Summary
... version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
... version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
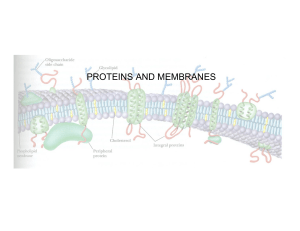
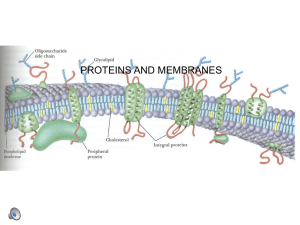
The CELL MEMBRANE (PLASMA MEMBRANE) as a
... Impermeable membranes: Neither water nor solute can move across the membrane. NOTHING gets in or out. This membrane wouldn’t be very useful either, as the cell could neither get nutrients nor dispose of waste…. SEMI-PERMEABLE MEMBRANE: A membrane through which only certain molecules may pass. In o ...
... Impermeable membranes: Neither water nor solute can move across the membrane. NOTHING gets in or out. This membrane wouldn’t be very useful either, as the cell could neither get nutrients nor dispose of waste…. SEMI-PERMEABLE MEMBRANE: A membrane through which only certain molecules may pass. In o ...
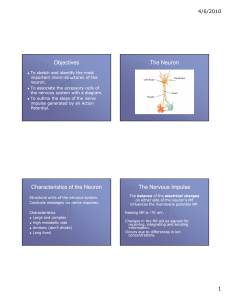
7. Describe what membrane potential is, and how
... 6. What is the purpose of the blood-brain barrier? • This restricts the passage of most substances into the brain • Allows the chemical environment of the CNS to be well controlled ...
... 6. What is the purpose of the blood-brain barrier? • This restricts the passage of most substances into the brain • Allows the chemical environment of the CNS to be well controlled ...
The Nervous System Nervous system links sensory receptors and
... For K+ - there is 30x more inside cell than outside - K+ will diffuse out due to a concentration difference - but it is also attracted to the negative charges inside the cell - if not held by negative charges it would move (out) until the membrane potential was -90 mV At rest, the concentration diff ...
... For K+ - there is 30x more inside cell than outside - K+ will diffuse out due to a concentration difference - but it is also attracted to the negative charges inside the cell - if not held by negative charges it would move (out) until the membrane potential was -90 mV At rest, the concentration diff ...
The Neuron - Austin Community College
... Their magnitude varies directly with the strength of the stimulus – the stronger the stimulus the more the voltage changes and the farther the current goes Sufficiently strong graded potentials can initiate action potentials if they maintain threshold by the time reach the trigger zone ...
... Their magnitude varies directly with the strength of the stimulus – the stronger the stimulus the more the voltage changes and the farther the current goes Sufficiently strong graded potentials can initiate action potentials if they maintain threshold by the time reach the trigger zone ...
Nerves Powerpoint
... on the outside of the cell – Typically the inside is -70mV compared to the outside ...
... on the outside of the cell – Typically the inside is -70mV compared to the outside ...
Chapter 11 Worksheet 2 The action potential: Fill in the blanks. The
... The dendrites receive signals from messenger molecules released from adjacent neurons called _________________________________. These molecules bind to receptors that act as ______________ gated ion channels. When these channels open they allow ions to flow in or out which produces small changes in ...
... The dendrites receive signals from messenger molecules released from adjacent neurons called _________________________________. These molecules bind to receptors that act as ______________ gated ion channels. When these channels open they allow ions to flow in or out which produces small changes in ...
Physio Lab 5 PhysioEx 3
... the RMP is a “diffusion potential” since it is due to the diffusion of potassium. There is also a small contribution to the RMP by the electrogenic sodium-potassium ATPase pump (which transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell while using ATP). This difference in e ...
... the RMP is a “diffusion potential” since it is due to the diffusion of potassium. There is also a small contribution to the RMP by the electrogenic sodium-potassium ATPase pump (which transports 3 sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell while using ATP). This difference in e ...
Nervous System
... Now we come to the point where information must be communicated from one neuron to another. This happens at synapses. In us virtually all synapses are chemical. ...
