Understanding-the.. - Windsor C
... • Action potential: when excited, pores open and + ions flow through axon “firing” an electrical pathway to the terminal button – Increase in + ions is called depolarization – the # of ions necessary for “firing” is called the threshold • Once the process starts, it cannot stop: All-ornone principle ...
... • Action potential: when excited, pores open and + ions flow through axon “firing” an electrical pathway to the terminal button – Increase in + ions is called depolarization – the # of ions necessary for “firing” is called the threshold • Once the process starts, it cannot stop: All-ornone principle ...
Bio70 Psychobiology Fall 2006 First Midterm October 12 Version A
... 35. In anatomy, the opposite of medial is: a. lateral. b. dorsal. c. ventral. d. rostral. 36. Cell bodies of sensory neurons are located in the: a. spinal cord. b. dorsal root ganglia. c. white matter. d. ventral roots. 37. Sympathetic is to ____ as parasympathetic is to ____. a. serotonin; dopamin ...
... 35. In anatomy, the opposite of medial is: a. lateral. b. dorsal. c. ventral. d. rostral. 36. Cell bodies of sensory neurons are located in the: a. spinal cord. b. dorsal root ganglia. c. white matter. d. ventral roots. 37. Sympathetic is to ____ as parasympathetic is to ____. a. serotonin; dopamin ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 3.1 Typical morphology of projection
... FIGURE 3.9 An “unrolled” Schwann cell in the PNS is illustrated in relation to the single axon segment that it myelinates. The broad stippled region is compact myelin surrounded by cytoplasmic channels that remain open even after compact myelin has formed, allowing an exchange of materials among th ...
... FIGURE 3.9 An “unrolled” Schwann cell in the PNS is illustrated in relation to the single axon segment that it myelinates. The broad stippled region is compact myelin surrounded by cytoplasmic channels that remain open even after compact myelin has formed, allowing an exchange of materials among th ...
Neuron Anatomy Activity - Ask a Biologist
... 1. Synapses: Send electrical impulses to neighboring neurons. 2. Myelin sheaths: Cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep electrical signals inside the cell, which allows them to move more quickly. 3. Axon: Transfers electrical impulse signals from the cell body to the synapse. 4. Soma: ...
... 1. Synapses: Send electrical impulses to neighboring neurons. 2. Myelin sheaths: Cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep electrical signals inside the cell, which allows them to move more quickly. 3. Axon: Transfers electrical impulse signals from the cell body to the synapse. 4. Soma: ...
Origin of Long- Term Memory - Neuromarketing Business Association
... It’s important to remember, that LTP is not a mechanism, but a outcome of the increased activity in two neurons, that result of a increase of APMA receptors, strengthen the synaptic connection, which allows the low frequent action potential a greater depolarization potential - This is the foundation ...
... It’s important to remember, that LTP is not a mechanism, but a outcome of the increased activity in two neurons, that result of a increase of APMA receptors, strengthen the synaptic connection, which allows the low frequent action potential a greater depolarization potential - This is the foundation ...
Cell Biology of the Nervous System
... • Associated with some diseases – Alzheimer’s disease – AIDS ...
... • Associated with some diseases – Alzheimer’s disease – AIDS ...
1050927abstract
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
Design a Neuron
... Axon terminals – release the electrical impulse as a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synapse to the next neuron or organ. ...
... Axon terminals – release the electrical impulse as a chemical called a neurotransmitter into the synapse to the next neuron or organ. ...
9-5_Neuronal connections of the cerebellar cortex excitatory
... a lot of spine. The little spine on it and each of these input makes a little input, but they can summate to activate the Purkinje cell. Parallel fiber axons are also the main excitatory input to the Golgi, stellate and basket cells. Mossy fibers contain all of the cerebellar inputs except one that ...
... a lot of spine. The little spine on it and each of these input makes a little input, but they can summate to activate the Purkinje cell. Parallel fiber axons are also the main excitatory input to the Golgi, stellate and basket cells. Mossy fibers contain all of the cerebellar inputs except one that ...
