Go to Classzone - Issaquah Connect
... 2. __________________unzip the DNA double helix exposing the nucleotide bases. 3. Nucleotides pair up with exposed bases on each side, and _____________________ bond these nucleotides together to make new strands. 4. Two identical strands of DNA are formed as a result of __________________. 5. Each ...
... 2. __________________unzip the DNA double helix exposing the nucleotide bases. 3. Nucleotides pair up with exposed bases on each side, and _____________________ bond these nucleotides together to make new strands. 4. Two identical strands of DNA are formed as a result of __________________. 5. Each ...
Intermediate Inheritance or Incomplete Dominance
... • Avery and other scientists discovered that DNA is the nucleic acid that stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation of an organism to the next ...
... • Avery and other scientists discovered that DNA is the nucleic acid that stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation of an organism to the next ...
Chapter 12 Assessment
... offspring. Some genetic disorders appear at birth, and others do not show up until later in life. For this project you will choose a particular genetic disorder and create a tri-fold brochure that could be displayed in the waiting room of a doctor's office. Make your brochure creative and informativ ...
... offspring. Some genetic disorders appear at birth, and others do not show up until later in life. For this project you will choose a particular genetic disorder and create a tri-fold brochure that could be displayed in the waiting room of a doctor's office. Make your brochure creative and informativ ...
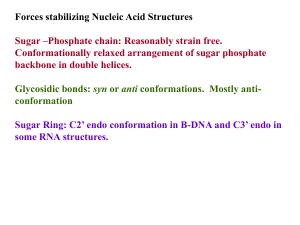
NA stabilization
... Other kind of pairings do occur in certain DNA and RNA structures. Watson Crick Base pairs are most stable as demonstrated by Lord and Rich by IR spectroscopy. ...
... Other kind of pairings do occur in certain DNA and RNA structures. Watson Crick Base pairs are most stable as demonstrated by Lord and Rich by IR spectroscopy. ...
Jeremy Narby`s spiral serpents of DNA: this is
... and animal creation and speciation—hundreds of millions of years of activity—took place on a scale and with a vividness impossible to describe. He learned that the dragonlike creatures were inside all forms of life, including humans. Harner later noted "In retrospect one could say they were almost l ...
... and animal creation and speciation—hundreds of millions of years of activity—took place on a scale and with a vividness impossible to describe. He learned that the dragonlike creatures were inside all forms of life, including humans. Harner later noted "In retrospect one could say they were almost l ...
Introduction
... HyTaq DNA Polymerase is a thermostable recombinant DNA polymerase, which exhibits very high activity in primer extension and other molecular biology applications. The enzyme is isolated from Thermus aquaticus and has a molecular weight of approximately 94 kDa. HyTaq DNA Polymerase has both a 5'→3' D ...
... HyTaq DNA Polymerase is a thermostable recombinant DNA polymerase, which exhibits very high activity in primer extension and other molecular biology applications. The enzyme is isolated from Thermus aquaticus and has a molecular weight of approximately 94 kDa. HyTaq DNA Polymerase has both a 5'→3' D ...
Introduction
... PCR to amplify a 132bp region of exon 8 containing the mutation causative for achondroplasia was carried out on 5, 10 or 20µl of DNA extracted from 400µl or 800µl of plasma, as well as on genomic DNA from an unaffected and a positive control. On an unaffected DNA sample, restriction digest of the PC ...
... PCR to amplify a 132bp region of exon 8 containing the mutation causative for achondroplasia was carried out on 5, 10 or 20µl of DNA extracted from 400µl or 800µl of plasma, as well as on genomic DNA from an unaffected and a positive control. On an unaffected DNA sample, restriction digest of the PC ...
Worksheet for videos below
... ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? __________ ...
... ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? __________ ...
Topic 11 DNA intro - Manhasset Public Schools
... of the ladder are made of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules. The sugar is deoxyribose. The rungs of the ladder are pairs of 4 types of nitrogen bases: Adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. The bases are known by their coded letters A, G, T, C. These bases always bond in a certain way as a ...
