chart answers - Wilson`s Web Page
... inner and outer membranes merge. They are selective to what will pass through them – RNA and some proteins can freely move between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Nucleoplasm contains water, ...
... inner and outer membranes merge. They are selective to what will pass through them – RNA and some proteins can freely move between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Nucleoplasm contains water, ...
Answers - Mosaiced.org
... permeability to Na+. (increase in K+ permeability much slower) 88. towards eqm potential for Na+ (ie. becomes more positive) 89. ++++ reduction in membrane permeability to Na+. Increase in membrane permeability to K+. 90. Open. Open. 91. Period during which Na+ channels will not open in response to ...
... permeability to Na+. (increase in K+ permeability much slower) 88. towards eqm potential for Na+ (ie. becomes more positive) 89. ++++ reduction in membrane permeability to Na+. Increase in membrane permeability to K+. 90. Open. Open. 91. Period during which Na+ channels will not open in response to ...
Neuron Anatomy Activity - Ask a Biologist
... 1. Synapses: Send electrical impulses to neighboring neurons. 2. Myelin sheaths: Cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep electrical signals inside the cell, which allows them to move more quickly. 3. Axon: Transfers electrical impulse signals from the cell body to the synapse. 4. Soma: ...
... 1. Synapses: Send electrical impulses to neighboring neurons. 2. Myelin sheaths: Cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep electrical signals inside the cell, which allows them to move more quickly. 3. Axon: Transfers electrical impulse signals from the cell body to the synapse. 4. Soma: ...
Lecture 3 Review
... This review is intended as a brief summary of the lecture. I hope it will help you to focus your studies. It is not intended to provide you with an exhaustive review of the material that was covered. It is also not intended to provide a review of everything you will need to know for the exam. If a t ...
... This review is intended as a brief summary of the lecture. I hope it will help you to focus your studies. It is not intended to provide you with an exhaustive review of the material that was covered. It is also not intended to provide a review of everything you will need to know for the exam. If a t ...
Neurobiology of the Senses
... 5 The Na+ channels close when cGMP detaches. The membrane’s permeability to Na+ decreases, and the rod hyperpolarizes. ...
... 5 The Na+ channels close when cGMP detaches. The membrane’s permeability to Na+ decreases, and the rod hyperpolarizes. ...
Supporting Cells - Net Start Class
... transmission occurs when the membrane potential is changed within a neuron. ► A stimulus causes the membrane to become permeable to sodium thus changing the membrane potential. ► A charge separation between the outside of the cell and the cytoplasm creates voltage across the membrane. This voltage ...
... transmission occurs when the membrane potential is changed within a neuron. ► A stimulus causes the membrane to become permeable to sodium thus changing the membrane potential. ► A charge separation between the outside of the cell and the cytoplasm creates voltage across the membrane. This voltage ...
Slideshow
... maintain a voltage difference across the cell membrane called a resting membrane potential. The inside of the cell is more negatively charged in comparison to the outside of the cell – this is shown by a negative sign in front of voltage, (ex., - 70 mV) The big players here are sodium and potassium ...
... maintain a voltage difference across the cell membrane called a resting membrane potential. The inside of the cell is more negatively charged in comparison to the outside of the cell – this is shown by a negative sign in front of voltage, (ex., - 70 mV) The big players here are sodium and potassium ...
Chapter 48 Reading Guide and Key Terms
... In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. How would this affect nervous system function? ...
... In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. How would this affect nervous system function? ...
Lect5
... Ion currents underlying the AP • Use voltage-clamp technique to measure currents • Measure currents in the presence and absence of Na+ ...
... Ion currents underlying the AP • Use voltage-clamp technique to measure currents • Measure currents in the presence and absence of Na+ ...
Nervous System - De Anza College
... axon that forms the specialized connection Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that send information from the transmitting neuron (presynaptic cell) to the receiving neuron (postsynaptic cell) Synaptic terminals ...
... axon that forms the specialized connection Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that send information from the transmitting neuron (presynaptic cell) to the receiving neuron (postsynaptic cell) Synaptic terminals ...
The Nervous System
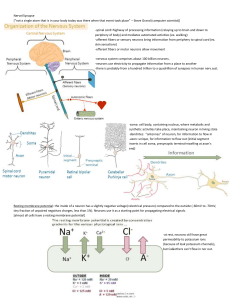
... At rest, inner environment has a higher concentration of K, the outer environment has a high Na concentration. The neuron’s cell membrane has active Na/K gates. When an impulse comes in contact with the membrane, it turns off the gate.[polarized] Na rushes in, K leaves and the electrical impulse pa ...
... At rest, inner environment has a higher concentration of K, the outer environment has a high Na concentration. The neuron’s cell membrane has active Na/K gates. When an impulse comes in contact with the membrane, it turns off the gate.[polarized] Na rushes in, K leaves and the electrical impulse pa ...
big
... Neurotransmitter stored in vesicles in axon of presynaptic cell is released into synaptic cleft as a result of depolarization (action potential). Neurotransmitter diffuses across cleft, binds to receptors, and causes a postsynaptic effect Neurotransmitter is taken back into the presynaptic cell (“re ...
