Learning: Relatively permanent change in behavior due to
... The Skinner box. This simple device, invented by B. F. Skinner, allows careful study of operant conditioning. When the rat presses the bar, a pellet of food or a drop of water is automatically released. (A photograph of a Skinner box appears in Chapter 2.) ...
... The Skinner box. This simple device, invented by B. F. Skinner, allows careful study of operant conditioning. When the rat presses the bar, a pellet of food or a drop of water is automatically released. (A photograph of a Skinner box appears in Chapter 2.) ...
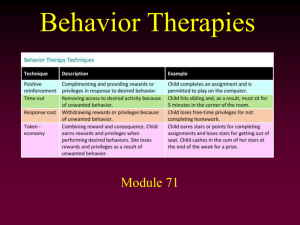
Module 71 - Behavioral Therapy
... unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior • The person is replacing a positive (relaxing) but harmful response with a negative/aversive response • Example with alcoholism: Lace a drink with a drug that makes the person becomes sick • Aversive conditioning is not very effective – Co ...
... unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior • The person is replacing a positive (relaxing) but harmful response with a negative/aversive response • Example with alcoholism: Lace a drink with a drug that makes the person becomes sick • Aversive conditioning is not very effective – Co ...
Principles of Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning, and
... is offered; not immediately observable. • Learned helplessness: after several failed attempts at something, the belief that the situation is uncontrollable. ...
... is offered; not immediately observable. • Learned helplessness: after several failed attempts at something, the belief that the situation is uncontrollable. ...
PsychSim5: Maze Learning 1 PsychSim 5: MAZE LEARNING Name
... the basic processes of classical conditioning: acquisition, generalization, discrimination training, and ...
... the basic processes of classical conditioning: acquisition, generalization, discrimination training, and ...
Basic Psychological Processes
... 81. Factors that can change or vary and are capable of being observed, measured, and verified are called ____________. a. Statistics ...
... 81. Factors that can change or vary and are capable of being observed, measured, and verified are called ____________. a. Statistics ...
I Love Learning
... 100 What type of learning takes place when we learn to associate 2 stimuli and we are unaware of it? Classical conditioning 200 When you reinforce the small steps along the way to building an overall behavior it is known as…shaping 300 What study showed that children imitate behaviors they see AND w ...
... 100 What type of learning takes place when we learn to associate 2 stimuli and we are unaware of it? Classical conditioning 200 When you reinforce the small steps along the way to building an overall behavior it is known as…shaping 300 What study showed that children imitate behaviors they see AND w ...
Unit 1: Introduction to Psychology
... Is behavior determined by heredity or environment? Sir Francis Galton – concluded that intelligence was hereditary / good marriages would supply the world with talented offspring. (1883). ...
... Is behavior determined by heredity or environment? Sir Francis Galton – concluded that intelligence was hereditary / good marriages would supply the world with talented offspring. (1883). ...
Operant Conditioning - Gordon State College
... Punishment: The process by which a consequence decreases the probability of the behavior that it follows. ...
... Punishment: The process by which a consequence decreases the probability of the behavior that it follows. ...
observational learning
... Punishment: The process by which a consequence decreases the probability of the behavior that it follows. ...
... Punishment: The process by which a consequence decreases the probability of the behavior that it follows. ...
Define the main biological influences of psychology
... premise that all behavior I obtained through conditioning. Conditioning happens through communication with the environment. According to behaviorism, behavior can be researched in a methodical and visible manner with no contemplation of internal mental states. There are two major types of conditioni ...
... premise that all behavior I obtained through conditioning. Conditioning happens through communication with the environment. According to behaviorism, behavior can be researched in a methodical and visible manner with no contemplation of internal mental states. There are two major types of conditioni ...
Chapter 1: The Science of Psychology Module 1: Psychology`s
... Adaptive behaviors become habits: the “flywheel of society.” Like physical traits, useful behavioral traits could be passed to future generations. ...
... Adaptive behaviors become habits: the “flywheel of society.” Like physical traits, useful behavioral traits could be passed to future generations. ...
B.F. Skinner
... Answer:The credit card is a positive reinforcement because it is given and it increases the behavior. Scenario 2: A lion in a circus learns to stand up on a chair and jump through a hoop to receive a food treat. Answer: The food treat is a positive reinforcement because it is given and it incr ...
... Answer:The credit card is a positive reinforcement because it is given and it increases the behavior. Scenario 2: A lion in a circus learns to stand up on a chair and jump through a hoop to receive a food treat. Answer: The food treat is a positive reinforcement because it is given and it incr ...
