Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses Quiz Answers
... nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse ...
... nodes of Ranvier b) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by nodes of Ranvier c) many dendrites and one axon covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse d) one dendrite and many axons covered with a myelin sheath interrupted by the synapse ...
Slide ()
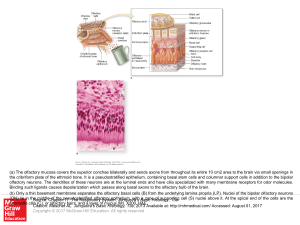
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
Slide ()
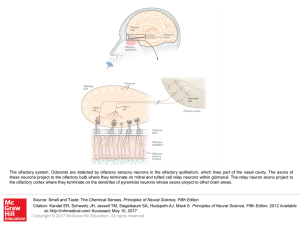
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
Bridget Lecture 2 Notes The Neurons o Functional classes (CNS
... ▪ Force of diffusion flows high to low into the cell ▪ Electrostatic pressure based on cell repulsion pushes the ion back out o Intracellular o Anion o High concentration K+ ...
... ▪ Force of diffusion flows high to low into the cell ▪ Electrostatic pressure based on cell repulsion pushes the ion back out o Intracellular o Anion o High concentration K+ ...
This Week in The Journal - Journal of Neuroscience
... presynaptic terminals. Later, abnormal mitochondriaappearedandtheirtransportratedeclined. Around the same time, the number of presynaptic vesicles decreased and their size increased, and synaptic fatigue during highfrequency stimulation increased. These data support the hypothesis that mitochondrial ...
... presynaptic terminals. Later, abnormal mitochondriaappearedandtheirtransportratedeclined. Around the same time, the number of presynaptic vesicles decreased and their size increased, and synaptic fatigue during highfrequency stimulation increased. These data support the hypothesis that mitochondrial ...
dendritic integration
... branches change our view of synaptic integration? The authors find that a spike in a single branch of the basal dendrites in a layer-5 pyramidal neuron produces a depolarization of about 10 mV in the soma. Because a depolarization of 15–20 mV is required to span the gap between the resting potential ...
... branches change our view of synaptic integration? The authors find that a spike in a single branch of the basal dendrites in a layer-5 pyramidal neuron produces a depolarization of about 10 mV in the soma. Because a depolarization of 15–20 mV is required to span the gap between the resting potential ...
Slide ()
... The olfactory epithelium. A. The olfactory epithelium contains sensory neurons interspersed with supporting cells as well as a basal layer of stem cells. Cilia extend from the dendrite of each neuron into the mucus lining the nasal cavity. An axon extends from the basal end of each neuron to the olf ...
... The olfactory epithelium. A. The olfactory epithelium contains sensory neurons interspersed with supporting cells as well as a basal layer of stem cells. Cilia extend from the dendrite of each neuron into the mucus lining the nasal cavity. An axon extends from the basal end of each neuron to the olf ...
Neurons - Seung Lab
... The axon is the output element. • Thin and often long. • A single axon leaves the soma, but may later branch, usually at right angles. • Action potentials travel from the soma to the presynaptic terminals. ...
... The axon is the output element. • Thin and often long. • A single axon leaves the soma, but may later branch, usually at right angles. • Action potentials travel from the soma to the presynaptic terminals. ...
Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
... The results reveal basic insights into the dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely disper ...
... The results reveal basic insights into the dendritic organization of sensory inputs to neurons of the visual cortex in vivo. • Identified discrete dendritic hotspots as synaptic entry sites for specific sensory features • Afferent sensory inputs with the same orientation preference are widely disper ...
Document
... 2. Begins with initial segment 3. May be absent (amacrine cells) 4. Unique in most cells 5. May be myelinated or no 6. Never contains ribosomes 7. Smooth contours, cylindrical shape 8. The thinnest process at the origin 9. Ramifies by branching at obtuse angles 10. Gives rise to branches of same dia ...
... 2. Begins with initial segment 3. May be absent (amacrine cells) 4. Unique in most cells 5. May be myelinated or no 6. Never contains ribosomes 7. Smooth contours, cylindrical shape 8. The thinnest process at the origin 9. Ramifies by branching at obtuse angles 10. Gives rise to branches of same dia ...
L3. Olfaction (Zoltán Nusser) Olfactory epithelium: Cilium and
... providing the main output of the bulb. The primary dendrite arborizes in a single glomerulus, many secondary dendrites are in the external plexiform layer, where they receive dendro-dendritic inhibition from granule cells Tufted cells (excitatory, glutamergic): principal cells of the MOB. Provide ...
... providing the main output of the bulb. The primary dendrite arborizes in a single glomerulus, many secondary dendrites are in the external plexiform layer, where they receive dendro-dendritic inhibition from granule cells Tufted cells (excitatory, glutamergic): principal cells of the MOB. Provide ...
A1985AUW1100002
... were maintained by the addition of summated. depolariiing atterpotentials. Third, the hippocampal neurons engaged a powerful recurrent inhibitory system, which gave rise to a prolonged inhibition of 200 to 400 msec, several orders of magnitude longer than the inhibition previously encountered in the ...
... were maintained by the addition of summated. depolariiing atterpotentials. Third, the hippocampal neurons engaged a powerful recurrent inhibitory system, which gave rise to a prolonged inhibition of 200 to 400 msec, several orders of magnitude longer than the inhibition previously encountered in the ...
