Stress, serotonin, and hippocampal neurogenesis
... posit that a downregulation of hippocampal neurogenesis underlies the disorder (Kempermann and Kronenberg, 2003), or suggest genetic or epigenetic factors for developing depression (Karg et al., 2011; Menke et al., 2012). The diathesis-stress model accounts for the interaction of a number of factors ...
... posit that a downregulation of hippocampal neurogenesis underlies the disorder (Kempermann and Kronenberg, 2003), or suggest genetic or epigenetic factors for developing depression (Karg et al., 2011; Menke et al., 2012). The diathesis-stress model accounts for the interaction of a number of factors ...
Affective percept and voluntary action: A hypothesis
... hand, "desire" is partly primary percept and partly secondary. It is evoked by inadequate pleasant stimuli, which signal the adequate ones. A small amount of food in the mouth and barely audible music are some examples. All these terms are used in their broad sense. Secondary stimuli often evoke ima ...
... hand, "desire" is partly primary percept and partly secondary. It is evoked by inadequate pleasant stimuli, which signal the adequate ones. A small amount of food in the mouth and barely audible music are some examples. All these terms are used in their broad sense. Secondary stimuli often evoke ima ...
Higginbotham H, Eom TY, Mariani LE, Bachleda A, Hirt J, Gukassyan V, Cusack CL, Lai C, Caspary T, Anton ES. Developmental Cell. 2012, Nov 13 23(5):925-38. Arl13b in primary cilia regulates the migration and placement of interneurons in the developing cerebral cortex.
... interneuronal placement within the cortex, but not for early postmigratory interneuronal differentiation. Conditional Deletion of Arll13b Disrupts Interneuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex We next examined Arl13bLox/Lox;Dlx5/6-CIE mice at times when interneurons are actively migratin ...
... interneuronal placement within the cortex, but not for early postmigratory interneuronal differentiation. Conditional Deletion of Arll13b Disrupts Interneuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex We next examined Arl13bLox/Lox;Dlx5/6-CIE mice at times when interneurons are actively migratin ...
The Olfactory Sensory Map in Drosophila
... not the environment per se that is mapped, but the various parts of the body, allowing an animal to determine with precision where it is being touched by a physical stimulus. The auditory system maps sound frequencies along a tonotopic axis in the cochlea and the auditory cortex, allowing sound to b ...
... not the environment per se that is mapped, but the various parts of the body, allowing an animal to determine with precision where it is being touched by a physical stimulus. The auditory system maps sound frequencies along a tonotopic axis in the cochlea and the auditory cortex, allowing sound to b ...
Where do mirror neurons come from?
... or before, the primary eliciting stimulus (grasping). In this study, a container was always presented in trials involving grasping before placing, and never in trials involving grasping before eating. Therefore, the presence or absence of a container could become a conditional cue differentially act ...
... or before, the primary eliciting stimulus (grasping). In this study, a container was always presented in trials involving grasping before placing, and never in trials involving grasping before eating. Therefore, the presence or absence of a container could become a conditional cue differentially act ...
The natural hallucinogen 5-MeO-DMT, component of Ayahuasca
... 5-HT2A-R agonist DOI (Celada et al., 2008), markedly disrupt cortical function in rodents. increasing pyramidal neuron discharge and reducing low frequency cortical oscillations (LFCO) in medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) (see (Celada et al., 2013) for review). Here we examined the effects of 5-MeO-DM ...
... 5-HT2A-R agonist DOI (Celada et al., 2008), markedly disrupt cortical function in rodents. increasing pyramidal neuron discharge and reducing low frequency cortical oscillations (LFCO) in medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) (see (Celada et al., 2013) for review). Here we examined the effects of 5-MeO-DM ...
Electrophysiological evidence that noradrenergic neurons of the rat
... arises from multiple distant sources and not only from interneurons as classically accepted. Among these afferents, GABAergic neurons located in the lateral preoptic area and the pontine ventral periaqueductal gray including the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) itself could be responsible for the reductio ...
... arises from multiple distant sources and not only from interneurons as classically accepted. Among these afferents, GABAergic neurons located in the lateral preoptic area and the pontine ventral periaqueductal gray including the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) itself could be responsible for the reductio ...
Validation of hippocampal volumes measured using a
... Manual hippocampal volumetry To reduce manual tracing errors, the coronal T1-W MR images were magnified four times and trilinear interpolation was performed. The entire hippocampus was measured from the anterior-most head to the posterior tail, including the cornu ammonis, gyrus dentatus, hippocampu ...
... Manual hippocampal volumetry To reduce manual tracing errors, the coronal T1-W MR images were magnified four times and trilinear interpolation was performed. The entire hippocampus was measured from the anterior-most head to the posterior tail, including the cornu ammonis, gyrus dentatus, hippocampu ...