... of the ladder are made of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules. The sugar is deoxyribose. The rungs of the ladder are pairs of 4 types of nitrogen bases: Adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. The bases are known by their coded letters A, G, T, C. These bases always bond in a certain way as a ...
Investigation 3 power point
... Steps of transcription cont. In eukaryotes, this marks a single gene. In prokaryotes, the marks several functionally related genes. When polymerase bind the DNA molecule separates. Only one separated chain called the template is used for transcription. Next, Polymerase attaches to the first nucleot ...
... Steps of transcription cont. In eukaryotes, this marks a single gene. In prokaryotes, the marks several functionally related genes. When polymerase bind the DNA molecule separates. Only one separated chain called the template is used for transcription. Next, Polymerase attaches to the first nucleot ...
Learning Targets
... labeling the parts of a nucleotide and matching the proper base pairs. Explain, using specific details about the model of DNA: The number of strands The shape What each strand is made up of The composition of the sides of the ladder The location of where the nitrogen bases attach An expl ...
... labeling the parts of a nucleotide and matching the proper base pairs. Explain, using specific details about the model of DNA: The number of strands The shape What each strand is made up of The composition of the sides of the ladder The location of where the nitrogen bases attach An expl ...
Genetics Review
... • Translation: In the cytoplasm, on the ribosome, the mRNA codon matches tRNA anticodon to bring the proper amino acid in for bonding. Once the whole mRNA is read by the ribosome, the stop codon ends the production of the peptide chain; the protein is complete! ...
... • Translation: In the cytoplasm, on the ribosome, the mRNA codon matches tRNA anticodon to bring the proper amino acid in for bonding. Once the whole mRNA is read by the ribosome, the stop codon ends the production of the peptide chain; the protein is complete! ...
Bio EOC Cram
... - bacteria, viruses, radioactive P & S - observed which material was injected (DNA) - Genetic material = DNA ...
... - bacteria, viruses, radioactive P & S - observed which material was injected (DNA) - Genetic material = DNA ...
Have your DNA and Eat it Too!
... the bases will produce a particular protein that controls specific cell functions. Each gene is a unit of inheritance and each chromosome will contain several thousand genes. ...
... the bases will produce a particular protein that controls specific cell functions. Each gene is a unit of inheritance and each chromosome will contain several thousand genes. ...
Chapter 20: DNA Technology & Genomics
... Gel used as a sieve to separate nucleic acids or proteins based on size & charge DNA (-) travels toward + electrode Long sequences remain toward top; short sequences move toward bottom banding pattern created Method which combines gel electrophoresis & nucleic acid hybridization ...
... Gel used as a sieve to separate nucleic acids or proteins based on size & charge DNA (-) travels toward + electrode Long sequences remain toward top; short sequences move toward bottom banding pattern created Method which combines gel electrophoresis & nucleic acid hybridization ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... sequential information. It states that such information cannot be transferred back from protein to either protein or nucleic acid.” Francis Crick, 1958 ...
... sequential information. It states that such information cannot be transferred back from protein to either protein or nucleic acid.” Francis Crick, 1958 ...
CHEM523 Test 3
... Your answers must be well organized and concise. You have 75 minutes to complete the exam. 1) (10 points) Draw the mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by DNA polymerase that occurs between deoxyribose at the end of a DNA chain and a deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate. Include the chemical structure of ...
... Your answers must be well organized and concise. You have 75 minutes to complete the exam. 1) (10 points) Draw the mechanism of the reaction catalyzed by DNA polymerase that occurs between deoxyribose at the end of a DNA chain and a deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate. Include the chemical structure of ...
HGP - eduBuzz.org
... Repeating sequences 2 – 4 nucleotide bases found in mostly in introns (‘junk’ DNA) The number of repeats varies from person to person, but follow patterns of Mendalian inheritance These sequences can be identified using probes. A probe is ...
... Repeating sequences 2 – 4 nucleotide bases found in mostly in introns (‘junk’ DNA) The number of repeats varies from person to person, but follow patterns of Mendalian inheritance These sequences can be identified using probes. A probe is ...
