Neuron and Neuroglial Review Worksheet
... Anatomy & Physiology Neuron and Neuroglial Worksheet A. First, label the parts of the neuron on the diagram below. Use the following wordbank to help you with your labeling: Cell body, Dendrite, Axon, Nucleus, Myelin Sheath, Axon Terminals, Node of Ranvier B. Match the anatomical terms given in Colu ...
... Anatomy & Physiology Neuron and Neuroglial Worksheet A. First, label the parts of the neuron on the diagram below. Use the following wordbank to help you with your labeling: Cell body, Dendrite, Axon, Nucleus, Myelin Sheath, Axon Terminals, Node of Ranvier B. Match the anatomical terms given in Colu ...
Unit IV-D Outline
... away from the cell body and send them either to other neurons or to effectors, range in length from less than a centimeter to more than one meter f. Schwann cells – produce layers of a white, fatty substance called myelin which covers the axon, gaps between neighboring cells are called nodes of Ranv ...
... away from the cell body and send them either to other neurons or to effectors, range in length from less than a centimeter to more than one meter f. Schwann cells – produce layers of a white, fatty substance called myelin which covers the axon, gaps between neighboring cells are called nodes of Ranv ...
here - York University
... The Basics The neuron is the fundamental unit for the nervous system. It contains 3 main structures: the cell body, the dendrite for input electrical signals, and the axon for output electrical signals. The segment connecting the axon and cell body is called the axonal intial segment (a.k.a. axonal ...
... The Basics The neuron is the fundamental unit for the nervous system. It contains 3 main structures: the cell body, the dendrite for input electrical signals, and the axon for output electrical signals. The segment connecting the axon and cell body is called the axonal intial segment (a.k.a. axonal ...
Neurons - Jordan High School
... Voltage-gated channels respond to changes in transmembrane potential ...
... Voltage-gated channels respond to changes in transmembrane potential ...
PNS and Transmission
... • Transmission is carried out by molecules called neurotransmitters. These are stored in vesicles in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse throug ...
... • Transmission is carried out by molecules called neurotransmitters. These are stored in vesicles in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse throug ...
CHAPTER 4 STRUCTURE AND CELL BIOLOGY OF THE NEURON
... The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles. It is the maintenance center of the neuron. It contains the cell's genetic material as well as the molecular machinery for synthesizing different chemical substances used for information transfer to other neurons, for maintenance and repair of ...
... The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles. It is the maintenance center of the neuron. It contains the cell's genetic material as well as the molecular machinery for synthesizing different chemical substances used for information transfer to other neurons, for maintenance and repair of ...
Document
... d. cell membrane: The outer, limiting membrane separating the cell's internal parts from the extracellular material and the external environment. 2. Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane. The cell membrane structure is a phospholipid bilayer. It has heads that face outward while t ...
... d. cell membrane: The outer, limiting membrane separating the cell's internal parts from the extracellular material and the external environment. 2. Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane. The cell membrane structure is a phospholipid bilayer. It has heads that face outward while t ...
48 - Groupfusion.net
... 4) The vesicles release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft 5)The neurotransmitter binds to the receptor portion of ligand-gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels. In the synapse illustrated here, both Na+ and K+ can diffuse through the channels 6) The neurotransmi ...
... 4) The vesicles release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft 5)The neurotransmitter binds to the receptor portion of ligand-gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels. In the synapse illustrated here, both Na+ and K+ can diffuse through the channels 6) The neurotransmi ...
PowerPoint
... membrane of the adjacent nerve cell, it changes the permeability of that membrane. • As a result, Na+ ions diffuse through the membrane into the cell. • If enough neurotransmitter is released by the axon terminal, so many Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron that the neuron becomes DEPOLARIZED. ...
... membrane of the adjacent nerve cell, it changes the permeability of that membrane. • As a result, Na+ ions diffuse through the membrane into the cell. • If enough neurotransmitter is released by the axon terminal, so many Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron that the neuron becomes DEPOLARIZED. ...
Nervous tissue
... Local Potentials • Local disturbances in membrane potential • occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance • depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradient ...
... Local Potentials • Local disturbances in membrane potential • occur when neuron is stimulated by chemicals, light, heat or mechanical disturbance • depolarization decreases potential across cell membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels • Na+ rushes in down concentration and electrical gradient ...
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
... Nerves – bundles of axons common to a section of the body • Types of Nerves: • Sensory: conduct impulses into the brain and spinal cord • Motor: carry impulses to muscles or gland ...
... Nerves – bundles of axons common to a section of the body • Types of Nerves: • Sensory: conduct impulses into the brain and spinal cord • Motor: carry impulses to muscles or gland ...
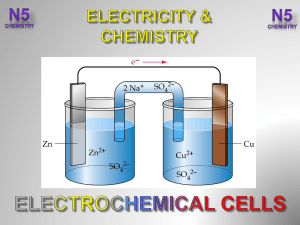
3.-Electrochemical-Cells-V2-
... are batteries which, when they go ‘flat’, can be charged and re-used. This means during recharging the chemicals used in the redox reactions are reformed. The lead-acid battery is the oldest type of rechargeable battery. The battery is made from plates and ...