Essentials in the neuronal organization of the CNS
... Anatomy Department finds essential to appreciate the structure and function of the central nervous system. It is important to see clearly, however, that this handout does not substitute for the textbooks, but it can be used best in combination with the texts and the illustrations found in them. It w ...
... Anatomy Department finds essential to appreciate the structure and function of the central nervous system. It is important to see clearly, however, that this handout does not substitute for the textbooks, but it can be used best in combination with the texts and the illustrations found in them. It w ...
Maruska & Tricas 2009b
... 2000; Fay and Edds-Walton 2000; Edds-Walton and Fay 1998, 2003, 2005, 2008). The TS is the primary midbrain auditory and mechanosensory processing center in fishes and is composed of two main nuclei: nucleus centralis (NC) and nucleus ventrolateralis (NVL). Nucleus centralis is the acoustic processi ...
... 2000; Fay and Edds-Walton 2000; Edds-Walton and Fay 1998, 2003, 2005, 2008). The TS is the primary midbrain auditory and mechanosensory processing center in fishes and is composed of two main nuclei: nucleus centralis (NC) and nucleus ventrolateralis (NVL). Nucleus centralis is the acoustic processi ...
Thalamocortical neuron loss and localized astrocytosis in the Cln3
... display a range of effects upon cortical thinning and neuronal loss between sensory and motor cortex (Bible et al., 2004; Cooper et al., 1999; Mitchison et al., 1999; Pontikis et al., 2004). Our analysis of these regions in homozygous Cln3 Dex7/8 mice also revealed different degrees of cortical thin ...
... display a range of effects upon cortical thinning and neuronal loss between sensory and motor cortex (Bible et al., 2004; Cooper et al., 1999; Mitchison et al., 1999; Pontikis et al., 2004). Our analysis of these regions in homozygous Cln3 Dex7/8 mice also revealed different degrees of cortical thin ...
cerebellar projections to the superior colliculus in the cat1
... injections were limited to the stratum griseum intermedium. Nonetheless, the labeling was certainly more conspicuous when the injections extended to the stratum griseum profundum. According to previous descriptions using other techniques, it is the posterior half of the medial cerebellar nucleus whi ...
... injections were limited to the stratum griseum intermedium. Nonetheless, the labeling was certainly more conspicuous when the injections extended to the stratum griseum profundum. According to previous descriptions using other techniques, it is the posterior half of the medial cerebellar nucleus whi ...
Neural circuits underlying the generation of theta oscillations
... et al., 1962), a structure well known for its direct cholinergic projections to the hippocampus. The MS together with the vertical and horizontal limb of the diagonal band of Broca (VDB and HDB) is a midline structure part of a vast region known as basal forebrain (Zaborszky et al., 2005). The MS pr ...
... et al., 1962), a structure well known for its direct cholinergic projections to the hippocampus. The MS together with the vertical and horizontal limb of the diagonal band of Broca (VDB and HDB) is a midline structure part of a vast region known as basal forebrain (Zaborszky et al., 2005). The MS pr ...
Insula function in anorexia nervosa
... various sensations as taste, the perception of pain, intestinal tension, itch, dyspnoea and temperature3. The integration of these interoceptive feelings are crucial for the establishing of the ‘self’ as it forms the link between cognitive and emotional processes and the current state of the body3. ...
... various sensations as taste, the perception of pain, intestinal tension, itch, dyspnoea and temperature3. The integration of these interoceptive feelings are crucial for the establishing of the ‘self’ as it forms the link between cognitive and emotional processes and the current state of the body3. ...
Topographic Organization of Connections Between the Hypothalamus and
... Prefrontal cortices have been implicated in autonomic function, but their role in this activity is not well understood. Orbital and medial prefrontal cortices receive input from cortical and subcortical structures associated with emotions. Thus, the prefrontal cortex may be an essential link for aut ...
... Prefrontal cortices have been implicated in autonomic function, but their role in this activity is not well understood. Orbital and medial prefrontal cortices receive input from cortical and subcortical structures associated with emotions. Thus, the prefrontal cortex may be an essential link for aut ...
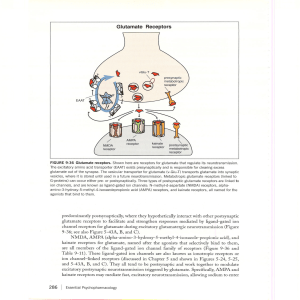
Glutamate Receptors
... loops? First, when descending corticobrainstem glutamate pathways have hypofunctioning NMDA receptors in the ventral tegmental area, this creates mesolimbic dopamine hyperactivity and positive symptoms of psychosis, as already eXplained above and illustrated in Figure 9-39B. The effects of this on C ...
... loops? First, when descending corticobrainstem glutamate pathways have hypofunctioning NMDA receptors in the ventral tegmental area, this creates mesolimbic dopamine hyperactivity and positive symptoms of psychosis, as already eXplained above and illustrated in Figure 9-39B. The effects of this on C ...