... Neurotransmitter stored in vesicles in axon of presynaptic cell is released into synaptic cleft as a result of depolarization (action potential). Neurotransmitter diffuses across cleft, binds to receptors, and causes a postsynaptic effect Neurotransmitter is taken back into the presynaptic cell (“re ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel (the receptor), it opens and allows ions to diffuse across the membrane Result- postsynaptic potential (change in membrane potential) Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) membrane potential brought down to threshold Inhibitiory postsynaptic potentials (IPS ...
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel (the receptor), it opens and allows ions to diffuse across the membrane Result- postsynaptic potential (change in membrane potential) Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) membrane potential brought down to threshold Inhibitiory postsynaptic potentials (IPS ...
Doktryna neuronu
... The arrow next to each current record reflects the magnitude of the net Na+ flux at that membrane potential. B. The end-plate current actually reverses at 0 mV because the ion channel is permeable to both Na+ and K+, which are able to move into and out of the cell simultaneously. The net current is ...
... The arrow next to each current record reflects the magnitude of the net Na+ flux at that membrane potential. B. The end-plate current actually reverses at 0 mV because the ion channel is permeable to both Na+ and K+, which are able to move into and out of the cell simultaneously. The net current is ...
Practice Exam 1
... 15) The neuron is depolarizing without using voltage-gated channels. 16) K+ is leaving the neuron through voltage-gated channels. 17) Which letter is lies closest to potassium’s equilibrium potential? 18) Eric licks the back of a new species of toad (Ooooo, not smart). Within minutes, all of his bod ...
... 15) The neuron is depolarizing without using voltage-gated channels. 16) K+ is leaving the neuron through voltage-gated channels. 17) Which letter is lies closest to potassium’s equilibrium potential? 18) Eric licks the back of a new species of toad (Ooooo, not smart). Within minutes, all of his bod ...
Name:
... membrane below that is depolarized showing all ions along with all gates. Show which gates are closed and which are opened. What gate(s ) did you manipulate and how? ...
... membrane below that is depolarized showing all ions along with all gates. Show which gates are closed and which are opened. What gate(s ) did you manipulate and how? ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... Sodium Potassium Pump Review • Form of active transport, uses ATP • Na+ ions are pumped out of the cell and exchanged for potassium ions from the outside of the cell • Remember this exchange is uneven. The sodium potassium pump is constantly pumping Na+ out and K+, but the concentration of Na+ is h ...
... Sodium Potassium Pump Review • Form of active transport, uses ATP • Na+ ions are pumped out of the cell and exchanged for potassium ions from the outside of the cell • Remember this exchange is uneven. The sodium potassium pump is constantly pumping Na+ out and K+, but the concentration of Na+ is h ...
ACTION POTENTIALS
... impulse: The signal transmitted along a nerve fiber, either in response to a stimulus (such as touch, pain or heat), or as an instruction from the brain (such as causing a muscle to contract). ...
... impulse: The signal transmitted along a nerve fiber, either in response to a stimulus (such as touch, pain or heat), or as an instruction from the brain (such as causing a muscle to contract). ...
Paper: A differentially amplified motion in the ear for near
... reticular lamina, where stereocilia reside, were enhanced, had different frequency dependence and a different timing from the commonly measured vibrations of the basilar membrane. However, the full resolution of this conundrum will probably require the development of new experimental techniques that ...
... reticular lamina, where stereocilia reside, were enhanced, had different frequency dependence and a different timing from the commonly measured vibrations of the basilar membrane. However, the full resolution of this conundrum will probably require the development of new experimental techniques that ...
Simplified view of how a neuron sends a signal
... complex sequence of events is so fast that a single neuron might perform its signaling function 100 to 200 times per second. Now, on to the target cell.... ...
... complex sequence of events is so fast that a single neuron might perform its signaling function 100 to 200 times per second. Now, on to the target cell.... ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These substances, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, as well as neuropeptides like substance Y and endorphins, are often referred to as neuromodulators. They are not directly involved in the fast f ...
... -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These substances, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, as well as neuropeptides like substance Y and endorphins, are often referred to as neuromodulators. They are not directly involved in the fast f ...
ppt
... drawing of the synapse where this toxin acts. 3. How will it affect individual action potentials and muscular contraction? (Draw effects on other side of ...
... drawing of the synapse where this toxin acts. 3. How will it affect individual action potentials and muscular contraction? (Draw effects on other side of ...
Patch clamp

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. The technique can be applied to a wide variety of cells, but is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells. It can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.The patch clamp technique is a refinement of the voltage clamp. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channel molecules for the first time, which improved understanding of the involvement of channels in fundamental cell processes such as action potentials and nerve activity. Neher and Sakmann received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1991 for this work.