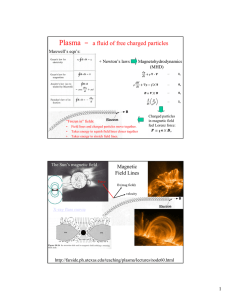
Introduction to Radioactivity and Radioactive decay
... nuclear force and the repulsive electrostatic force between protons has interesting implications for the stability of a nucleus. Atoms with very low atomic numbers have about the same number of neutrons and protons; as Z gets larger, however, stable nuclei will have more neutrons than protons. Event ...
... nuclear force and the repulsive electrostatic force between protons has interesting implications for the stability of a nucleus. Atoms with very low atomic numbers have about the same number of neutrons and protons; as Z gets larger, however, stable nuclei will have more neutrons than protons. Event ...
View PDF
... Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
... Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the electrons Electrons have so little mass that atoms must contain other particles that account for most of the mass ...
file ppt - quantware mips center
... same energy – the results of measurements in a closed system do not depend on exact microscopic conditions or phase relationships if the eigenstates at the same energy have similar macroscopic properties ...
... same energy – the results of measurements in a closed system do not depend on exact microscopic conditions or phase relationships if the eigenstates at the same energy have similar macroscopic properties ...
PHY2115 - College of DuPage
... 12. Explain the importance of photo-electric effect in the basis of quantum theory 13. Recognize the meaning of quantum mechanical wave function in terms of probability 14. Solve the time independent Schrodinger wave equation for simple cases (such as the infinite square well) and use this solution ...
... 12. Explain the importance of photo-electric effect in the basis of quantum theory 13. Recognize the meaning of quantum mechanical wave function in terms of probability 14. Solve the time independent Schrodinger wave equation for simple cases (such as the infinite square well) and use this solution ...
Homework 1 Solution
... make sure you answer the question and not stop just because the math is done. The following example contains the minimum required explanation. Example Question How much time does it take a 1 kg mass, when released from rest, to fall a distance of 1 meter? Example Solution 1. This part states the mo ...
... make sure you answer the question and not stop just because the math is done. The following example contains the minimum required explanation. Example Question How much time does it take a 1 kg mass, when released from rest, to fall a distance of 1 meter? Example Solution 1. This part states the mo ...
4 slides per page() - Wayne State University Physics and
... Elementary particle interactions The scattering of two electrons via a coulomb force This virtual photon is said to mediate the electromagnetic force. The virtual photon can never be detected because it only lasts for a vanishing small time. ...
... Elementary particle interactions The scattering of two electrons via a coulomb force This virtual photon is said to mediate the electromagnetic force. The virtual photon can never be detected because it only lasts for a vanishing small time. ...
Ununpentium does not occur naturally in the Earth`s crust. Following
... the atomic nucleus. A pure chemical substance composed of atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus [703]. [return] neutron – an elementary particle with no net charge and a rest mass of about 1.675 × 10–27 kg, slightly more than that of the proton. All atoms contain neutrons in th ...
... the atomic nucleus. A pure chemical substance composed of atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus [703]. [return] neutron – an elementary particle with no net charge and a rest mass of about 1.675 × 10–27 kg, slightly more than that of the proton. All atoms contain neutrons in th ...
Electron Configuration and Chemical Periodicity
... spinning charge – has a magnetic moment • The magnetic moment is quantized – only two orientations of the spin are allowed in a magnetic field ...
... spinning charge – has a magnetic moment • The magnetic moment is quantized – only two orientations of the spin are allowed in a magnetic field ...
Chapter 12 Nuclear Physics
... times smaller than the atom itself. Although the “surface” of a nucleus is not a sharp boundary, experiments determined an approximate radius for each nucleus. The radius is found to depend on the mass, which in turn depends on the total number A of neutrons and protons, usually called mass number. ...
... times smaller than the atom itself. Although the “surface” of a nucleus is not a sharp boundary, experiments determined an approximate radius for each nucleus. The radius is found to depend on the mass, which in turn depends on the total number A of neutrons and protons, usually called mass number. ...
Math Module II Review
... repulsion of the electromagnetic force and keeping the protons together in the nucleus. ...
... repulsion of the electromagnetic force and keeping the protons together in the nucleus. ...
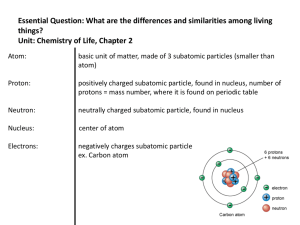
Atoms and Elements
... Building Blocks of Matter Atom- A basic unit of matter consisting of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. • Element- A pure chemical substance composed of one type of atom. • Periodic Table of the Elements- An arrangement of elements in columns based on a s ...
... Building Blocks of Matter Atom- A basic unit of matter consisting of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. • Element- A pure chemical substance composed of one type of atom. • Periodic Table of the Elements- An arrangement of elements in columns based on a s ...
Late 1800`s
... • The same situation exists for neutrons • These short range proton-neutron, proton- proton, neutronneutron forces hold the nuclear particles together are called nuclear forces. • M:\downloaded clips\clips chapter 3\Nuclear_Stability nuclear forces 3.2.asx ...
... • The same situation exists for neutrons • These short range proton-neutron, proton- proton, neutronneutron forces hold the nuclear particles together are called nuclear forces. • M:\downloaded clips\clips chapter 3\Nuclear_Stability nuclear forces 3.2.asx ...
Spin-spin splitting in NMR spectrum
... Br and Bs are the magnetic fields at which resonance occurs for the reference and the given group respectively r & s - screenings constants depending upon the electron density around proton for reference and sample respectively - ...
... Br and Bs are the magnetic fields at which resonance occurs for the reference and the given group respectively r & s - screenings constants depending upon the electron density around proton for reference and sample respectively - ...
Modified from College Physics, 8th Ed., Serway and Vuille. For the
... Section 30.8: Quarks and Color and Section 30.9: Electroweak Theory and the Standard Model Recent theories postulate that all hadrons are composed of smaller units known as quarks which have fractional electric charges and baryon numbers of 1/3 and come in six "flavors": up, down, strange, charmed, ...
... Section 30.8: Quarks and Color and Section 30.9: Electroweak Theory and the Standard Model Recent theories postulate that all hadrons are composed of smaller units known as quarks which have fractional electric charges and baryon numbers of 1/3 and come in six "flavors": up, down, strange, charmed, ...
Wavefunctions and Bound Systems
... Wavefunction “psi” solves Schroedinger’s equation and contains, in its components, all of the information we need to determine values of observables… ...
... Wavefunction “psi” solves Schroedinger’s equation and contains, in its components, all of the information we need to determine values of observables… ...
1. The gravitational force is the fundamental force that exists
... C) All nuclei with atomic number greater than 83 are unstable. As the nucleus gets larger, the short– range strong force begins to be overpowered by the long–range electrostatic repulsion. 24. Why are there only 118 elements on the periodic table? B ) Because there is an upper limit to how many prot ...
... C) All nuclei with atomic number greater than 83 are unstable. As the nucleus gets larger, the short– range strong force begins to be overpowered by the long–range electrostatic repulsion. 24. Why are there only 118 elements on the periodic table? B ) Because there is an upper limit to how many prot ...