Aim: What is the structure of the DNA molecule?
... DNA is a special molecule found in the cells which make up a chromosome. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell. (Therefore DNA is in the nucleus) There are 46 pairs of chromosomes in the human cell. DNA is an instruction manual for all the processes that the organism does. DNA has all the i ...
... DNA is a special molecule found in the cells which make up a chromosome. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of a cell. (Therefore DNA is in the nucleus) There are 46 pairs of chromosomes in the human cell. DNA is an instruction manual for all the processes that the organism does. DNA has all the i ...
FREE Sample Here
... Restriction endonucleases are enzymes that are produced by bacteria and __________ degrade viral proteins degrade DNA have no laboratory applications degrade lipids ...
... Restriction endonucleases are enzymes that are produced by bacteria and __________ degrade viral proteins degrade DNA have no laboratory applications degrade lipids ...
NUCLEIC ACID
... At the end of lecture the student should be able to: • Define nucleic acids • Discuss the structure and types of nucleic acids; DNA and RNA • Differentiate between DNA and RNA • Define central dogma and justify its relation with living state ...
... At the end of lecture the student should be able to: • Define nucleic acids • Discuss the structure and types of nucleic acids; DNA and RNA • Differentiate between DNA and RNA • Define central dogma and justify its relation with living state ...
slides
... between individuals is quite small. • Out of 3 billion nucleotides, only roughly 3 million base pairs (0.1%) are different between individual genomes of humans. • Although there is a finite number of possible variations, the number is so high (43,000,000) that we can assume no two individual people ...
... between individuals is quite small. • Out of 3 billion nucleotides, only roughly 3 million base pairs (0.1%) are different between individual genomes of humans. • Although there is a finite number of possible variations, the number is so high (43,000,000) that we can assume no two individual people ...
Unit 5 Review
... 13. Number the steps of DNA replication in the correct order (1, 2, 3) _______ Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing. _______ DNA unwinds. _______ The DNA of the daughter strands winds with together with its parent strand. 14. Show the complimentary base pairing that would oc ...
... 13. Number the steps of DNA replication in the correct order (1, 2, 3) _______ Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing. _______ DNA unwinds. _______ The DNA of the daughter strands winds with together with its parent strand. 14. Show the complimentary base pairing that would oc ...
cDNA libraries, Microarray Analysis
... uses RNA as a template to make a complimentary single stranded DNA -Second strand synthesis ...
... uses RNA as a template to make a complimentary single stranded DNA -Second strand synthesis ...
chapter 11, 12, 13 practice questions
... change? What kind of mutation is this (point mutation or frameshift mutation)? F) Delete the 7th base in the original strand of DNA. How many amino acids are affected in the change? What kind of mutation is this (point mutation or frameshift mutation)? 2. Refer to Figure 11.12 on pg. 300 and describ ...
... change? What kind of mutation is this (point mutation or frameshift mutation)? F) Delete the 7th base in the original strand of DNA. How many amino acids are affected in the change? What kind of mutation is this (point mutation or frameshift mutation)? 2. Refer to Figure 11.12 on pg. 300 and describ ...
Name:
... the bases ----------------------------10.Which bases are the purines? 11. Which bases are the pyrimidines? 12. Label the following molecule. C ...
... the bases ----------------------------10.Which bases are the purines? 11. Which bases are the pyrimidines? 12. Label the following molecule. C ...
File
... As shown in Figure 1, DNA looks like an incredibly long twisted ladder. This shape is called a double helix. The sides of the ladder are a linked chain of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules (called the backbone). The rungs connected to the sugar molecules are known as bases. ...
... As shown in Figure 1, DNA looks like an incredibly long twisted ladder. This shape is called a double helix. The sides of the ladder are a linked chain of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules (called the backbone). The rungs connected to the sugar molecules are known as bases. ...
DNA Extraction KEY
... 4. What do you think might happen if alcohol was added quickly and the two layers mixed? The DNA wouldn’t separate as easily—would have to wait. 5. Describe the appearance of the DNA you extracted (color, shape, texture, consistency). Color- clear; shape-tubular; texture- _____; consistency-_______ ...