Week 1
... • Communication between neurons happen through synapses – Electrical synapses (gap junctions) • Direct electrical contact between two cells through membrane proteins which span both the connecting cells • Typically found between coupled GABAergic interneurons ...
... • Communication between neurons happen through synapses – Electrical synapses (gap junctions) • Direct electrical contact between two cells through membrane proteins which span both the connecting cells • Typically found between coupled GABAergic interneurons ...
6.1 Overview of the Nervous System
... 3. axons – transmit impulses away from the cell body b. myelin sheaths cover axons and increase the rate of impulse transmission, appear white (White matter); Gray matter is non-myelinated nerve fibers c. insulated gaps between Schwann Cells are call nodes of Ranvier ...
... 3. axons – transmit impulses away from the cell body b. myelin sheaths cover axons and increase the rate of impulse transmission, appear white (White matter); Gray matter is non-myelinated nerve fibers c. insulated gaps between Schwann Cells are call nodes of Ranvier ...
Synapses
... the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
Lecture 2 (Neurons)
... ER, mitochondria, golgi complex, etc). Is where most the synthesis of new cellular products occurs. ...
... ER, mitochondria, golgi complex, etc). Is where most the synthesis of new cellular products occurs. ...
bio 342 human physiology
... Components of a reflex arc Axonal regeneration Ohm’s Law Origin of resting membrane potential Equilibrium Potentials (Nernst potentials) ...
... Components of a reflex arc Axonal regeneration Ohm’s Law Origin of resting membrane potential Equilibrium Potentials (Nernst potentials) ...
Slide ()
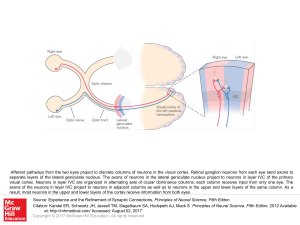
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
Neurons
... • Vary in size and structure, but have common features: 1. Cell Body 2. Dendrites 3. Axon ...
... • Vary in size and structure, but have common features: 1. Cell Body 2. Dendrites 3. Axon ...
Chemical Transmission BETWEEN Neurons
... Principles of Biological Psychology Everything psychological is simultaneously biological. The nervous system is complexity built from simplicity. The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... Principles of Biological Psychology Everything psychological is simultaneously biological. The nervous system is complexity built from simplicity. The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
Real Neurons for Engineers
... recurrent signaling within a small network. • Long-term plasticity is believed to involve changes in receptor densities on the post-synaptic side and vesicle densities on the pre-synaptic side. ...
... recurrent signaling within a small network. • Long-term plasticity is believed to involve changes in receptor densities on the post-synaptic side and vesicle densities on the pre-synaptic side. ...
Neurons and Glia Three basic neurons: ∼ Multipolar: Neurons by
... Neurons and Glia Three basic neurons: ∼ Multipolar: ◊ Neurons by far the most common ◊ They possess an axon and a number of dendrites ∼ Bipolar: ◊ Neurons with a centrally placed cell body ◊ 1 axon extends away from cell body ◊ 1 dendrite extends from axon ◊ Occur in afferent pathways of the visual, ...
... Neurons and Glia Three basic neurons: ∼ Multipolar: ◊ Neurons by far the most common ◊ They possess an axon and a number of dendrites ∼ Bipolar: ◊ Neurons with a centrally placed cell body ◊ 1 axon extends away from cell body ◊ 1 dendrite extends from axon ◊ Occur in afferent pathways of the visual, ...
eprint_11_20575_1347
... Line brain ventricles and spinal cord central canal Help form choroid plexuses that secrete CSF ...
... Line brain ventricles and spinal cord central canal Help form choroid plexuses that secrete CSF ...
receptor
... starts to salivate and his stomach starts to grumble. Model the neurons and their connections required to smell breakfast and have the reaction of mouth salivating and stomach grumbling. Group 3: As Joe opens the door to leave for school, he realizes it’s colder than he thought. He walks back inside ...
... starts to salivate and his stomach starts to grumble. Model the neurons and their connections required to smell breakfast and have the reaction of mouth salivating and stomach grumbling. Group 3: As Joe opens the door to leave for school, he realizes it’s colder than he thought. He walks back inside ...