The Mystery of Matter: The Course
... are bound together by the shortrange nuclear (strong) force. • Protons and neutrons have masses around 938 MeV, differing by only 780 keV = 0.08%. Both have spin 1/2 hbar. ...
... are bound together by the shortrange nuclear (strong) force. • Protons and neutrons have masses around 938 MeV, differing by only 780 keV = 0.08%. Both have spin 1/2 hbar. ...
1 - contentextra
... Electromagnetic spectrum The range of electromagnetic radiation or waves including, in order of decreasing frequency, rays, X-rays, UV radiation, visible light, IR radiation, microwaves, and radio waves. (See Table 3 of the IB Data booklet). Electron Negatively charged particle present in all atom ...
... Electromagnetic spectrum The range of electromagnetic radiation or waves including, in order of decreasing frequency, rays, X-rays, UV radiation, visible light, IR radiation, microwaves, and radio waves. (See Table 3 of the IB Data booklet). Electron Negatively charged particle present in all atom ...
Lecture 1
... 1930 There are just three fundamental particles: protons, electrons, and photons. Born, after learning of the Dirac equation, said, “Physics as we know it will be over in six months.” 1930 Pauli suggests the neutrino to explain the continuous electron spectrum for β decay. 1931 Dirac realizes that t ...
... 1930 There are just three fundamental particles: protons, electrons, and photons. Born, after learning of the Dirac equation, said, “Physics as we know it will be over in six months.” 1930 Pauli suggests the neutrino to explain the continuous electron spectrum for β decay. 1931 Dirac realizes that t ...
BASICS OF BOSE-EINSTEIN CONDENSATION THEORY Y. Castin
... Tc ' 0.4K but then one expects a solid phase. • He4 does not solidify. Experiences superfluid transition at ∼ 2K but is a liquid, not a gas (condensate fraction < 0.1). • Only polarized hydrogen is gaseous at 1 atm, 0 K. ...
... Tc ' 0.4K but then one expects a solid phase. • He4 does not solidify. Experiences superfluid transition at ∼ 2K but is a liquid, not a gas (condensate fraction < 0.1). • Only polarized hydrogen is gaseous at 1 atm, 0 K. ...
Chapter 4 Assignment Answers 34. An atom is the smallest particle
... b. Thomson observed the same cathode rays with all of the different metals that he used. 39. Two electrons should repel each other. 40. The mass of a neutron is equal to the mass of a proton: 1 amu. However a proton is (+) charged and a neutron is neutral. 41. When an atom loses electrons, there are ...
... b. Thomson observed the same cathode rays with all of the different metals that he used. 39. Two electrons should repel each other. 40. The mass of a neutron is equal to the mass of a proton: 1 amu. However a proton is (+) charged and a neutron is neutral. 41. When an atom loses electrons, there are ...
Basic Atomic Theory, The Structure of Matter Atomic Structure
... Basic Atomic Theory, The Structure of Matter The field of study we call electricity is the investigation of the forces created by charged particles, especially electrons, and the motion and interactions of those particles. The electron is a fundamental component of matter and is considered to have t ...
... Basic Atomic Theory, The Structure of Matter The field of study we call electricity is the investigation of the forces created by charged particles, especially electrons, and the motion and interactions of those particles. The electron is a fundamental component of matter and is considered to have t ...
GCSE worksheet on the development of the model of the atom
... Instructions for teachers – print page 2 in A3. The idea behind this activity is that students have to read the text about each atomic model and then use this information to draw a model of the atom at each key point along its development. Students will need an understanding of current atomic theory ...
... Instructions for teachers – print page 2 in A3. The idea behind this activity is that students have to read the text about each atomic model and then use this information to draw a model of the atom at each key point along its development. Students will need an understanding of current atomic theory ...
Snímek 1
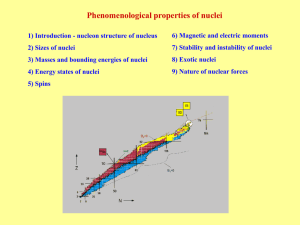
... Magic numbers – observed values of N and Z with increased stability. At 1896 H. Becquerel observed first sign of instability of nuclei – radioactivity. Instable nuclei irradiate: Alpha decay → nucleus transformation by 4He irradiation Beta decay → nucleus transformation by e-, e+ irradiation or capt ...
