Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
the nervous system
... the neuron membranes • The space between neurons is called the synapse • Neurotransmitters carry impulses across the synapse ...
... the neuron membranes • The space between neurons is called the synapse • Neurotransmitters carry impulses across the synapse ...
One difference between axons and dendrites is that
... One thing that differentiates neurons from other body cells is that only neurons A. contain mitochondria. B. have a nucleus in their cell body. C. have an outer membrane that acts as a filter. D. have axons and dendrites. One difference between axons and dendrites is that A. axons carry signals to t ...
... One thing that differentiates neurons from other body cells is that only neurons A. contain mitochondria. B. have a nucleus in their cell body. C. have an outer membrane that acts as a filter. D. have axons and dendrites. One difference between axons and dendrites is that A. axons carry signals to t ...
L8_Nerve_tissue_and_organs
... • All neurons have a cell body (pericaryon) and processes, the axon and dendrites • Dendrites are neuronal processes that receive stimuli from other nerve cells or from the environment • Axons are neuronal processes that transmit stimuli to other neurons or to effector cells • There is only one axon ...
... • All neurons have a cell body (pericaryon) and processes, the axon and dendrites • Dendrites are neuronal processes that receive stimuli from other nerve cells or from the environment • Axons are neuronal processes that transmit stimuli to other neurons or to effector cells • There is only one axon ...
Slide ()
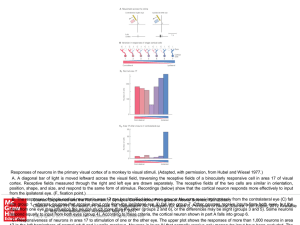
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
presentation
... n Constant PSP = 180mv n Gaussian PSP generates spikes with more timing reliable n Ion-channel variability is included (Gaussian) ...
... n Constant PSP = 180mv n Gaussian PSP generates spikes with more timing reliable n Ion-channel variability is included (Gaussian) ...
Cortical region interactions and the functional role of apical
... a distinctive morphology, as illustrated in Figure 1, that is characterized by two separate dendritic arbors: the basal dendrites which occupy the same layer as the cell body, and the apical dendrites which ascend into more superficial layers. For pyramidal cells in layer VI the apical dendrite exte ...
... a distinctive morphology, as illustrated in Figure 1, that is characterized by two separate dendritic arbors: the basal dendrites which occupy the same layer as the cell body, and the apical dendrites which ascend into more superficial layers. For pyramidal cells in layer VI the apical dendrite exte ...
Nervous System The nervous system is divided into two parts: 1
... 1. Multipolar - several dendrites and one axon. e.g., motor neuron (ventral horn cell) 2. Bipolar - have a process at each end. This type of neuron is relatively rare. They are found in acustic and vestibular nuclei associated with CN VIII, they act as olfactory receptors in CN I, and they are also ...
... 1. Multipolar - several dendrites and one axon. e.g., motor neuron (ventral horn cell) 2. Bipolar - have a process at each end. This type of neuron is relatively rare. They are found in acustic and vestibular nuclei associated with CN VIII, they act as olfactory receptors in CN I, and they are also ...
Neuroanatomy
... 1. Parallel processing within functional systems 2. Axons with common origins and terminations form bundles ...
... 1. Parallel processing within functional systems 2. Axons with common origins and terminations form bundles ...
What is the structure of the neuron? (continued)
... than neurons. • Surround and support neurons, control the supply of nutrients to neurons, assist in the exchange of chemicals between neurons, destroy and remove damaged neurons. ...
... than neurons. • Surround and support neurons, control the supply of nutrients to neurons, assist in the exchange of chemicals between neurons, destroy and remove damaged neurons. ...
Laboratory 9
... Contain some cell organelles Cell membrane contains receptors to respond to stimuli Transmit graded potentials towards the soma ...
... Contain some cell organelles Cell membrane contains receptors to respond to stimuli Transmit graded potentials towards the soma ...
