Unit 8.1 Nuclear Chemistry - Review Radioactivity
... the force is observed between hadrons as the nuclear force. As has been shown by many failed free quark searches, the elementary particles affected are unobservable directly. This phenomenon is called confinement, a theory which allows only hadrons to be seen. ...
... the force is observed between hadrons as the nuclear force. As has been shown by many failed free quark searches, the elementary particles affected are unobservable directly. This phenomenon is called confinement, a theory which allows only hadrons to be seen. ...
Unit 5 File
... Unit 5 Vocabulary Atom- the basic particle from which all elements are made Theory-an unifying explanation for a broad range of hypotheses and observations Electron- a tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the outside of the nucleus of an atom Model-a representation of a complex object ...
... Unit 5 Vocabulary Atom- the basic particle from which all elements are made Theory-an unifying explanation for a broad range of hypotheses and observations Electron- a tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the outside of the nucleus of an atom Model-a representation of a complex object ...
Basic Physics Concepts Useful in Astronomy
... o Electron wants to get to a low energy o Photon – Particle of light o An electron can go up a level via absorbing a photon (photon energy amount depends on what level it wants to go to) o An electron can go down a level by spitting out a photon (photon energy amount depends on what level it wants t ...
... o Electron wants to get to a low energy o Photon – Particle of light o An electron can go up a level via absorbing a photon (photon energy amount depends on what level it wants to go to) o An electron can go down a level by spitting out a photon (photon energy amount depends on what level it wants t ...
ELECTRON CLOUD MODEL
... around the nucleus. This cloud area shows that electrons do not orbit the nucleus in definite paths, but are likely to be in a given region at any particular time. ‘Modern Electron ...
... around the nucleus. This cloud area shows that electrons do not orbit the nucleus in definite paths, but are likely to be in a given region at any particular time. ‘Modern Electron ...
03 Homework File
... Course title, week number and student’s name should appear on every sheet of the worked exercises, which should be securely bound together. Marked exercises will be returned in the box provided on the first floor the following week. The number of marks for each part is shown in []. Remember to use s ...
... Course title, week number and student’s name should appear on every sheet of the worked exercises, which should be securely bound together. Marked exercises will be returned in the box provided on the first floor the following week. The number of marks for each part is shown in []. Remember to use s ...
1991B5 A polonium nucleus of atomic number 84
... What is the velocity of the alpha particle? (Neglect relativistic effects for this calculation.) c. Where does the kinetic energy of the alpha particle come from? Explain briefly. d. Suppose that the fermium-252 nucleus could undergo a decay in which a β- particle was produced. How would this affect ...
... What is the velocity of the alpha particle? (Neglect relativistic effects for this calculation.) c. Where does the kinetic energy of the alpha particle come from? Explain briefly. d. Suppose that the fermium-252 nucleus could undergo a decay in which a β- particle was produced. How would this affect ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide
... 13. How many energy levels are needed to contain the 26 electrons of an iron atom? __________ 14. The atomic number of calcium is 20. How many valence electrons does an atom of chlorine have? ________ 15. In an electron dot diagram, the dots represent _____________ in the atom. 16. Neutral particle ...
... 13. How many energy levels are needed to contain the 26 electrons of an iron atom? __________ 14. The atomic number of calcium is 20. How many valence electrons does an atom of chlorine have? ________ 15. In an electron dot diagram, the dots represent _____________ in the atom. 16. Neutral particle ...
Nuclear Binding Energy -
... discovered earlier by J.J. Thomson himself. Knowing that atoms are electrically neutral, Thomson postulated that there must be a positive charge as well. In his plum pudding model, Thomson suggested that an atom consisted of negative electrons randomly scattered within a sphere of positive charge. E ...
... discovered earlier by J.J. Thomson himself. Knowing that atoms are electrically neutral, Thomson postulated that there must be a positive charge as well. In his plum pudding model, Thomson suggested that an atom consisted of negative electrons randomly scattered within a sphere of positive charge. E ...