... Magic numbers – observed values of N and Z with increased stability. At 1896 H. Becquerel observed first sign of instability of nuclei – radioactivity. Instable nuclei irradiate: Alpha decay → nucleus transformation by 4He irradiation Beta decay → nucleus transformation by e-, e+ irradiation or capt ...
Document
... In 1926 Schrodinger wrote an equation that described both the particle and wave nature of the e-. The Schrödinger equation plays the role of Newton's laws and conservation of energy in classical mechanics - i.e., it predicts the future behavior of a dynamic system. Wave function (Ψ) describes : 1. e ...
... In 1926 Schrodinger wrote an equation that described both the particle and wave nature of the e-. The Schrödinger equation plays the role of Newton's laws and conservation of energy in classical mechanics - i.e., it predicts the future behavior of a dynamic system. Wave function (Ψ) describes : 1. e ...
Forces Fundamental interactions in particle physics
... From 2008 a new collider (pp) at CERN, called LHC, will search for new physics and new interactions. Open questions on fundamental interactions: - Is there new physics, which would allow to exactly unify the interactions at high energies? - “Dark Matter” in the universe asks for new particles and in ...
... From 2008 a new collider (pp) at CERN, called LHC, will search for new physics and new interactions. Open questions on fundamental interactions: - Is there new physics, which would allow to exactly unify the interactions at high energies? - “Dark Matter” in the universe asks for new particles and in ...
t 1/2
... Figure 13.1b: Apparatus used by J. J. Thomson (1897) to measure the charge-to-mass ratio of the electron. The evacuated tube is similar to a TV picture tube. The negatively charged particles emitted from the cathode are deflected by either an electric field or a magnetic field. The parallel plates ...
... Figure 13.1b: Apparatus used by J. J. Thomson (1897) to measure the charge-to-mass ratio of the electron. The evacuated tube is similar to a TV picture tube. The negatively charged particles emitted from the cathode are deflected by either an electric field or a magnetic field. The parallel plates ...
Classical Mechanics and Minimal Action
... is minimal. The quantity S is referred to as the Action and the integrand L(q, q̇, t) the Lagrangian. The Lagrangian of a physical system is defined to be the difference between kinetic- and potential energy. That is, if T is the kinetic energy and V the potential energy, then L = T − V. The princip ...
... is minimal. The quantity S is referred to as the Action and the integrand L(q, q̇, t) the Lagrangian. The Lagrangian of a physical system is defined to be the difference between kinetic- and potential energy. That is, if T is the kinetic energy and V the potential energy, then L = T − V. The princip ...
Greek Alphabet Fundamental constants: Useful conversions:
... binding (zero net charge between protons). Metallic Bond: Many electrons (one or more per atom) shared between a large number N of atoms -> positively charged “rest atoms” in “Fermi gas” of electrons. Electron energy eigenstates are clustered in “bands”; highest (partially or totally unoccupied) ban ...
... binding (zero net charge between protons). Metallic Bond: Many electrons (one or more per atom) shared between a large number N of atoms -> positively charged “rest atoms” in “Fermi gas” of electrons. Electron energy eigenstates are clustered in “bands”; highest (partially or totally unoccupied) ban ...
e563_e581
... solving for M at h=0. Find M(T) for TTc and identify the exponent in ~(TcT).
E572: Mean Field: antiferomagnetism
Antiferromagnetism is a phenomenon akin to f ...
... solving for M at h=0. Find M(T) for T
Worksheet 2.1 - contentextra
... Noble gas arrangement An arrangement with an octet of electrons in an energy level, or a pair of electrons in the first shell. Nuclear charge The nuclear charge is the total charge of all the protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleon A particle in a nucleus, either a neutron or proton. The nucleon ...
... Noble gas arrangement An arrangement with an octet of electrons in an energy level, or a pair of electrons in the first shell. Nuclear charge The nuclear charge is the total charge of all the protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleon A particle in a nucleus, either a neutron or proton. The nucleon ...
lecture 8
... the nuclear potential well, the Coulombic barrier, and quantummechanical barrier tunneling. Why not just create a nucleus with neutrons only, or just a single proton and varying numbers of neutrons, in which case there would be no “battle”? Recall our earlier example of the isotopes of hydrogen; a m ...
... the nuclear potential well, the Coulombic barrier, and quantummechanical barrier tunneling. Why not just create a nucleus with neutrons only, or just a single proton and varying numbers of neutrons, in which case there would be no “battle”? Recall our earlier example of the isotopes of hydrogen; a m ...