Multisensory Integration in the Ventral Intraparietal Area of the
... were prepared for chronic recording of eye position and single-neuron activity in VIP. A single surgery was induced with Zoletil 20 (6 mg/kg) and atropine (0.25 mg) and maintained under isoflurane anesthesia (2.5%). A search coil was implanted subconjunctivally to measure eye position (Judge et al., ...
... were prepared for chronic recording of eye position and single-neuron activity in VIP. A single surgery was induced with Zoletil 20 (6 mg/kg) and atropine (0.25 mg) and maintained under isoflurane anesthesia (2.5%). A search coil was implanted subconjunctivally to measure eye position (Judge et al., ...
The neuropharmacology of impulsive behaviour
... findings have implicated the orbitofrontal cortex in impulsive action [20], whereas, to date, damage to this brain area was mainly found to produce or alter delay aversion [21– 24] and not impulsive action [25]. In addition, a role for limbic regions such as the habenula and hippocampus in impulsive ...
... findings have implicated the orbitofrontal cortex in impulsive action [20], whereas, to date, damage to this brain area was mainly found to produce or alter delay aversion [21– 24] and not impulsive action [25]. In addition, a role for limbic regions such as the habenula and hippocampus in impulsive ...
Chapter 02: Biopsychology, Neuroscience, and Human Nature
... Incorrect. Down syndrome is not an adaptive quality of human beings; rather, it is an illness that is caused by having one too many chromosomes. d. language Correct. The ability to use language as a means of communication is certainly adaptive to human beings. e. the ability to program a cell phone ...
... Incorrect. Down syndrome is not an adaptive quality of human beings; rather, it is an illness that is caused by having one too many chromosomes. d. language Correct. The ability to use language as a means of communication is certainly adaptive to human beings. e. the ability to program a cell phone ...
intraoperative motor evoked potential monitoring
... Electrodes are placed at international 10–20 system central (C) sites approximately overlying motor cortex, or at slightly anterior C+1 cm or C+2 cm sites [37–39, 46]; there is currently no evidence for an efficacy difference between these choices. The latter locations may reduce stimulus artifact b ...
... Electrodes are placed at international 10–20 system central (C) sites approximately overlying motor cortex, or at slightly anterior C+1 cm or C+2 cm sites [37–39, 46]; there is currently no evidence for an efficacy difference between these choices. The latter locations may reduce stimulus artifact b ...
Cell Type-Specific, Presynaptic LTP of Inhibitory Synapses on Fast
... SEM unless otherwise mentioned. For statistical analysis, values before and after TBS obtained from the same cell and values between two groups of cells were compared with paired and unpaired t tests, respectively, when the values showed the normal distribution. The statistical evaluation of normal ...
... SEM unless otherwise mentioned. For statistical analysis, values before and after TBS obtained from the same cell and values between two groups of cells were compared with paired and unpaired t tests, respectively, when the values showed the normal distribution. The statistical evaluation of normal ...
Word doc - Center for Neural Science
... However, the narrow receptive fields thus derived may be misleading, and underestimate the spectral breadth of inputs to cortical neurons, as evidenced by a number of studies. Blockade of intracortical inhibition results in an expansion of frequency receptive fields derived from extracellular spike ...
... However, the narrow receptive fields thus derived may be misleading, and underestimate the spectral breadth of inputs to cortical neurons, as evidenced by a number of studies. Blockade of intracortical inhibition results in an expansion of frequency receptive fields derived from extracellular spike ...
... (ADHD) have consistently found global reductions of total brain volume with frontalstriatal regions, cerebellum and parieto-temporal regions particularly affected relative to typically developing subjects. The adult diagnosis of ADHD requires onset in childhood, but persistence of ADHD into adulthoo ...
Contribution of Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus Neurons to
... the major ascending arousal systems in the brain stem and is linked to motor, limbic, and sensory systems. Based on previous studies, we hypothesized that PPTN would be related to the integrative control of movement, reinforcement, and performance of tasks in behaving animals. To investigate how PPT ...
... the major ascending arousal systems in the brain stem and is linked to motor, limbic, and sensory systems. Based on previous studies, we hypothesized that PPTN would be related to the integrative control of movement, reinforcement, and performance of tasks in behaving animals. To investigate how PPT ...
Basal Ganglia - Adaptive Behaviour Research Group
... The main output nuclei of the basal ganglia are the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr), and the entopeduncular nucleus (EP). Output structures provide extensively branched efferents to the thalamus (which project back to the cerebral cortex), and to pre-motor areas of the midbrain and brainstem. ...
... The main output nuclei of the basal ganglia are the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr), and the entopeduncular nucleus (EP). Output structures provide extensively branched efferents to the thalamus (which project back to the cerebral cortex), and to pre-motor areas of the midbrain and brainstem. ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.