Nuclear Physics
... • New attractive force. • Dramatically stronger than Coulomb force at short distances. • Doesn’t depend on sign of charge. • This is the ‘strong interaction’, one of the four fundamental interactions: electromagnetic interaction strong interaction weak interaction gravitational interaction 14 ...
... • New attractive force. • Dramatically stronger than Coulomb force at short distances. • Doesn’t depend on sign of charge. • This is the ‘strong interaction’, one of the four fundamental interactions: electromagnetic interaction strong interaction weak interaction gravitational interaction 14 ...
here
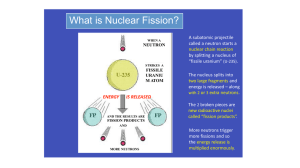
... The nucleus splits into two large fragments and energy is released – along with 2 or 3 extra neutrons. The 2 broken pieces are new radioactive nuclei called “fission products”. ...
... The nucleus splits into two large fragments and energy is released – along with 2 or 3 extra neutrons. The 2 broken pieces are new radioactive nuclei called “fission products”. ...
Pair Tutoring
... The conversion of one element into another; may be natural or artificial The length of time necessary for one-half an amount of a radioactive nuclide to disintegrate The splitting of an atomic nucleus into smaller fragments, accompanied by the release of neutrons and a large amount of energy A nucle ...
... The conversion of one element into another; may be natural or artificial The length of time necessary for one-half an amount of a radioactive nuclide to disintegrate The splitting of an atomic nucleus into smaller fragments, accompanied by the release of neutrons and a large amount of energy A nucle ...
Atomic shell model
... Bartlet, Elsasser, 1934: „independent particule model” Jensen and Göppert-Mayer, 1949: atomic shell model All of the nucleon create a collective potentialfield, wherein nucleons can move independently from each other. The nucleons Schrödinger equation’s with quantified parameters ( energy, angular m ...
... Bartlet, Elsasser, 1934: „independent particule model” Jensen and Göppert-Mayer, 1949: atomic shell model All of the nucleon create a collective potentialfield, wherein nucleons can move independently from each other. The nucleons Schrödinger equation’s with quantified parameters ( energy, angular m ...
Key Terms alpha particle - A positively charged particle
... with the simultaneous release of energy. ...
... with the simultaneous release of energy. ...
Atomic Nucleus web
... • arrangements of the fundamental particles (proton, neutron) in the different energy shells (levels) • describe the structure of the nucleus in terms of energy levels • the shells for protons and for neutrons are independent of each other • nuclei with certain number of nucleons have higher binding ...
... • arrangements of the fundamental particles (proton, neutron) in the different energy shells (levels) • describe the structure of the nucleus in terms of energy levels • the shells for protons and for neutrons are independent of each other • nuclei with certain number of nucleons have higher binding ...