... Now we come to the point where information must be communicated from one neuron to another. This happens at synapses. In us virtually all synapses are chemical. ...
SBI4U - 9.2
... • The resting membrane normally had a potential near – 70 mV and registered + 40 mV when the nerve became excited • The voltage difference across a nerve cell membrane during the resting stage is called the resting potential • The reversal of potential is described as an action potential – the volt ...
... • The resting membrane normally had a potential near – 70 mV and registered + 40 mV when the nerve became excited • The voltage difference across a nerve cell membrane during the resting stage is called the resting potential • The reversal of potential is described as an action potential – the volt ...
Structures and Functions Lecture 2
... • Synaptotagmin protein binds Ca2+ and promotes fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
... • Synaptotagmin protein binds Ca2+ and promotes fusion of synaptic vesicles with axon membrane • Exocytosis of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft occurs • Higher impulse frequency more released ...
Bioenergetics - Eastern Michigan University
... • It uses ATP to actively pump Na+ out of the cell and K+ into the cell • It takes energy (ATP) to maintain the pump and the gradient ...
... • It uses ATP to actively pump Na+ out of the cell and K+ into the cell • It takes energy (ATP) to maintain the pump and the gradient ...
File - Mrs. Burchette`s Class
... • At first the concentration of solute is very high on the left. • But over time, the water moves across the semi-permeable membrane, and dilutes the particles. • Video ...
... • At first the concentration of solute is very high on the left. • But over time, the water moves across the semi-permeable membrane, and dilutes the particles. • Video ...
Neurons
... Voltage causes electrically charged particles, ions, to move across cell membranes. Major ions in neurons: • Sodium (Na+) • Potassium (K+) • Calcium (Ca2+) • Chloride (Cl–) Membrane potentials are measured with electrodes. • The resting potential of an axon is –60 to –70 millivolts (mV). • The insid ...
... Voltage causes electrically charged particles, ions, to move across cell membranes. Major ions in neurons: • Sodium (Na+) • Potassium (K+) • Calcium (Ca2+) • Chloride (Cl–) Membrane potentials are measured with electrodes. • The resting potential of an axon is –60 to –70 millivolts (mV). • The insid ...
PROTEINS AND MEMBRANES
... "We wondered if more common, apparently harmless [changes] in the gene might give rise to an altered degree of pain threshold," says Geoffrey Woods, a medical geneticist at Cambridge University in the U.K., who discovered the genetic ...
... "We wondered if more common, apparently harmless [changes] in the gene might give rise to an altered degree of pain threshold," says Geoffrey Woods, a medical geneticist at Cambridge University in the U.K., who discovered the genetic ...
Normal Cellular Physiology
... d. there are three pathways for exocytosis 27. Regarding endocytosis, which is true? a. refers to phagocytosis but not pinocytosis b. rafts are cell membrane areas rich in sphingolipids c. clathrin-mediated endocytosis and caveolae-dependent uptake are the same process d. substance must be in soluti ...
... d. there are three pathways for exocytosis 27. Regarding endocytosis, which is true? a. refers to phagocytosis but not pinocytosis b. rafts are cell membrane areas rich in sphingolipids c. clathrin-mediated endocytosis and caveolae-dependent uptake are the same process d. substance must be in soluti ...
NERVES
... (millimolar). In the cytosol, the Na concentration is 15 mM. Therefore, the Na concentration gradient is 150/15 = 10. › (Outside concentration/Inside Concentration) ...
... (millimolar). In the cytosol, the Na concentration is 15 mM. Therefore, the Na concentration gradient is 150/15 = 10. › (Outside concentration/Inside Concentration) ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CH 48 AND 49
... Sense receptors send info to sense neurons which send info to interneurons which send info to motor neurons which send info to muscles or glands ...
... Sense receptors send info to sense neurons which send info to interneurons which send info to motor neurons which send info to muscles or glands ...
Lecture 2 - Nerve Impulse
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
Patch clamp

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. The technique can be applied to a wide variety of cells, but is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells. It can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.The patch clamp technique is a refinement of the voltage clamp. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channel molecules for the first time, which improved understanding of the involvement of channels in fundamental cell processes such as action potentials and nerve activity. Neher and Sakmann received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1991 for this work.