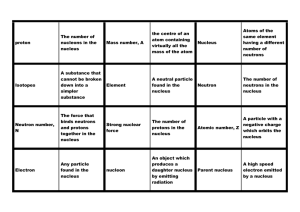
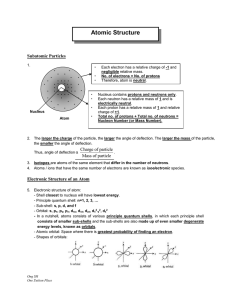
19.1 Reinforcement WKT to project
... 1. How is the chemical symbol of an element determined? 2. Of what are atoms composed? 3. Are electrons, protons, or neutrons the smallest particles? If not, what are? 4. How many types of quarks are there and what is the name of one of them? 5. Why do scientists use models to study atoms? 6. Why ha ...
... 1. How is the chemical symbol of an element determined? 2. Of what are atoms composed? 3. Are electrons, protons, or neutrons the smallest particles? If not, what are? 4. How many types of quarks are there and what is the name of one of them? 5. Why do scientists use models to study atoms? 6. Why ha ...
Nuclear atom 1 - schoolphysics
... Nuclear and atomic physics 1 1. Describe briefly the two conflicting theories of the structure of the atom. 2. Why was the nuclear model of Rutherford accepted as correct? 3. What would have happened if neutrons had been used in Rutherford’s experiment? Explain your answer. 4. What would have happen ...
... Nuclear and atomic physics 1 1. Describe briefly the two conflicting theories of the structure of the atom. 2. Why was the nuclear model of Rutherford accepted as correct? 3. What would have happened if neutrons had been used in Rutherford’s experiment? Explain your answer. 4. What would have happen ...
CH17 Self Assessment
... I will describe the ongoing development of models of the structure of matter. To meet an acceptable standard I will be able to: ...
... I will describe the ongoing development of models of the structure of matter. To meet an acceptable standard I will be able to: ...
WestFest: Sixty Years of Fireballs
... Fermi proposed the following necessary conditions for the method to apply: 1. “…only states that are easily accessible from the initial state may actually attain statistical equilibrium…” 2. “…photons (which) could be created will certainly not have time to develop (statistical equilibrium)…” 3. “N ...
... Fermi proposed the following necessary conditions for the method to apply: 1. “…only states that are easily accessible from the initial state may actually attain statistical equilibrium…” 2. “…photons (which) could be created will certainly not have time to develop (statistical equilibrium)…” 3. “N ...
Course Outline
... COURSE OBJECTIVE To enable the students understand the laws that govern the structure and properties of the atom, molecules and the nucleus. Also to provide an introduction to the elementary particles. ...
... COURSE OBJECTIVE To enable the students understand the laws that govern the structure and properties of the atom, molecules and the nucleus. Also to provide an introduction to the elementary particles. ...
Chapter 11 Vocabulary 1. Atom – the smallest particle into which an
... 2. Electrons – the negatively charged particles found in all atoms. 3. Nucleus – the tiny, extremely dense, positively charged region in the center of the atom. 4. Electron clouds – the regions inside an atom where electrons are likely to be found. 5. Protons – the positively charged particles of th ...
... 2. Electrons – the negatively charged particles found in all atoms. 3. Nucleus – the tiny, extremely dense, positively charged region in the center of the atom. 4. Electron clouds – the regions inside an atom where electrons are likely to be found. 5. Protons – the positively charged particles of th ...
Atomic-Structure-Concise-Notes
... - In a nutshell, atoms consists of various principle quantum shells, in which each principle shell consists of smaller sub-shells and the sub-shells are also made up of even smaller degenerate energy levels, known as orbitals. - Atomic orbital: Space where there is greatest probability of finding an ...
... - In a nutshell, atoms consists of various principle quantum shells, in which each principle shell consists of smaller sub-shells and the sub-shells are also made up of even smaller degenerate energy levels, known as orbitals. - Atomic orbital: Space where there is greatest probability of finding an ...
Section 25.2 Name_____________________
... Nuclei with too many neutrons undergo ______________ emission as neutrons are converted to protons and give off a high-speed electron. A ____________________ is a particle with a positive charge and the mass of an electron. Every radioisotope decays at a characteristic _______________. A ___________ ...
... Nuclei with too many neutrons undergo ______________ emission as neutrons are converted to protons and give off a high-speed electron. A ____________________ is a particle with a positive charge and the mass of an electron. Every radioisotope decays at a characteristic _______________. A ___________ ...