... 4. What do you think might happen if alcohol was added quickly and the two layers mixed? The DNA wouldn’t separate as easily—would have to wait. 5. Describe the appearance of the DNA you extracted (color, shape, texture, consistency). Color- clear; shape-tubular; texture- _____; consistency-_______ ...
Human Genomic DNA Quality Controls for aCGH and Microarray
... DNA from research laboratories can be of uneven quality. Our DNA comes from immortalized cell lines, where the sequences are validated and the DNA is unchanging. ...
... DNA from research laboratories can be of uneven quality. Our DNA comes from immortalized cell lines, where the sequences are validated and the DNA is unchanging. ...
Ch. 11
... 2. There are 4 different nitrogen bases that make up DNA. The bases pair together as follows: ___________ and _____ 3. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick proposed that DNA consists of 4 nucleotides found inside the nucleus in the form of a ____________________________ B. Replication of DNA a. _ ...
... 2. There are 4 different nitrogen bases that make up DNA. The bases pair together as follows: ___________ and _____ 3. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick proposed that DNA consists of 4 nucleotides found inside the nucleus in the form of a ____________________________ B. Replication of DNA a. _ ...
1 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... 4. Which of the following contributes significantly to variation in nuclear genome size among plants. a. amounts of highly repetitive DNA b. amount of selfish DNA (e.g., such as transposons) c. frequency of introns d. a and b e. all of the above 5. Which of the following is incorrect concerning the ...
... 4. Which of the following contributes significantly to variation in nuclear genome size among plants. a. amounts of highly repetitive DNA b. amount of selfish DNA (e.g., such as transposons) c. frequency of introns d. a and b e. all of the above 5. Which of the following is incorrect concerning the ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... Which of the following clusters of terms accurately describes DNA as it is generally viewed to exist in prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 1. Double-stranded, parallel, (A+T)/(C+G)= variable, (A+G)/(C+T)=1.0 2. Single-stranded, antiparallel, (A+T)/(C+G)=1.0, (A+G)/C+T)=1.0 3. Double-stranded, antiparallel, ...
... Which of the following clusters of terms accurately describes DNA as it is generally viewed to exist in prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 1. Double-stranded, parallel, (A+T)/(C+G)= variable, (A+G)/(C+T)=1.0 2. Single-stranded, antiparallel, (A+T)/(C+G)=1.0, (A+G)/C+T)=1.0 3. Double-stranded, antiparallel, ...
DNA Structure Copy Cats Protein Nucleic Acids RANDOM!
... Photo 51 was taken by which scientist? (This was an integral part in discovering the structure – yet they didn’t receive credit for it) ...
... Photo 51 was taken by which scientist? (This was an integral part in discovering the structure – yet they didn’t receive credit for it) ...
Biotechnology
... RECOMBINANT DNA The process of altering the genetic material of cells or organisms to allow them to make new substances is called genetic engineering. Recombinant DNA results when DNA from two organisms is joined ...
... RECOMBINANT DNA The process of altering the genetic material of cells or organisms to allow them to make new substances is called genetic engineering. Recombinant DNA results when DNA from two organisms is joined ...
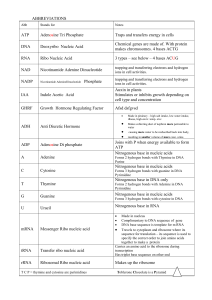
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
Biology Test Topics Chapters 11-12 Slideshows
... Polymer (macromolecule) and monomer (name and three parts and also list the four types of bases that can be present in this monomer) Be able to label a diagram of DNA Bonding type between sugar and phosphate molecules Bonding type between bases Shape of DNA Major contributions of the fol ...
... Polymer (macromolecule) and monomer (name and three parts and also list the four types of bases that can be present in this monomer) Be able to label a diagram of DNA Bonding type between sugar and phosphate molecules Bonding type between bases Shape of DNA Major contributions of the fol ...
Recombination
... A. The sizes of DNA molecules can be determined by the position to which they migrate in a gel. B. Smaller DNA molecules move faster and farther than larger ones. C. Gels used for electrophoresis of DNA are made out of agarose. D. DNA molecules move through the gel towards the negative electrode. ...