DP Physics Unit 7 Quiz Review: Name
... A nuclide is a type of atom whose nuclei have specific numbers of protons and neutrons (both are called nucleons). Therefore, nuclides are composite particles of nucleons. According to the standard model, up and down quarks are the basic components of nucleons. Thus, nuclides can also be considered ...
... A nuclide is a type of atom whose nuclei have specific numbers of protons and neutrons (both are called nucleons). Therefore, nuclides are composite particles of nucleons. According to the standard model, up and down quarks are the basic components of nucleons. Thus, nuclides can also be considered ...
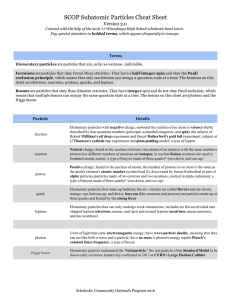
SCOP Subatomic Particles Cheat Sheet
... Fermions are particles that obey FermiDirac statistics. They have a halfinteger spin and obey the Pauli exclusion principle , which means that only one fermion can occupy a quantum state at a time. The fermions on this sheet are ...
... Fermions are particles that obey FermiDirac statistics. They have a halfinteger spin and obey the Pauli exclusion principle , which means that only one fermion can occupy a quantum state at a time. The fermions on this sheet are ...
Lesson 12.04 Study Sheet.
... If we add the mass of the nucleons and compare it to the mass of the nucleus, then we will find that some mass is missing. The difference in mass is called the mass defect (∆m): ∆m = mass of protons + mass of neutrons – mass of nucleus Einstein discovered that matter could be converted to energy (an ...
... If we add the mass of the nucleons and compare it to the mass of the nucleus, then we will find that some mass is missing. The difference in mass is called the mass defect (∆m): ∆m = mass of protons + mass of neutrons – mass of nucleus Einstein discovered that matter could be converted to energy (an ...
Week 1: Nuclear timeline (pdf, 233 KB)
... site found by searching on the name of the various discoverers. These articles not only describe the other discoveries made by these scientists but also describe their personalities and other activities. They make for very interesting reading. They weren’t all boy scouts.! ...
... site found by searching on the name of the various discoverers. These articles not only describe the other discoveries made by these scientists but also describe their personalities and other activities. They make for very interesting reading. They weren’t all boy scouts.! ...
TIMELINE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... site found by searching on the name of the various discoverers. These articles not only describe the other discoveries made by these scientists but also describe their personalities and other activities. They make for very interesting reading. They weren’t all boy scouts. The reader must understand ...
... site found by searching on the name of the various discoverers. These articles not only describe the other discoveries made by these scientists but also describe their personalities and other activities. They make for very interesting reading. They weren’t all boy scouts. The reader must understand ...
Energy Levels of Helium Nucleus
... Copyright © 2013 Cvavb Chandra Raju. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ...
... Copyright © 2013 Cvavb Chandra Raju. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ...
hrs_chemvocab_sa - parklandhonorsbiology
... Part One Use the same scantron as the scientific vocabulary to answer questions 26. Matter ...
... Part One Use the same scantron as the scientific vocabulary to answer questions 26. Matter ...
Honors Biology Summer Assignment Basic Chemistry Vocabulary
... Part One Use the same scantron as the scientific vocabulary to answer questions 26. Matter ...
... Part One Use the same scantron as the scientific vocabulary to answer questions 26. Matter ...
Slides
... GENIE vs. NuWro by MINERvA (testing GENIE) Relatively new components (introduced or developed recently also in GENIE and NEUT): 1) Meson exchange currents (two-nucleon currents): first generator ever! 2) Random phase approximation (matter polarization on top of RFG) 3) Spectral function (nucleon sel ...
... GENIE vs. NuWro by MINERvA (testing GENIE) Relatively new components (introduced or developed recently also in GENIE and NEUT): 1) Meson exchange currents (two-nucleon currents): first generator ever! 2) Random phase approximation (matter polarization on top of RFG) 3) Spectral function (nucleon sel ...