Physics 2 Homework 21 2013 In 1909 British physicist
... which possesses the properties of both particle and wave. One of the important properties of such an object is that it does not “like” when we try to confine it in a small volume. As we try to „squeeze‟ it, its energy increases greatly. That is why, in spite of strong attraction force, the electron ...
... which possesses the properties of both particle and wave. One of the important properties of such an object is that it does not “like” when we try to confine it in a small volume. As we try to „squeeze‟ it, its energy increases greatly. That is why, in spite of strong attraction force, the electron ...
PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics Lecture 5 Angular momentum Nucleon magnetic moments
... Quantum mechanics has only two values of for the projection of the magnetic dipole on the B axis, ±1 . ...
... Quantum mechanics has only two values of for the projection of the magnetic dipole on the B axis, ±1 . ...
Physics 12 Assignmen.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • quantum number • Bohr radius • ground state • excited states • binding energy (or ionization energy) 2. In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, what keeps the electrons from flying off into space? 3. How can the spectrum of hydrogen contain so many lines when hydrogen contains only one electr ...
... • quantum number • Bohr radius • ground state • excited states • binding energy (or ionization energy) 2. In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, what keeps the electrons from flying off into space? 3. How can the spectrum of hydrogen contain so many lines when hydrogen contains only one electr ...
Physics 12 Assignment - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... quantum number Bohr radius ground state excited states binding energy (or ionization energy) 2. In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, what keeps the electrons from flying off into space? 3. How can the spectrum of hydrogen contain so many lines when hydrogen contains only one electr ...
... quantum number Bohr radius ground state excited states binding energy (or ionization energy) 2. In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, what keeps the electrons from flying off into space? 3. How can the spectrum of hydrogen contain so many lines when hydrogen contains only one electr ...
Nuclear Physics
... Nuclear Physics For nuclei and particles, we use this notation: A ZX , where X is either the symbol for the element or for the particle ...
... Nuclear Physics For nuclei and particles, we use this notation: A ZX , where X is either the symbol for the element or for the particle ...
10. Nuclear fusion in stars
... 10.2 Slow fusion: the tunnel effect In the quantum-mechanical theory forces between particles act by the transfer of virtual particles, that do not satisfy Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle and can thus not be observed. Written in terms of the particle energy, the uncertainty principle states for t ...
... 10.2 Slow fusion: the tunnel effect In the quantum-mechanical theory forces between particles act by the transfer of virtual particles, that do not satisfy Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle and can thus not be observed. Written in terms of the particle energy, the uncertainty principle states for t ...
Basic properties of atomic nuclei
... (a) What is the energy difference between the states with the nuclear spin angular momentum components parallel and anti parallel to the field? Which state is lower in energy, the one with its spin component parallel to the fleld or the one with its spin component antiparallel to the field? How do y ...
... (a) What is the energy difference between the states with the nuclear spin angular momentum components parallel and anti parallel to the field? Which state is lower in energy, the one with its spin component parallel to the fleld or the one with its spin component antiparallel to the field? How do y ...
Modern Physics TEST
... All of the following statements about the electromagnetic force are true except which one? a. It is one of the four fundamental forces in the universe. b. It exerts a force on either charged or uncharged particles. c. It obeys the inverse-square law. d. It is produced by—and produces—electric and ma ...
... All of the following statements about the electromagnetic force are true except which one? a. It is one of the four fundamental forces in the universe. b. It exerts a force on either charged or uncharged particles. c. It obeys the inverse-square law. d. It is produced by—and produces—electric and ma ...
Unit 6 Science Vocabulary Emily 6th
... 5. an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers such that elements with similar properties fall in the same group 6. the smallest particle into which an element can be divided. 7. uncharged particles that are found within the nucleus of an atom. 8. the center of an atom made up of ...
... 5. an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers such that elements with similar properties fall in the same group 6. the smallest particle into which an element can be divided. 7. uncharged particles that are found within the nucleus of an atom. 8. the center of an atom made up of ...
Untitled - Crossword Labs
... 3. a region around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found. 6. the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 7. the smallest particle into which an element can be divided. 8. the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. 9. negatively charged parti ...
... 3. a region around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found. 6. the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. 7. the smallest particle into which an element can be divided. 8. the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. 9. negatively charged parti ...
Exercise Sheet 1 to Particle Physics I
... emitted electrons observed. Which energies do the electrons have? What is the maximal energy? Why is there something unnatural - if at all? Discuss in class and with your fellow students why we one can discuss this problem in such general terms without having to consider a specific model. Which kind ...
... emitted electrons observed. Which energies do the electrons have? What is the maximal energy? Why is there something unnatural - if at all? Discuss in class and with your fellow students why we one can discuss this problem in such general terms without having to consider a specific model. Which kind ...