here - University of Kent
... Since nuclei have spin angular momentum, just as electrons do, we need Skyrmions to spin when we want to describe nuclei as Skyrmions. Energies and allowed spin values of nuclei have so far almost exclusively been calculated by assuming that Skyrmions do not deform as they spin. We compute in the fi ...
... Since nuclei have spin angular momentum, just as electrons do, we need Skyrmions to spin when we want to describe nuclei as Skyrmions. Energies and allowed spin values of nuclei have so far almost exclusively been calculated by assuming that Skyrmions do not deform as they spin. We compute in the fi ...
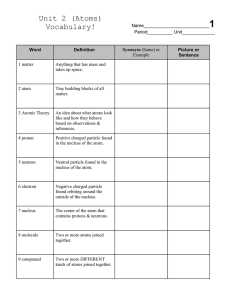
Structure of Matter Vocab Structure of Matter vocab
... Describes an atom whose outer energy level is completely filled with electrons ...
... Describes an atom whose outer energy level is completely filled with electrons ...
Nuclear Physics - Coweta County Schools
... A nucleus of equal mass positive protons and neutral neutrons, surrounded by almost massless, negative electrons Atomic number = # protons Atomic mass = # protons + neutrons Most atoms are neutral, so electrons = protons The nucleus, although containing the most mass, takes up very little ...
... A nucleus of equal mass positive protons and neutral neutrons, surrounded by almost massless, negative electrons Atomic number = # protons Atomic mass = # protons + neutrons Most atoms are neutral, so electrons = protons The nucleus, although containing the most mass, takes up very little ...
Structure of the Atom
... Modern Atomic Theory All matter is composed of atoms Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. However, these changes CAN occur in nuclear reactions! Atoms of an element have a characteristic average mass which is unique to that element. Atoms of any one ...
... Modern Atomic Theory All matter is composed of atoms Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. However, these changes CAN occur in nuclear reactions! Atoms of an element have a characteristic average mass which is unique to that element. Atoms of any one ...
24.5 Nuclear Equations - The Free Learning Channel
... carries a charge of + 23 , and the down quark carries a charge of − 31 . Determine by the final charge on the proton and neutron what combination of three up and down quarks are required to make a proton and what combination will make a neutron. 4. Only one particle is missing from this equation. Wha ...
... carries a charge of + 23 , and the down quark carries a charge of − 31 . Determine by the final charge on the proton and neutron what combination of three up and down quarks are required to make a proton and what combination will make a neutron. 4. Only one particle is missing from this equation. Wha ...
Study Guide Chapter 11 – Introduction to Atoms
... Study Guide Chapter 11 Atom – the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance. Dalton – developed the first modern atomic theory Thomson – discovered there are small particles inside the atom called electrons A. Plum pudding model – electrons mixed througho ...
... Study Guide Chapter 11 Atom – the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still be the same substance. Dalton – developed the first modern atomic theory Thomson – discovered there are small particles inside the atom called electrons A. Plum pudding model – electrons mixed througho ...
Nuclear and Particle Physics
... Nuclear and Particle Physics d = 3.0 x 10-14 m This would be a maximum possible radius for a gold atom In general, radius of an atom is 10-10 m and the nucleus is 10-15 m ...
... Nuclear and Particle Physics d = 3.0 x 10-14 m This would be a maximum possible radius for a gold atom In general, radius of an atom is 10-10 m and the nucleus is 10-15 m ...
PHYS6520 Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2013 HW #3
... Later on in this course we will compare this expression to the result of solving the Dirac equation in the presence of the Coulomb potential. (2) These questions are meant to associate numbers with atomic hydrogen phenomena. (a) The red n = 3 → 2 Balmer transition has a wavelength λ ≈ 656 nm. Calcul ...
... Later on in this course we will compare this expression to the result of solving the Dirac equation in the presence of the Coulomb potential. (2) These questions are meant to associate numbers with atomic hydrogen phenomena. (a) The red n = 3 → 2 Balmer transition has a wavelength λ ≈ 656 nm. Calcul ...