Programmed Instruction - Dallas Area Network for Teaching
... * the response is followed (reinforced) by the stimulus * the response is voluntary ...
... * the response is followed (reinforced) by the stimulus * the response is voluntary ...
Leading Through Motivation
... “People will do what they can do when they want to do it.” The question is ‘what makes them want to do it?’ Vroom suggests that the motivation to work depends on the relationships between the following three expectancy ...
... “People will do what they can do when they want to do it.” The question is ‘what makes them want to do it?’ Vroom suggests that the motivation to work depends on the relationships between the following three expectancy ...
Essential Questions, Vocabulary, and Review Charts
... Operant Conditioning - learning in which behaviors are strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Thorndike’s law of effect – behavior followed by favorable consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences becomes less likely Sha ...
... Operant Conditioning - learning in which behaviors are strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Thorndike’s law of effect – behavior followed by favorable consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences becomes less likely Sha ...
cognitive learning
... Organism learns the meaning of various objects and events and learned responses depend on meanings assigned to stimuli. Eg: Tolman trained a rat to turn right in order to get food. When placed on opposite side instead of turning right, rat moved towards food. So, rat formed a cognitive map to get fo ...
... Organism learns the meaning of various objects and events and learned responses depend on meanings assigned to stimuli. Eg: Tolman trained a rat to turn right in order to get food. When placed on opposite side instead of turning right, rat moved towards food. So, rat formed a cognitive map to get fo ...
Modeling - worldowiki
... the effect of popular sports figures on youngsters—that’s modeling). Cognitive modeling—where teachers deliberately model strategies they want students to use. Vicarious learning—we watch others and adjust our own behavior based on what happens to them. ...
... the effect of popular sports figures on youngsters—that’s modeling). Cognitive modeling—where teachers deliberately model strategies they want students to use. Vicarious learning—we watch others and adjust our own behavior based on what happens to them. ...
Chapter 9: Behavioral Learning
... Learning is described in terms of relationships among observable events (stimuli and responses). Learning involves a behavior change. Learning is most likely to take place when stimuli and responses occur close together in time (Contiguity). Many species of animals -including humans- learn in simila ...
... Learning is described in terms of relationships among observable events (stimuli and responses). Learning involves a behavior change. Learning is most likely to take place when stimuli and responses occur close together in time (Contiguity). Many species of animals -including humans- learn in simila ...
Animal Behavior
... • Migrates upward during the day and descends at night • Also migrate from the west to the east during the day and return in the evening ...
... • Migrates upward during the day and descends at night • Also migrate from the west to the east during the day and return in the evening ...
Chapter 1
... neither the experimenter nor participant is aware of the group to which participant is ...
... neither the experimenter nor participant is aware of the group to which participant is ...
Module 22 Powerpoint
... learn new behaviors and skills without a direct experience of conditioning? Yes, and one of the ways we do so is by observational learning: watching what happens when other people do a behavior and learning from their experience. Skills required: mirroring, being able to picture ourselves doing ...
... learn new behaviors and skills without a direct experience of conditioning? Yes, and one of the ways we do so is by observational learning: watching what happens when other people do a behavior and learning from their experience. Skills required: mirroring, being able to picture ourselves doing ...
cognitive_theories
... Psychologist study cognition from this perspective through a mental act that processes the knowledge that is acquired. The perspective of the cognitive is therefore concerned with mental functions such as attention, memory and perception. It basically view people from the perspective of the computer ...
... Psychologist study cognition from this perspective through a mental act that processes the knowledge that is acquired. The perspective of the cognitive is therefore concerned with mental functions such as attention, memory and perception. It basically view people from the perspective of the computer ...
Behaviorism What is Learning? - University of California, Irvine
... • Behavior is Determined, Not Chosen – Therefore, freedom is an illusion – So is dignity (virtue) – If behavior is programmed, then why not try to create a Utopian society? • Walden II ...
... • Behavior is Determined, Not Chosen – Therefore, freedom is an illusion – So is dignity (virtue) – If behavior is programmed, then why not try to create a Utopian society? • Walden II ...
Behaviorism_298 (English) - UC Irvine, OpenCourseWare
... What’s Wrong With Behaviorism? Noam Chomsky’s Critique of Skinner’s Book, “Verbal Behavior” Language can’t be learned only through reinforcement The brain must be a built-in (innate) language ...
... What’s Wrong With Behaviorism? Noam Chomsky’s Critique of Skinner’s Book, “Verbal Behavior” Language can’t be learned only through reinforcement The brain must be a built-in (innate) language ...