BOX 11.1 NEURONAL CABLE THEORY AND COMPUTATIONAL
... this equation to analyze voltage changes in simple linear cables, he also applied it to branching cables and showed that it could be used to analyze dendrites with arbitrary branching geometries. Indeed, one of Rall’s (1959) key contributions was his analysis of the effects of branching in cables: p ...
... this equation to analyze voltage changes in simple linear cables, he also applied it to branching cables and showed that it could be used to analyze dendrites with arbitrary branching geometries. Indeed, one of Rall’s (1959) key contributions was his analysis of the effects of branching in cables: p ...
Nerve Histology Microscope Lab PRE-LAB
... neurotransmitter that inhibits surrounding neural messages allowing them master control over motor movements. The loss of or damage to Purkinje cells can give rise to certain neurological diseases. During embryonic growth, Purkinje cells can be permanently destroyed by exposure to alcohol thereby co ...
... neurotransmitter that inhibits surrounding neural messages allowing them master control over motor movements. The loss of or damage to Purkinje cells can give rise to certain neurological diseases. During embryonic growth, Purkinje cells can be permanently destroyed by exposure to alcohol thereby co ...
here
... vision, taste touch) to the CNS. Relay Neurons – Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other. Only found in brain and spinal cord. Motor Neurons – form synapses with muscles and control their contractions. ...
... vision, taste touch) to the CNS. Relay Neurons – Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other. Only found in brain and spinal cord. Motor Neurons – form synapses with muscles and control their contractions. ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... 2.2.i How can biomedical professionals help treat, cure and improve the quality of life of those suffering from nervous system disorders? The main person that treats neurological disorders is a Neurologist (one who studies nerves). That’s a special kind of doctor that specializes in the nervous syst ...
... 2.2.i How can biomedical professionals help treat, cure and improve the quality of life of those suffering from nervous system disorders? The main person that treats neurological disorders is a Neurologist (one who studies nerves). That’s a special kind of doctor that specializes in the nervous syst ...
Slide 1
... • List the different parts of a neuron? • What are the functions of a neuron? • List the different types of glia cells and name one function for each? ...
... • List the different parts of a neuron? • What are the functions of a neuron? • List the different types of glia cells and name one function for each? ...
Lecture 6
... the brain with a surface of 2000cm^2. At the back is the occipital area important for visual processing (the later takes up 40% of the brain) very high visual resolution (& capability for associative and therefore creative thinking?). Frontal area important for short term working memory, and plann ...
... the brain with a surface of 2000cm^2. At the back is the occipital area important for visual processing (the later takes up 40% of the brain) very high visual resolution (& capability for associative and therefore creative thinking?). Frontal area important for short term working memory, and plann ...
File
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
Cellular Neuroanatomy II
... Axons can be distinguished from dendrites by several features including shape, length, myelination and function. Dendrites often taper off in shape, are shorter (usually <200 mm) and branch profusely at all angles. They do not have myelin sheaths, and receive electrochemical signals. In contrast, ax ...
... Axons can be distinguished from dendrites by several features including shape, length, myelination and function. Dendrites often taper off in shape, are shorter (usually <200 mm) and branch profusely at all angles. They do not have myelin sheaths, and receive electrochemical signals. In contrast, ax ...
Nervous_System_Neurons
... Endorphins are neurotransmitters produced in the brain that reduce pain They have also been known to induce euphoria. Drugs such as morphine, heroine and cocaine are classic endorphin-releasing entities Laughter, chocolate, acupuncture, exercise trigger an endorphin release “runner’s high” ...
... Endorphins are neurotransmitters produced in the brain that reduce pain They have also been known to induce euphoria. Drugs such as morphine, heroine and cocaine are classic endorphin-releasing entities Laughter, chocolate, acupuncture, exercise trigger an endorphin release “runner’s high” ...
PNS and Transmission
... Transmission • Transmission is carried out by molecules called neurotransmitters. These are stored in vesicles in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and ...
... Transmission • Transmission is carried out by molecules called neurotransmitters. These are stored in vesicles in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and ...