... A. The sizes of DNA molecules can be determined by the position to which they migrate in a gel. B. Smaller DNA molecules move faster and farther than larger ones. C. Gels used for electrophoresis of DNA are made out of agarose. D. DNA molecules move through the gel towards the negative electrode. ...
Document
... In 1928, Frederick Griffith found that some chemical factor from heat-killed bacteria of one strain could change the inherited characteristics of another strain. He called the process transformation because one type of bacteria (a harmless form) had been changed permanently into another (a disease-c ...
... In 1928, Frederick Griffith found that some chemical factor from heat-killed bacteria of one strain could change the inherited characteristics of another strain. He called the process transformation because one type of bacteria (a harmless form) had been changed permanently into another (a disease-c ...
PreAP Biology Study Guide Unit 4: Molecular Genetics 4.1 What are
... and not proteins, were the macromolecules that were passed on to the next generation and actually contained the “information” for creating a organism. This experiment which involved the radioactive elements Phosphorus 32 and Sulfur 35 went on to become known as the Hershey-Chase experiment. In no mo ...
... and not proteins, were the macromolecules that were passed on to the next generation and actually contained the “information” for creating a organism. This experiment which involved the radioactive elements Phosphorus 32 and Sulfur 35 went on to become known as the Hershey-Chase experiment. In no mo ...
DNA

Deoxyribonucleic acid (/diˌɒksiˌraɪbɵ.njuːˌkleɪ.ɨk ˈæsɪd/; DNA) is a molecule that carries most of the genetic instructions used in the development, functioning and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses. DNA is a nucleic acid; alongside proteins and carbohydrates, nucleic acids compose the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Most DNA molecules consist of two biopolymer strands coiled around each other to form a double helix. The two DNA strands are known as polynucleotides since they are composed of simpler units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogen-containing nucleobase—either cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), or thymine (T)—as well as a monosaccharide sugar called deoxyribose and a phosphate group. The nucleotides are joined to one another in a chain by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next, resulting in an alternating sugar-phosphate backbone. According to base pairing rules (A with T, and C with G), hydrogen bonds bind the nitrogenous bases of the two separate polynucleotide strands to make double-stranded DNA. The total amount of related DNA base pairs on Earth is estimated at 5.0 x 1037, and weighs 50 billion tonnes. In comparison, the total mass of the biosphere has been estimated to be as much as 4 TtC (trillion tons of carbon).DNA stores biological information. The DNA backbone is resistant to cleavage, and both strands of the double-stranded structure store the same biological information. Biological information is replicated as the two strands are separated. A significant portion of DNA (more than 98% for humans) is non-coding, meaning that these sections do not serve as patterns for protein sequences.The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions to each other and are therefore anti-parallel. Attached to each sugar is one of four types of nucleobases (informally, bases). It is the sequence of these four nucleobases along the backbone that encodes biological information. Under the genetic code, RNA strands are translated to specify the sequence of amino acids within proteins. These RNA strands are initially created using DNA strands as a template in a process called transcription.Within cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. During cell division these chromosomes are duplicated in the process of DNA replication, providing each cell its own complete set of chromosomes. Eukaryotic organisms (animals, plants, fungi, and protists) store most of their DNA inside the cell nucleus and some of their DNA in organelles, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts. In contrast, prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) store their DNA only in the cytoplasm. Within the chromosomes, chromatin proteins such as histones compact and organize DNA. These compact structures guide the interactions between DNA and other proteins, helping control which parts of the DNA are transcribed.First isolated by Friedrich Miescher in 1869 and with its molecular structure first identified by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, DNA is used by researchers as a molecular tool to explore physical laws and theories, such as the ergodic theorem and the theory of elasticity. The unique material properties of DNA have made it an attractive molecule for material scientists and engineers interested in micro- and nano-fabrication. Among notable advances in this field are DNA origami and DNA-based hybrid materials.The obsolete synonym ""desoxyribonucleic acid"" may occasionally be encountered, for example, in pre-1953 genetics.