3-8_NeuronDiversity_SalmaA
... Dendrites: the ‘input’ of the neuron, means tree in Greek. Soma: the cell’s body, has typical organells. Axon: the ‘output’ of the neuron, transfer information to other neurons. The space between neighbouring cell is known as the synaptic cleft, and is approximately 20 nm thick. The purpose of ...
... Dendrites: the ‘input’ of the neuron, means tree in Greek. Soma: the cell’s body, has typical organells. Axon: the ‘output’ of the neuron, transfer information to other neurons. The space between neighbouring cell is known as the synaptic cleft, and is approximately 20 nm thick. The purpose of ...
Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term…
... This is mostly review for those of you that took 2606 The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells ...
... This is mostly review for those of you that took 2606 The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells ...
research Nerve Cells, Axons, Dendrites, and Synapses: The
... The nerve cells and their axons, dendrites, and synapses form the most important components of the nervous system and as such are the foundation for rehabilitation. A nerve cell (neuron) is the structural unit of the nervous system. Axons and dendrites are the parts of the neuron that make contact w ...
... The nerve cells and their axons, dendrites, and synapses form the most important components of the nervous system and as such are the foundation for rehabilitation. A nerve cell (neuron) is the structural unit of the nervous system. Axons and dendrites are the parts of the neuron that make contact w ...
Slide ()
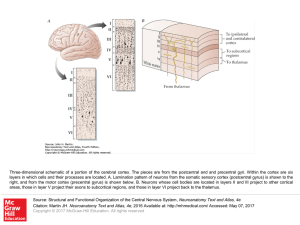
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
R24Summary Statement - University of Illinois Archives
... biological locus for understanding potentiation, learning, and memory. The proposal claims, with some justice, that the geometry of neurons gives students of this biology an advantage over those who study information processing in other kinds of cells. The geometrical specializations of neurons plac ...
... biological locus for understanding potentiation, learning, and memory. The proposal claims, with some justice, that the geometry of neurons gives students of this biology an advantage over those who study information processing in other kinds of cells. The geometrical specializations of neurons plac ...
CORTEX I. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS a. Cerebral cortex = grey
... *Prominent layer 4 in primary sensory areas = granular cortex (regions that lack prominent layer 4 = agranular) b. Myelin Stains (ie Weigert stain) i. Vertical bundles – radiate through cortex, contain efferents to white matter 1. Adjacent cortical columns – have different receptive field properties ...
... *Prominent layer 4 in primary sensory areas = granular cortex (regions that lack prominent layer 4 = agranular) b. Myelin Stains (ie Weigert stain) i. Vertical bundles – radiate through cortex, contain efferents to white matter 1. Adjacent cortical columns – have different receptive field properties ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Dendrites receive signals – axons send them. There are hundreds of dendrites but usually just one axon. Axons can be very long (> 1 m) while dendrites are < 2 mm. Axons have the same diameter the entire length – dendrites taper. Axons have terminals (synapses) and no ribosomes. Dendrites have spines ...
... Dendrites receive signals – axons send them. There are hundreds of dendrites but usually just one axon. Axons can be very long (> 1 m) while dendrites are < 2 mm. Axons have the same diameter the entire length – dendrites taper. Axons have terminals (synapses) and no ribosomes. Dendrites have spines ...
The Brain and Behavior
... the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One axon communicates with the spinal cord; one with either the skin or muscle. ...
... the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One axon communicates with the spinal cord; one with either the skin or muscle. ...
3-2_UniqueFt_of_Neurons
... glial cells: they live in structural and functional symbiosis with the neurons, supporting them through various ways, including physical protection and regulating the internal environment (of the brain for example) neurofilaments: the major component of the neural cytoskeleton, assembled into larger ...
... glial cells: they live in structural and functional symbiosis with the neurons, supporting them through various ways, including physical protection and regulating the internal environment (of the brain for example) neurofilaments: the major component of the neural cytoskeleton, assembled into larger ...
Neuroanatomy - UCSD Cognitive Science
... Dendrites generally receive synaptic input (i.e. are postsynaptic) and axons generally send synaptic output (i.e., are presynaptic) Dynamic polarization (processes of input, integration, output) may be considered “computation.” However, DP is NOT independent of the neuroanatomy and can occur in both ...
... Dendrites generally receive synaptic input (i.e. are postsynaptic) and axons generally send synaptic output (i.e., are presynaptic) Dynamic polarization (processes of input, integration, output) may be considered “computation.” However, DP is NOT independent of the neuroanatomy and can occur in both ...
17-01-05 1 Golgi - stained neurons Neuronal function
... # of inputs to cell determined by size and complexity of the dendritic “arbor” - can release transmitter in some neurons - contain ribosomes which means they can potentially make proteins locally! - vary in diameter… generally thick proximal, thinner distally -contain lots of actin Axons: ...
... # of inputs to cell determined by size and complexity of the dendritic “arbor” - can release transmitter in some neurons - contain ribosomes which means they can potentially make proteins locally! - vary in diameter… generally thick proximal, thinner distally -contain lots of actin Axons: ...
Laminar and Columnar organization of the cerebral cortex
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...