Biology Name DNA Worksheet Period ______ Use your textbook to
... Explain why DNA replication is necessary for the continuation of life. ...
... Explain why DNA replication is necessary for the continuation of life. ...
Lecture 4
... from A to T occur or A to C occur. • To determine this we manually create a set of “true” alignments and estimate the likelihood of A changing to C, for example, by counting the number of time A changes to C and computing related statistics. • Now we have a realistic “scoring matrix” which can be us ...
... from A to T occur or A to C occur. • To determine this we manually create a set of “true” alignments and estimate the likelihood of A changing to C, for example, by counting the number of time A changes to C and computing related statistics. • Now we have a realistic “scoring matrix” which can be us ...
Answers11.february
... are RNA sequences are DNA sequences are only found in eukaryotes contain no genes contain at least one gene can replicate ...
... are RNA sequences are DNA sequences are only found in eukaryotes contain no genes contain at least one gene can replicate ...
Questions11.february
... are RNA sequences are DNA sequences are only found in eukaryotes contain no genes contain at least one gene can replicate ...
... are RNA sequences are DNA sequences are only found in eukaryotes contain no genes contain at least one gene can replicate ...
SBI4U Molecular genetics UNIT_AK
... ___ 12.Which of the following post-transcriptional modifications is carried out in a prokaryotic ...
... ___ 12.Which of the following post-transcriptional modifications is carried out in a prokaryotic ...
DNA

Deoxyribonucleic acid (/diˌɒksiˌraɪbɵ.njuːˌkleɪ.ɨk ˈæsɪd/; DNA) is a molecule that carries most of the genetic instructions used in the development, functioning and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses. DNA is a nucleic acid; alongside proteins and carbohydrates, nucleic acids compose the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Most DNA molecules consist of two biopolymer strands coiled around each other to form a double helix. The two DNA strands are known as polynucleotides since they are composed of simpler units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogen-containing nucleobase—either cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), or thymine (T)—as well as a monosaccharide sugar called deoxyribose and a phosphate group. The nucleotides are joined to one another in a chain by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next, resulting in an alternating sugar-phosphate backbone. According to base pairing rules (A with T, and C with G), hydrogen bonds bind the nitrogenous bases of the two separate polynucleotide strands to make double-stranded DNA. The total amount of related DNA base pairs on Earth is estimated at 5.0 x 1037, and weighs 50 billion tonnes. In comparison, the total mass of the biosphere has been estimated to be as much as 4 TtC (trillion tons of carbon).DNA stores biological information. The DNA backbone is resistant to cleavage, and both strands of the double-stranded structure store the same biological information. Biological information is replicated as the two strands are separated. A significant portion of DNA (more than 98% for humans) is non-coding, meaning that these sections do not serve as patterns for protein sequences.The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions to each other and are therefore anti-parallel. Attached to each sugar is one of four types of nucleobases (informally, bases). It is the sequence of these four nucleobases along the backbone that encodes biological information. Under the genetic code, RNA strands are translated to specify the sequence of amino acids within proteins. These RNA strands are initially created using DNA strands as a template in a process called transcription.Within cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. During cell division these chromosomes are duplicated in the process of DNA replication, providing each cell its own complete set of chromosomes. Eukaryotic organisms (animals, plants, fungi, and protists) store most of their DNA inside the cell nucleus and some of their DNA in organelles, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts. In contrast, prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) store their DNA only in the cytoplasm. Within the chromosomes, chromatin proteins such as histones compact and organize DNA. These compact structures guide the interactions between DNA and other proteins, helping control which parts of the DNA are transcribed.First isolated by Friedrich Miescher in 1869 and with its molecular structure first identified by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, DNA is used by researchers as a molecular tool to explore physical laws and theories, such as the ergodic theorem and the theory of elasticity. The unique material properties of DNA have made it an attractive molecule for material scientists and engineers interested in micro- and nano-fabrication. Among notable advances in this field are DNA origami and DNA-based hybrid materials.The obsolete synonym ""desoxyribonucleic acid"" may occasionally be encountered, for example, in pre-1953 genetics.