N - KTH
... The total binding energy B(A,Z) is defined as the total minimum work that an external agent must do to disintegrate the whole nucleus completely. By doing so the nucleus would no longer be existent but disintegrated into separated nucleons. ...
... The total binding energy B(A,Z) is defined as the total minimum work that an external agent must do to disintegrate the whole nucleus completely. By doing so the nucleus would no longer be existent but disintegrated into separated nucleons. ...
PH4041 – Atomic, Nuclear, and Particle Physics
... the atom, including its nucleus, the classification of fundamental particles and the means by which they interact. The syllabus includes: electron cloud model of an atom, electron spin and magnetic moment, spin-orbit interactions, revision of single-electron atom and brief qualitative extension to m ...
... the atom, including its nucleus, the classification of fundamental particles and the means by which they interact. The syllabus includes: electron cloud model of an atom, electron spin and magnetic moment, spin-orbit interactions, revision of single-electron atom and brief qualitative extension to m ...
06-Nuclear shorter
... In β− decay, the weak force converts a neutron into a proton while emitting an electron and an antineutrino ...
... In β− decay, the weak force converts a neutron into a proton while emitting an electron and an antineutrino ...
So why are some isotopes stable and some unstable (radioactive)
... When an atom forms from sub-atomic particles, the atoms weigh less than the sum of the particles. This “lost” weight (mass defect) is converted to energy according to e=mc2. This energy must be replaced to each nucleon in order for an atom to break apart, so the lower this energy per nucleon, the mo ...
... When an atom forms from sub-atomic particles, the atoms weigh less than the sum of the particles. This “lost” weight (mass defect) is converted to energy according to e=mc2. This energy must be replaced to each nucleon in order for an atom to break apart, so the lower this energy per nucleon, the mo ...
25.2 section summary
... Nuclei that lie outside the band of stability undergo spontaneous radioactive decay. Nuclei with too many neutrons undergo beta emission as neutrons are converted to protons. A positron is a particle with a positive charge and the mass of an electron. Every radioisotope decays at a characteristic ra ...
... Nuclei that lie outside the band of stability undergo spontaneous radioactive decay. Nuclei with too many neutrons undergo beta emission as neutrons are converted to protons. A positron is a particle with a positive charge and the mass of an electron. Every radioisotope decays at a characteristic ra ...
Document
... Neutrons are emitted when 235U undergoes fission These neutrons are then available to trigger fission in other nuclei This process is called a chain reaction ...
... Neutrons are emitted when 235U undergoes fission These neutrons are then available to trigger fission in other nuclei This process is called a chain reaction ...
IPS Unit 8 – Periodic Table Structure of the Atom Worksheet
... 3. Are electrons, protons, or neutrons the smallest particles? If not, what are? ...
... 3. Are electrons, protons, or neutrons the smallest particles? If not, what are? ...
Rutherford Model of the Atom Objective
... charge repelling the positively charged alpha particles. He said that it must be in the center of the atom and he called it the nucleus. ...
... charge repelling the positively charged alpha particles. He said that it must be in the center of the atom and he called it the nucleus. ...
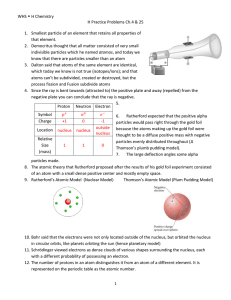
1-12
... 8. The atomic theory that Rutherford proposed after the results of his gold foil experiment consisted of an atom with a small dense positive center and mostly empty space. 9. Rutherford’s Atomic Model (Nuclear Model) Thomson’s Atomic Model (Plum Pudding Model) ...
... 8. The atomic theory that Rutherford proposed after the results of his gold foil experiment consisted of an atom with a small dense positive center and mostly empty space. 9. Rutherford’s Atomic Model (Nuclear Model) Thomson’s Atomic Model (Plum Pudding Model) ...