... are batteries which, when they go ‘flat’, can be charged and re-used. This means during recharging the chemicals used in the redox reactions are reformed. The lead-acid battery is the oldest type of rechargeable battery. The battery is made from plates and ...
Sending Signals Notes
... • DEPOLARIZED = Inside the membrane becomes more positive than outside. • This causes a THRESHOLD to be REACHED and an impulse (ACTION POTENTIAL) begins in the second cell. • After the neurotransmitter relays it message it is rapidly REMOVED or DESTROYED, thus halting its effect. • The molecules of ...
... • DEPOLARIZED = Inside the membrane becomes more positive than outside. • This causes a THRESHOLD to be REACHED and an impulse (ACTION POTENTIAL) begins in the second cell. • After the neurotransmitter relays it message it is rapidly REMOVED or DESTROYED, thus halting its effect. • The molecules of ...
Chapter Two - CogConfluence
... membrane or plasma membrane. It separates the extracellular (outside) environment from the cytosol, which is the intracellular (inside) fluid. It is semipermeable, meaning that some things are allowed through while others are not. Anions and cations are among the things that cannot pass a pure plasm ...
... membrane or plasma membrane. It separates the extracellular (outside) environment from the cytosol, which is the intracellular (inside) fluid. It is semipermeable, meaning that some things are allowed through while others are not. Anions and cations are among the things that cannot pass a pure plasm ...
Cells
... of your life, both into and out of each cell: This is not a random process! Each cell has a variety of different processes to regulate this exchange so that The right materials cross the membrane In the right concentrations At the right time In the right direction etc. ...
... of your life, both into and out of each cell: This is not a random process! Each cell has a variety of different processes to regulate this exchange so that The right materials cross the membrane In the right concentrations At the right time In the right direction etc. ...
1 Neurons 2 Electrical activity of neurons at rest.
... Neurons are electrically active. They produce large electrical signals called “action potentials” or “spikes” or “nerve impulses” that can travel down the axon and are reliably transmitted to other neurons. Action potentials are considered to be stereotypical and are the main communication units in ...
... Neurons are electrically active. They produce large electrical signals called “action potentials” or “spikes” or “nerve impulses” that can travel down the axon and are reliably transmitted to other neurons. Action potentials are considered to be stereotypical and are the main communication units in ...
External anatomy of the ear
... Sectional View of the Cochlear as it will appear on a microscope slide ...
... Sectional View of the Cochlear as it will appear on a microscope slide ...
Anatomy and Physiology 241 Lecture Objectives The Nervous
... telodendria, synaptic terminal, node of Ranvier. Give function of each of these. Tell which cells myelinate axons in both the PNS and the CNS. Describe the synapse in detail. Define sensory neuron, motor neuron, interneuron and give the function and location of each. Know the difference, location an ...
... telodendria, synaptic terminal, node of Ranvier. Give function of each of these. Tell which cells myelinate axons in both the PNS and the CNS. Describe the synapse in detail. Define sensory neuron, motor neuron, interneuron and give the function and location of each. Know the difference, location an ...
chapter 48
... 1) _______________________________ the gated Na+ and K+ gates are _________________ (so only the sodium potassium pump and ungated channels are moving ions to maintain resting potential) 2) ___________________________ triggered by an action potential which signals the opening of ____ gates, and ...
... 1) _______________________________ the gated Na+ and K+ gates are _________________ (so only the sodium potassium pump and ungated channels are moving ions to maintain resting potential) 2) ___________________________ triggered by an action potential which signals the opening of ____ gates, and ...
Your Nervous System
... sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after depolarization; the neuron cannot be stimulated ...
... sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after depolarization; the neuron cannot be stimulated ...
CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
... Action potentials are conducted over the surface of individual cells because active depolarization in any one area of the membrane produces local currents in the intracellular and extracellular fluids which passively depolarize immediately adjacent areas of the membrane to their voltage threshold fo ...
... Action potentials are conducted over the surface of individual cells because active depolarization in any one area of the membrane produces local currents in the intracellular and extracellular fluids which passively depolarize immediately adjacent areas of the membrane to their voltage threshold fo ...
Impulse Conduction Practice Questions
... a. Which area of the graph indicates the diffusion of Na+ ions into the neurons? Explain your answer. (2 marks) ...
... a. Which area of the graph indicates the diffusion of Na+ ions into the neurons? Explain your answer. (2 marks) ...
Patch clamp

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. The technique can be applied to a wide variety of cells, but is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells. It can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.The patch clamp technique is a refinement of the voltage clamp. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channel molecules for the first time, which improved understanding of the involvement of channels in fundamental cell processes such as action potentials and nerve activity. Neher and Sakmann received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1991 for this work.