particular emotional effect on behaviour. Then the child sits in the dentist's chair and experiences pain (UCS) which in turn elici ...